|
1825 Monetary Lane Suite #104 Carrollton, TX
Do a presentation at NTLUG.
What is the Linux Installation Project?
Real companies using Linux!
Not just for business anymore.
Providing ready to run platforms on Linux
|
Show Descriptions... (Show All/All+Images)
(Single Column)

- Fedora 42 freerdp Important Denial Service Issues CVE-2026-53fe996a57
Update to 3.23.0 to fix CVE-2026-26965, CVE-2026-26955, CVE-2026-26271, CVE-2026-25997, CVE-2026-25959, CVE-2026-25955, CVE-2026-25954, CVE-2026-25953, CVE-2026-25952, CVE-2026-25942, CVE-2026-25941

- Stable kernels for Friday the 13th
Greg Kroah-Hartman has announced the release of the 6.19.8, 6.18.18, and 6.12.77 stable kernels. Each of thesekernels includes a number of important fixes; users are advised toupgrade.
- An investigation of the forces behind the age-verification bills
Reddit user "Ok_Lingonberry3296" has posted theresults of an extensive investigation into the companies that arepushing US state legislatures to enact age-verification bills.
I've been pulling public records on the wave of "age verification" bills moving through US state legislatures. IRS 990 filings, Senate lobbying disclosures, state ethics databases, campaign finance records, corporate registries, WHOIS lookups, Wayback Machine archives. What started as curiosity about who was pushing these bills turned into documenting a coordinated influence operation that, from a privacy standpoint, is building surveillance infrastructure at the operating system level while the company behind it faces zero new requirements for its own platforms.
(See also this article for a look at theCalifornia law.)
- A set of AppArmor vulnerabilities
Qualys has sent out asomewhat breathless advisory describing a number of vulnerabilities inthe AppArmor security module, which is used in a number of Debian-baseddistributions (among others).
This "CrackArmor" advisory exposes a confused-deputy flaw allowing unprivileged users to manipulate security profiles via pseudo-files, bypass user-namespace restrictions, and execute arbitrary code within the kernel. These flaws facilitate local privilege escalation to root through complex interactions with tools like Sudo and Postfix, alongside denial-of-service attacks via stack exhaustion and Kernel Address Space Layout Randomization (KASLR) bypasses via out-of-bounds reads.
- Security updates for Friday
Security updates have been issued by Debian (chromium, kernel, and multipart), Fedora (dnf5, dr_libs, easyrpg-player, libmaxminddb, python3.12, strongswan, task, and udisks2), Oracle (.NET 10.0, .NET 8.0, .NET 9.0, gnutls, ImageMagick, kernel, libvpx, mingw-libpng, nginx:1.26, python3.11, and uek-kernel), Red Hat (delve, git-lfs, mingw-libpng, osbuild-composer, and rhc-worker-playbook), SUSE (cjson, curl, dnsdist, libsoup2, postgresql16, postgresql17, postgresql18, python-lxml_html_clean, python-pypdf2, python36, and thunderbird), and Ubuntu (dotnet8, dotnet9, dotnet10, freetype, golang-github-go-git-go-git, golang-golang-x-net, openssh, python-cryptography, sudo, and util-linux).
- [$] Practical uses for a null filesystem
One of the first changes merged for the upcoming 7.0 release was nullfs,an empty filesystem that cannot actually contain any files. One mightlogically wonder why the kernel would need such a thing. It turns out,though, that there are places where a null filesystem can come in handy.For 7.0, nullfs will be used to make life a bit easier for initprograms; future releases will likely use nullfs to increase the isolationof kernel threads from the init process.
- Two stable kernels for Thursday
Sasha Levin has announced the release of the 6.19.7 and 6.18.17 stable kernels. As usual, eachcontains important fixes throughout the tree; users are advised toupgrade.
- Security updates for Thursday
Security updates have been issued by AlmaLinux (gimp, git-lfs, grafana-pcp, kernel, mysql8.4, nfs-utils, opentelemetry-collector, osbuild-composer, postgresql:16, and python3.12), Debian (imagemagick and netty), Fedora (dr_libs and python-lxml-html-clean), Slackware (libarchive and libxml2), SUSE (busybox, coredns, firefox, freerdp, ghostty, gnutls, go1.25, go1.26, GraphicsMagick, grype, helm, helm3, ImageMagick, perl-Compress-Raw-Zlib, python, python311-lxml_html_clean, python311-PyPDF2, tomcat11, and traefik), and Ubuntu (curl, gimp, and libpng).
- [$] LWN.net Weekly Edition for March 12, 2026
Inside this week's LWN.net Weekly Edition:
Front: Chardet; Linux and age verification; Debian AI; Python lazy imports; Python type-system PEP; PQC HTTPS certificates; MGLRU; Fedora strategy. Briefs: LLM vulnerability; NTP security; OpenWrt 25.12.0; SUSE sale; Buildroot 2026.02; digiKam 9.0.0; Rust 1.94.0; Quotes; ... Announcements: Newsletters, conferences, security updates, patches, and more.
- [$] California's Digital Age Assurance Act and Linux distributions
A recently enacted law in California imposes an age-verification requirement onoperating-system providers beginning next year. The language of the DigitalAge Assurance Act does not restrict its requirements to proprietary or commercialoperating systems; projects like Debian, FreeBSD, Fedora, and others seem to be onthe hook just as much as Apple or Microsoft. There is some hope that the law will beamended, but there is no guarantee that it will be. This means that the developercommunities behind Linux distributions are having to discuss whether and how tocomply with the law with little time and even less legal guidance.
- Introducing Moonforge: a Yocto-based Linux OS (Igalia Blog)
Igalia has announcedthe Moonforge Linuxdistribution, based on OpenEmbeddedand Yocto.
Moonforge is an operating system framework for Linux devices thatsimplifies the process of building and maintaining custom operatingsystems.
It provides a curated collection of Yocto layers and configurationfiles that help developers generate immutable, maintainable, andeasily updatable operating system images.
The goal is to offer the best possible developer experience forteams building embedded Linux products. Moonforge handles the complexaspects of operating system creation, such as system integration,security, updates, and infrastructure, so developers can focus onbuilding and deploying their applications or devices.
- [$] HTTPS certificates in the age of quantum computing
There has been ongoing discussion in theInternet Engineering Task Force (IETF)about how to protect internet traffic against future quantum computers. So far,that work has focused on key exchange as the most urgent problem; now,a new IETF working group is looking at adopting post-quantum cryptographyfor authentication and certificate transparency as well. The main challenge todoing so is the increased size ofcertificates — around 40 times larger. The techniques that the working group is investigatingto reduce that overhead could have efficiency benefits for traditionalcertificates as well.
- Security updates for Wednesday
Security updates have been issued by AlmaLinux (kernel, kernel-rt, libvpx, nfs-utils, nginx:1.26, osbuild-composer, postgresql, postgresql:12, postgresql:13, postgresql:15, postgresql:16, and python-pyasn1), Debian (imagemagick), Fedora (perl-Crypt-SysRandom-XS and systemd), Mageia (yt-dlp), Oracle (delve, gimp, git-lfs, go-rpm-macros, image-builder, kernel, libpng, libvpx, mysql8.4, nfs-utils, osbuild-composer, postgresql16, postgresql:12, postgresql:13, postgresql:15, postgresql:16, python-pyasn1, python3, python3.12, python3.9, and thunderbird), SUSE (python-aiohttp, python-maturin, python311-pymongo, rclone, and util-linux), and Ubuntu (linux-nvidia, linux-nvidia, linux-nvidia-6.8, linux-nvidia-lowlatency, and python-geopandas).
- [$] Disabling Python's lazy imports from the command line
The advent of lazy imports in the Python language is upon us, now that PEP 810 ("Explicit lazyimports") was accepted by the steeringcouncil and the feature will appear in the upcoming Python 3.15 releasein October. There are a number of good reasons,performance foremost, for wanting to defer spending—perhaps wasting—thetime to do an import before a needed symbol is used. However, there arealso good reasons not to want that behavior, at least in some cases. Thetension between those two positions is what led to an earlier PEP rejection,but it is also playing into a recent discussion of the API used to controllazy imports.
- SUSE may be for sale, again
Reuters is reportingthat private-equity firm EQT may be looking to sell SUSE:
EQT has hired investment bank Arma Partners to sound out a group ofprivate equity investors for a possible sale of the company, said thesources, who requested anonymity to discuss confidential matters. The deliberations are at an early stage and there is no certainty that EQTwill proceed with a transaction, the sources said.
SUSE has traded hands a number of times over the years. Mostrecently it was acquired byEQT in 2018, was listedon the Frankfurt Stock Exchange in 2021, and then takenprivate again by EQT in August 2023.

- Linux 6.12 Through Linux 7.0 File-System Benchmarks For EXT4 + XFS
Earlier this month were various Linux 7.0 file-system benchmarks showing how XFS is leading the race in the overall upstream Linux file-system performance on this forthcoming kernel. Stemming from that testing some premium supporters requested a fresh look at the historical performance of XFS as well as EXT4. So today's article is a look at how XFS and EXT4 have performed on every kernel release going back to Linux 6.12 LTS.
- Forlinx Showcases i.MX95-Based FET-MX95xx-C SoM at Embedded World 2026
Forlinx has introduced the FET-MX95xx-C SoM built around NXP’s i.MX95 applications processor family and demonstrated a multimodal industrial security solution at Embedded World 2026. The demo combines the i.MX95 processor with an Ara240 AI computing card to accelerate edge inference workloads. The module integrates the NXP i.MX9596 processor, which combines six Arm Cortex-A55 cores running […]
- BeagleBadge wearable platform boasts TI AM62L SoC, ePaper display, and Linux support
The BeagleBoard.org Foundation has introduced BeagleBadge, an open-source wearable development platform for IoT and embedded applications. The badge integrates a 4.2-inch ePaper display, onboard sensors, wireless connectivity, and expansion interfaces in a compact board for prototyping wearable and interactive systems. The platform is built around the Texas Instruments AM62L Sitara SoC. The AM62L32 integrates a […]

- System76 CEO Sees 'Real Possibility' Colorado's Age-Verification Bill Excludes Open-Source
Last week System76 CEO Carl Richell criticized age-verification laws for operating systems — but he now sees a "real possibility" Colorado's law might exclude open-source. Phoronix reports that the System76 CEO met with the state Senator who co-authored Colorado's bill, and then posted on X.com that the Senator "suggested excluding open source software from the bill." Richell: This appears to be a real possibility. Amendments are expected... It's my hope we can move fast enough to influence excluding open source.. No illusions, it's an uphill battle, but we have an open door to advocate for the open source community. Vague language has been a recurring problem with new state age-verification legislation. Richell pointed out later that "In one proposed bill, Garmin would have to verify the age of their watch customers at device setup." Richell also sees New York's bill as "unlikely to be applicable to Linux distributions," since its language calls for "commercially reasonable age assurance" that free operating systems could use — and Richell isn't sure one exists as described by the bill. "As written today, it's extremely broad and vague and that makes it scary." Richell answered several follow-up questions about operating system age-verification laws. "What about California?" someone asked... Richell: We hope to make sensible, strong arguments for excluding open source which then becomes a standard for other states. It's going to be difficult. Q: Open source is not the only target to exclude. Please ensure that the bill is amended so that it does not require applications that have no possible use for the age bracket to ask about it. Richell: We discussed this as well. I proposed that apps that do not require age to modify app behavior or access by some other legislation be barred from reading age brackets to better protect privacy.
 
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
- US Set To Receive $10 Billion Fee For Brokering TikTok Deal
The deal to take control of TikTok's U.S. business came with an unusual condition, according to people familiar with the matter. The investors — which include Oracle, Abu Dhabi investor MGX, and private-equity firm Silver Lake — "paid the Treasury Department about $2.5 billion when the deal closed in January," reports the Wall Street Journal, "and are set to make several additional payments until hitting the $10 billion total."The $10 billion payment would be nearly unprecedented for a government helping arrange a transaction, historians have said... Investment bankers advising on a typical deal receive fees of less than 1% of the transaction value, and the percentage generally gets smaller as the deal size increases. Bank of America is in line to make some $130 million for advising railroad operator Norfolk Southern on its $71.5 billion sale to Union Pacific, one of the largest fees on record for a single bank on a deal. Administration officials have said the fee is justified given Trump's role in saving TikTok in the U.S. and navigating negotiations with China to get the deal done while addressing the security concerns of lawmakers... The TikTok fee extracted from private-sector investors is the administration's latest transaction involving the nation's largest businesses. Trump took a nearly 10% stake in semiconductor company Intel and has agreed to take a chunk of chip sales to China from Nvidia in exchange for granting export licenses. The administration has also taken equity stakes in other companies and has a say in the operations of U.S. Steel following a "golden share" agreement with Japan's Nippon Steel in its takeover. Reuters notes earlier this month, a lawsuit was filed by investors in two of TikTok's social media rivals, seeking to reverse the approval of the deal. Thanks to long-time Slashdot reader schwit1 for sharing the news.
 
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
- How a Species Evolved Fast Enough to Save Itself from Extinction
California saw its worst drought in 10,000 years between 2012 and 2015, remembers the Washington Post. And yet genetic analyses of California's scarlet monkeyflower "found that many rapidly evolved... allowing them to cope with water scarcity and rebound from decline.""The fact that certain organisms are able to adapt just because of genetics that are already present is a great source of hope," said Daniel Anstett, a plant biologist at Cornell University and lead author on a new study on the issue. "It's one more arrow in the quiver of different ways that populations might be able to survive the massive climate change we're inflicting on the planet." The recovery of [Sequoia National Park's] scarlet monkeyflowers offers rare, real-world evidence of what scientists call "evolutionary rescue," according to the study published Thursday in the journal Science. It suggests that some species may be able to evolve quickly enough to keep up with the accelerating consequences of human-caused warming — essentially saving themselves from extinction. This discovery could help people decide how to distribute limited conservation funds by pinpointing which species have enough genetic diversity to be resilient, ecologists Mark Urban and Laurinne Balstad, who were not involved in the study, wrote in a separate analysis published by Science. "The challenge going forward is to identify when evolutionary rescue is possible, when it is not, and how to rescue those species that cannot rescue themselves," Urban and Balstad wrote.
 
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
- AI's Productivity Boost? Just 16 Minutes Per Week, Claims Study
"A new study suggests the productivity boost from AI may be far smaller than executives claim," writes Slashdot reader BrianFagioli:According to research cited in Foxit's State of Document Intelligence report, while 89% of executives and 79% of end users say AI tools make them feel more productive, the actual time savings shrink dramatically once people account for reviewing and validating AI-generated output. The survey of 1,000 desk-based workers and 400 executives in the United States and United Kingdom found executives believe AI saves them about 4.6 hours per week, but they spend roughly 4 hours and 20 minutes verifying those results. End users reported a similar pattern, estimating 3.6 hours saved but 3 hours and 50 minutes spent reviewing AI work. Once that "verification burden" is factored in, executives gain just 16 minutes per week, while end users actually lose about 14 minutes.
 
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
- U.S. State Bans on Lab-Grown Meats Challenged in Court
Last June Texas Agriculture Commissioner Sid Miller said in a statement that Texans "have a God-given right to know what's on their plate, and for millions of Texans, it better come from a pasture, not a lab. It's plain cowboy logic that we must safeguard our real, authentic meat industry from synthetic alternatives." But California company Wildtype sells lab-grown salmon — and is suing Texas over its ban on cell-cultivated meat, the Austin Chronicle reported this week. The company's founder says lab-grown salmon eliminates the mercury, microplastic, and antibiotic contamination commonly found in seafood. And one chef in Austin, Texas says lab-grown salmon is "awesome" and "something new"-- at the only Texas restaurant that was serving it last summer:Just two months after the salmon hit the menu, Texas banned the sale of cell-cultivated meat...A lawsuit from Wildtype and one other FDA-approved cultivated meat company [argues] it's anti-capitalism and unconstitutional... This law "was not enacted to protect the health and safety of Texas consumers — indeed, it allows the continued distribution of cultivated meat to consumers so long as it is not sold. Instead, SB 261 was enacted to stifle the growth of the cultivated meat industry to protect Texas' conventional agricultural industry from innovative competition that is exclusively based outside of Texas...." [according to the lawsuit]. It was filed in September, immediately after the ban took effect, and cell-cultivated companies are awaiting judgment. That Texas ban would last two years, notes U.S. News and World Reports, adding that Alabama, Florida, Indiana, Mississippi, Montana, and Nebraska have also passed bans, some temporary "on the manufacturing, sale or distribution of cell-cultured meat." Meanwhile, a new five-year moratorium on lab-grown meat was signed this week by the governor of South Dakota "after rejecting a permanent ban last month," reports South Dakota Searchlight:The new law bars the sale, manufacture or distribution of "cell-cultured protein" products from July 1 this year through June 30, 2031. Violations are punishable by up to 30 days in jail, a fine of up to $500, or both. "But supporters of lab-grown meat are not going down without a fight," adds U.S. News and World Reports, with another lawsuit also filed challenging a ban in Florida:When Florida Gov. Ron DeSantis signed the ban in Florida, he described it as "fighting back against the global elite's plan to force the world to eat meat grown in a petri dish or bugs to achieve their authoritarian goals." He added that his administration "will save our beef."
 
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
- Meta Plans Sweeping Layoffs As AI Costs Mount
An anonymous reader quotes a report from Reuters: Meta is planning sweeping layoffs that could affect 20% or more of the company, three sources familiar with the matter told Reuters, as Meta seeks to offset costly artificial intelligence infrastructure bets and prepare for greater efficiency brought about by AI-assisted workers. No date has been set for the cuts and the magnitude has not been finalized, the people said. Top executives have recently signaled the plans to other senior leaders at Meta and told them to begin planning how to pare back, two of the people said. If Meta settles on the 20% figure, the layoffs will be the company's most significant since a restructuring in late 2022 and early 2023 that it dubbed the "year of efficiency." It employed nearly 79,000 people as of December 31, according to its latest filing. The speculation follows a recent report from The New York Times claiming that Meta has delayed the release of its next major AI model after falling behind competing systems from Google, OpenAI, and Anthropic.
 
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
- Two Long-Lost Episodes of 'Doctor Who' Found
Longtime Slashdot reader tsuliga writes: Two new episodes of Doctor Who that were previously lost have been found. The original Doctor Who episodes were wiped or deleted by the BBC because they were not aware of the future use of re-runs of these shows. Ninety-five of the 253 episodes from the program's first six years are currently missing. How many more episodes are out there waiting to be rediscovered? "The main broadcasters in the UK in the 1960s, 70s, up to the 80s really, junked quite a lot of content," said Justin Smith, a cinema professor at England's De Montfort University and film archivist. "In some ways finding missing 'Doctor Whos' is the holy grail" of classic TV discoveries, Smith said. The two episodes were "The Nightmare Begins" and "Devil's Planet," both of which aired during the show's third series in 1965. It features William Hartnell as the Doctor in a story involving archvillains the Daleks -- pepperpot-shaped metal aggressors whose favorite word is "Exterminate!" Smith said that for fans of the show, "it's got it all, it really has. It is intergalactic, it's got some great performances. It stands up really, really well."
 
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
- ChatGPT, Other Chatbots Approved For Official Use In the Senate
An anonymous reader quotes a report from the New York Times: A top Senate administrator on Monday gave aides the green light to use three artificial intelligence chatbots for official work, a reflection of how widespread the use of the products has become in workplaces around the globe. The chief information officer for the Senate sergeant-at-arms, who oversees the chamber's computers as well as security, said in a one-page memo reviewed by The New York Times that aides could use Google's Gemini chat, OpenAI's ChatGPT or Microsoft Copilot, which is already integrated into Senate platforms. Copilot "can help with routine Senate work, including drafting and editing documents, summarizing information, preparing talking points and briefing material, and conducting research and analysis," the memo said. The document later added that "data shared with Copilot Chat stays within the secure Microsoft 365 Government environment and is protected by the same controls that safeguard other Senate data." It's unclear how widely AI is used in the Senate or how widespread it might become, as individual offices and committees set their own rules. The chamber has also not publicly released comprehensive guidance on chatbots, the report notes. In contrast, the House has clearer policies allowing the general use of AI for limited internal tasks but restricting it from sensitive data or for being used for deepfakes and certain decision-making activities.
 
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
- Instagram Discontinues End-To-End Encryption For DMs
Meta plans to remove end-to-end encryption (E2EE) from Instagram direct messages by May 8, 2026. "Very few people were opting in to end-to-end encrypted messaging in DMs, so we're removing this option from Instagram in the coming months," says Meta. "Anyone who wants to keep messaging with end-to-end encryption can easily do that on WhatsApp." The Hacker News reports: The American company first began testing E2EE for Instagram direct messages in 2021 as part of CEO Mark Zuckerberg's "privacy-focused vision for social networking." The feature is currently "only available in some areas" and is not enabled by default. Weeks into the Russo-Ukrainian war in February 2022, the company made encrypted direct messaging available to all adult users in both countries. Last week, TikTok said it would not introduce E2EE, arguing it makes users less safe by preventing police and safety teams from being able to read direct messages if needed.
 
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
- Qatar Helium Shutdown Puts Chip Supply Chain On a Two-Week Clock
Iranian drone strikes shut down a major helium facility in Qatar, removing about 30% of global helium supply and raising concerns for the semiconductor industry, which relies on the gas for chip fabrication. "QatarEnergy declared force majeure on existing contracts on March 4, freeing it from supply obligations to customers," reports Tom's Hardware. The industry outlet Gasworld reports that no imminent restart is planned. From the report: Helium consultant Phil Kornbluth, speaking at a Gasworld webinar on March 4, said that if the outage extends beyond roughly two weeks, industrial gas distributors could be forced to relocate cryogenic equipment and revalidate supplier relationships, a process that could stretch over months regardless of when Qatari output resumes. South Korea is among the most exposed countries, which, according to the Korea International Trade Association, imported 64.7% of its helium from Qatar in 2025. The country relies heavily on helium imports to cool silicon wafers during fabrication and is understood to have no viable substitute. The country's Ministry of Trade, Industry and Resources has reportedly launched an investigation into supply and demand for 14 semiconductor materials and equipment types with high dependence on Middle Eastern sources, Nikkei reported on Wednesday. Bromine, which is used in circuit formation, is another big concern, with South Korea sourcing 90% of its imports from Israel, also party to the ongoing conflict in Iran.
 
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
- Don't Get Used To Cheap AI
AI services may not stay cheap for long, as companies like OpenAI and Anthropic are currently subsidizing usage to rapidly grow market share. As these companies move toward profitability and potential IPOs, Axios reports that investors will likely push them to increase prices and improve margins. An anonymous reader shares an excerpt from the report: Flashback: Silicon Valley has seen this movie before. The so-called "millennial lifestyle subsidy" meant VC money helped underwrite cheap Uber rides and DoorDash deliveries. Before that, Amazon built its base with low prices, free shipping and, for years, no sales tax in most states. Eventually, all of these companies had to charge enough to cover costs -- and make a profit. Follow the money: The current iteration of AI subsidies won't last forever. Both OpenAI and Anthropic are widely expected to go public. Public investors will demand earnings growth and expanding margins. Even as chips get more efficient, total spending keeps rising. Labs need more capacity, more upgrades and more supply to meet demand. The bottom line: The costs of AI will keep going down. But total spend from customers will need to keep going up if AI companies are going to become profitable and investors are ever going to get returns on their massive investments.
 
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
- Digg Relaunch Fails
sdinfoserv writes: After running a Reddit clone for a couple of months, the Digg beta shut down again. The website is a splash memo from CEO Justin Mezzell, blaming the latest "Hard Reset" on bots. "Building on the internet in 2026 is different," writes Mezzell. "We learned that the hard way. Today we're sharing difficult news: we've made the decision to significantly downsize the Digg team..." The decision was made after struggling to gain traction and an overwhelming influx of AI-driven bots and spam. "When the Digg beta launched, we immediately noticed posts from SEO spammers noting that Digg still carried meaningful Google link authority," says Mezzell. "Within hours, we got a taste of what we'd only heard rumors about. The internet is now populated, in meaningful part, by sophisticated AI agents and automated accounts. We knew bots were part of the landscape, but we didn't appreciate the scale, sophistication, or speed at which they'd find us." "We banned tens of thousands of accounts. We deployed internal tooling and industry-standard external vendors. None of it was enough. When you can't trust that the votes, the comments, and the engagement you're seeing are real, you've lost the foundation a community platform is built on." Despite the setback, Digg plans to rebuild with a smaller team, with founder Kevin Rose returning to work full-time on a new direction for the platform. "Starting the first week of April, Kevin will be putting his focus back on the company he built twenty+ years ago," writes Mezzell. "He'll continue as an advisor to True Ventures, but Digg will be his primary focus." Slashback: The Rise of Digg.com
 
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
- Backblaze Hosts 314 Trillion Digits of Pi Online
BrianFagioli shares a report from NERDS.xyz: Cloud storage company Backblaze has partnered with StorageReview to make a massive dataset containing 314 trillion digits of Pi publicly accessible. The digits were calculated by StorageReview in December 2025 after months of heavy computation designed to stress modern hardware. The dataset now hosted in the cloud weighs in at over 130TB, while the full working dataset used during the calculation reached about 2.1PB when intermediate checkpoints were included. The report notes that the Pi digits have been broken into roughly 200GB chunks to make it more practical for researchers or enthusiasts to download. Here's what StorageReview founder Brian Beeler said about the project: "Pushing [Pi] to 314 trillion digits was far more than a headline number. It was a sustained, months-long computational challenge that stressed every layer of modern infrastructure, from high core-count CPUs to massive high-speed storage, and it gave us valuable insight into how extreme, real-world workloads behave at scale. Making this dataset available in the Backblaze cloud takes the project a step further by opening access to one of the largest raw outputs ever generated in a single-system calculation. Hosting multi-petabyte files for the broader community is no small feat, and we appreciate Backblaze stepping up to ensure researchers, developers, and enthusiasts can explore and build on this record-setting achievement."
 
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
- Meta Delays Rollout of New AI Model After Performance Concerns
Meta has delayed the release of its next major AI model after internal tests showed it lagging behind competing systems from Google, OpenAI, and Anthropic. The New York Times reports: The model, code-named Avocado, outperformed Meta's previous A.I. model and did better than Google's Gemini 2.5 model from March, two of the people said. But it has not performed as strongly as Gemini 3.0 from November, they said. As a result, Meta has delayed Avocado's release to at least May from this month, the people said. They added that the leaders of Meta's A.I. division had instead discussed temporarily licensing Gemini to power the company's A.I. products, though no decisions have been reached. [...] It takes time to improve A.I. models, and Meta can still catch up to rivals, A.I. experts said. But a longer timeline has set in at the company, with Mr. Zuckerberg tempering expectations for Avocado in the past few months. "I expect our first models will be good, but more importantly will show the rapid trajectory we're on," he said on a call with investors in January. A Meta spokesperson said in a statement: "As we've said publicly, our next model will be good but, more importantly, show the rapid trajectory we're on, and then we'll steadily push the frontier over the course of the year as we continue to release new models. We're excited for people to see what we've been cooking very soon."
 
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
- Live Nation Execs Brag About 'Robbing' Ticket Buyers In Slack DMs
An anonymous reader quotes a report from Pitchfork: Earlier this week, the U.S. Department of Justice and Live Nation reached a settlement in the DOJ's antitrust lawsuit against the concert giant. During the trial, which lasted only a week, representatives for Live Nation had moved to exclude a collection of Slack direct messages from 2022 between two of the company's regional directors from the evidence presented to the jury. Bloomberg and a number of other publications have, as of today (March 12), successfully petitioned New York federal judge Arun Subramanian to release the chats. The conversations are between Ben Baker, now head of ticketing for Venue Nation, and Jeff Weinhold, currently a senior director in the ticketing department. Baker and Weinhold joke about overcharging and price-gouging fans -- "Robbing them blind, baby," Baker brags in one exchange pertaining to a Kid Rock show in Tampa Bay -- as well as being able to raise prices on ancillary services such as parking seemingly at will. "These people are so stupid," Baker writes. "I almost feel bad taking advantage of them BAHAHAHAHAHA." Live Nation described the messages as "off-the-cuff banter, not policy, decision-making, or facts of consequence." In a statement the company has since added: "The Slack exchange from one junior staffer to a friend absolutely doesn't reflect our values or how we operate."
 
Read more of this story at Slashdot.

- Claude charts a new course with charts, of course
Conversations with Anthropic's models may now be accompanied by interactive apps
Seeing is believing, or so it was said up until AI required questioning everything. But even when braced to resist the slop roulette of online interaction, pictures are worth a thousand tokens.…
- Watchdog boss calls Capita's £370M DWP win 'extraordinary' amid pension portal dumpster fire
PAC chair asks Cabinet Office if anyone bothered telling dept about the shambles before handing over the keys
The chair of the UK Parliament's public spending watchdog has dubbed the Department for Work and Pensions' (DWP) decision to award Capita a £370 million shared service contract "extraordinary," given the outsourcing firm's "failings" in supporting the Civil Service Pension Scheme (CSPS).…
- AI Burning Man happens next week –what to expect at Nvidia GTC 2026
From Groq-ing about tokenomics to OpenClaw and the silicon that powers it, our predictions for the hottest ticket in town
Nvidia has a bit of a problem. Popular generative AI workloads like code assistants and agentic systems generate massive quantities of tokens and need to move them at speed. But the GPU giant's chips currently struggle to deliver.…
- Pentagon AI chief praises Palantir tech for speeding battlefield strikes
Going from eight systems to one means fewer people make decisions to unleash Epic Fury
As the US continues its strikes on Iran as part of Operation Epic Fury, speakers at Palantir's AIPCON event on Thursday said the company’s Maven Smart System product has shortened the time it takes the Department of Defense to select and hit targets on the battlefield during the conflict.…
- Rogue AI agents can work together to hack systems and steal secrets
Prompt like a hard-ass boss who won't tolerate failure and bots will find ways to breach policy
AI agents work together to bypass security controls and stealthily steal sensitive data from within the enterprise systems in which they operate, according to tests carried out by frontier security lab Irregular.…
- District denies enrollment to child based on license plate reader data
Automated checks raised doubts, though key questions remain unanswered
American parents of school-aged children may want to pay attention to where their cars are parked and for how long, as license plate reader data is now being cited by at least one school district when challenging whether students live where they say they do.…
- Microsoft Copilot now boarding your health information
It's safe and secure, Redmond insists, but don't expect medical advice
Microsoft wants to store your healthcare data so that its AI "delivers personalized health insights that you can act on," but without the liability that comes with actual medical advice.…
- Oracle tops up restructuring fund for FY26 by $500M
Pot of money grows to $2.1BN for fiscal '26, as Big Red exec says AI helping smaller engineering teams do more
Oracle has increased funding for its restructuring plans for the current financial year by $500 million, with some observers anticipating a spate of job losses.…
- Musk makes the Macrohard joke again
The idea being that fleets of AI agents could emulate the 'function of entire companies'
Elon Musk wheeled out his "Macrohard" dad joke again in the form of a supposed fleet of "Digital Optimus" agents that he claims would be capable of "emulating the function of entire companies."…
- Users protest as Google Antigravity price floats upward
Google evolves its pricing for agentic AI tool, pointing devs towards on-demand credits or $250 per month Ultra plan
Developers using Google's Antigravity agentic AI coding tool are complaining about higher prices following an announcement yesterday that the company is evolving its AI plans.…
- Quicksort inventor Tony Hoare reaches the base case at 92
Classicist, philosopher, wit, and one of the greatest British computer scientists of all time
Obit Professor Charles Anthony Richard Hoare has died at the age of 92. Known to many computer science students as C. A. R. Hoare, and to his friends as Tony, he was not only one of the greatest minds in the history of programming – he also came up with a number of the field's pithiest quotes.…
- CISA warns max-severity n8n bug is being exploited in the wild
No rest for project maintainers battered by slew of vulnerability disclosures
The US Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) has confirmed that hackers are exploiting a max-severity remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability in workflow automation platform n8n.…
- Campaigners claim NHS Palantir system could be accessed by police and immigration
US spy-tech biz and platform provider retorts that this would be against the current law and a breach of its contract
Medical and legal rights campaigners are warning that the Palantir data platform, designed to be at the heart of England's health system, risks enabling UK immigration and policing departments to access confidential patient information.…
- Smart mirror shows dumb Windows in elevator
All aboard the elevator where only Microsoft knows where you're going
Bork!Bork!Bork! Smart mirrors are all the rage. However, rather than a list of headlines and tasks to do today, an unhappy Windows installation can make a smart mirror seem very dumb indeed.…
- So much for power to the people – AI datacenters could jump UK grid queue
Plan to fast-track bit barn connections leaves housing developers fuming and billpayers on the hook
The British government is consulting on reforms to prioritize "strategically important" grid connections – including datacenters – amid reports of delays stretching more than a decade on some projects.…
- China’s CERT warns OpenClaw can inflict nasty wounds
Like deleting data, exposing keys, and loading malicious content - which may be why Beijing has reportedly banned it
China’s National Computer Network Emergency Response Technical Team has warned locals that the OpenClaw agentic AI tool poses significant security risks.…
- Atlassian to shed ten percent of staff, because AI
Company is ‘reshaping our skill mix’ amid long share price slide and SaaSpocalypse whispers
Australian collaborationware company Atlassian has announced it will shed ten percent of staff – around 1,600 people.…
- Perplexity Comet hurtling toward Amazon ban
Court issues preliminary injunction but delays it to allow an appeal
Perplexity's AI browser Comet has been banned from accessing Amazon's website after the e-commerce giant obtained a court-ordered preliminary injunction.…
- Iran plots 'infrastructure warfare' against US tech giants
State news published a list of nearly 30 sites that could be targeted
Iran has reportedly designated Amazon, Google, IBM, Microsoft, Nvidia, Oracle, and Palantir facilities as legitimate targets of retaliatory strikes, according to an Al Jazeera report citing Iran’s state-affiliated Tasnim news agency.…

- From DHCP to SZTP – The Trust Revolution
By Juha Holkkola, FusionLayer Group The Dawn of Effortless Connectivity In the transformative years of the late 1990s, a quiet revolution took place, fundamentally altering how we connect to networks. The introduction of DHCP answered a crucial question, Where are you on the network?!, by automating IP address assignment. This innovation eradicated the manual configuration [0]
The post From DHCP to SZTP – The Trust Revolution appeared first on Linux.com.

- OpenRazer 3.12 Released With Support For Newer Razer Products On Linux
OpenRazer 3.12 was just released today as the newest update to these independently-maintained, open-source drivers for Razer devices on Linux. Paired with the likes of the Polychromatic GUI, OpenRazer allows for a pleasant experience for the Razer gaming peripherals under Linux...
- Panther Lake Tuning For The Intel Idle Driver In Linux 7.1
While the Linux support for Intel Core Ultra Series 3 Panther Lake is largely in good shape as shown in my numerous articles over the past month and a half, there are occasional missing remnants landing in the kernel. As the latest example, or the upcoming Linux 7.1 kernel, the unified Panther Lake C-States table is being added for the Intel Idle driver...
- Linux 6.12 Through Linux 7.0 File-System Benchmarks For EXT4 + XFS
Earlier this month were various Linux 7.0 file-system benchmarks showing how XFS is leading the race in the overall upstream Linux file-system performance on this forthcoming kernel. Stemming from that testing some premium supporters requested a fresh look at the historical performance of XFS as well as EXT4. So today9s article is a look at how XFS and EXT4 have performed on every kernel release going back to Linux 6.12 LTS.
- Intel NPU Driver 1.30 Released For Linux
For going along with the Intel IVPU kernel accelerator driver in the mainline Linux kernel is the Intel NPU driver support in user-space. Released yesterday was the Intel NPU Driver 1.30 milestone for advancing the Intel NPU user-space support on Linux with this open-source support for Core Ultra SoCs...
- GNOME Infrastructure Now Battling Bots & AI Scrapers Using Fastly
GNOME's GitLab infrastructure has already been using Anubis for a while to help fend off bots and AI scraper traffic from wreacking havoc on their server resources and also their hosting budget. GNOME recently began redirecting some GitLab traffic to their GitHub repositories as another step in dealing with bots/scrapers. Now they have taken an added step of using the commercial, closed-source Fastly in their battle with bots...
- TrueNAS Connect Announced For Offering Enterprise Features Without The Hardware
Last year TrueNAS unified their SCALE and CORE offerings as part of solidifying their enterprise storage efforts around Linux from their prior FreeBSD base. This year the developers at iXsystems have another change in store with announcing TrueNAS Connect as a new bridge for accessing TrueNAS enterprise storage features without having to invest in their hardware...
- systemd 260-rc3 Released With AI Agents Documentation Added
The first release candidate of systemd 260 arrived in late February with the new mstack feature, dropping System V service scripts support, and other changes. A week after that systemd 260-rc2 released with a few more changes and now another week later is systemd 260-rc3...
- AMD ZenDNN 5.2 Brings A Major Redesign, AOCC 5.1 Recently Released
AMD today released ZenDNN 5.2 as the latest versio nof their deep nueral network library that now introduces their next-generation runtime architecture. ZenDNN 5.2 is designed to deliver better performance and geater scalability over earlier versions of this AMD library that began as their take on Intel's open-source oneDNN...
- Intel CPU Security Mitigation Costs From Haswell Through Panther Lake
Over the past month on Phoronix there have been a lot of benchmarks of Intel9s new Core Ultra Series 3 "Panther Lake" with the Core Ultra X7 358H. One of the areas of Panther Lake not explored yet is around the CPU security mitigation impact, which is the focus of today9s benchmarking. The performance tests today are not only looking at the impact of the Core Ultra X7 SoC at its default versus running in a "mitigations=off" configuration but also comparing the overall CPU security mitigation impact with the run-time toggle going back all the way to Intel Haswell era laptops.
- AMD HDR/Color Improvement For Their Linux Driver & KDE - Co-Developed By Claude Code
Introduced with Linux 6.19 was the long in development DRM Color Pipeline API while it's not the end of the road yet on enhancing the Linux desktop for modern high dynamic range (HDR) displays and color pipeline handling. AMD engineer Harry Wentland has more improvements pending for the AMDGPU driver as well as example compositor/desktop-side integration with KDE's KWin...
- Spotify’s new Taste Profile feature lets users fine-tune their algorithm’s recommendations
You're responsible for your own Spotify algorithm now. On stage at SXSW, Spotify's co-CEO, Gustav Söderström, announced the Taste Profile feature, which allows users to personally customize exactly what they want to listen to, whether it's music, audiobooks or podcasts. This AI-powered feature is still in beta, and it will be available to Premium users in New Zealand in the coming weeks.
From its short video demo, Spotify's Taste Profile feature will show you a summary of your listening habits and offer a "Tell us more" prompt at the bottom. With the new prompt, users can inform the AI what they want to see more of or if they want to get rid of a genre that keeps popping up in their algorithm. Spotify said that the Taste Profile will take into consideration more ambiguous prompts, too, like if you're training for a marathon and want upbeat music or want to listen to news podcasts during your commute to work. Spotify added that Taste Profile is an optional feature, and unwilling users can "leave it and enjoy Spotify as usual."
With Taste Profile, Spotify is continuing its momentum of offering AI features, like the Prompted Playlist feature that was made available last month. Unlike the existing AI Playlist feature, Prompted Playlist lets you put in specific requests to generate a playlist, like only including songs from a specific TV show. Like Taste Profile, the Prompted Playlist feature saw beta testing in New Zealand first, before expanding to US and Canadian users a month later.
This article originally appeared on Engadget at https://www.engadget.com/entertainment/music/spotifys-new-taste-profile-feature-lets-users-fine-tune-their-algorithms-recommendations-191104626.html?src=rss
- What to read this weekend: Locked in with The Iron Garden Sutra
Need something new for your reading list? This week, we recommend A.D. Sui's The Iron Garden Sutra, a meditative horror sci-fi/fantasy and murder mystery.
I don't typically gravitate toward locked room mysteries, but the description of this book ticked all the right boxes to win me over: "a death monk and a team of researchers trapped onboard a spaceship of the dead encounter something beyond human understanding." It has all the makings of a compelling murder mystery, which is fine on its own, but thanks to the philosophical musings of its main character, Vessel Iris, and a setting that almost demands existential contemplation, it becomes something much deeper.
Vessel Iris is a monk some time in the far future whose mission is to perform funeral rites for the dead so their souls may reach their ultimate destination, according to the beliefs of his religion, the Starlit Order. "Vessels" like Iris share their mind with an AI companion, which creates a really interesting dynamic for the reader, as there is a constant dialogue going on between the two from the start (carrying a tone that sometimes verges on "old married couple," which I quite enjoyed). Iris shows up to an ancient ship called the Counsel of Nicaea expecting to perform his duties for the long-deceased on board and instead finds himself facing a group of researchers who are very much not dead — and a jumbled mess of bones from the hundreds of bodies they disturbed by moving, which he'll have to sort in order to properly bless.
Despite being a ghost ship in most respects, it turns out the Nicaea is alive with vegetation and gardens that would have once supported the humans that lived there. And, there's seemingly something else, as Iris' AI begins to pick up strange pings from a presence on the ship, and one by one the team of researchers starts getting picked off. As everything unravels, Iris begins to question his faith and his purpose.
This was such a great read, and I was excited to learn it's the first in a two-book series, The Cosmic Wheel series. Fans of horror sci-fi/sci-fantasy should definitely check this one out.
This article originally appeared on Engadget at https://www.engadget.com/entertainment/what-to-read-this-weekend-locked-in-with-the-iron-garden-sutra-172342019.html?src=rss
- Meta is reportedly planning to cut up to 20 percent of its staff in upcoming layoffs
Meta could be preparing for one of the largest layoffs in its history, according to a financial report, the company's employee headcount was 78,865 as of December 31, 2025, while revenue reached nearly $60 billion for the fourth quarter and more than $200 billion for the entire year. A Meta spokesperson told Reuters that this was "speculative reporting about theoretical approaches."
Meta is no stranger to major layoffs. Earlier this year, Meta targeted about 1,000 employees in its layoffs with the Reality Labs division that's responsible for the company's virtual reality and metaverse efforts. Early last year, Meta laid off about five percent of its workforce, following a smaller round of firings that same month. Meanwhile, the company has been spending heavily to acquire AI startups, like Moltbook, a social network designed for AI agents, and Manus, a startup focused on AI agents for task automation.
This article originally appeared on Engadget at https://www.engadget.com/big-tech/meta-is-reportedly-planning-to-cut-up-to-20-percent-of-its-staff-in-upcoming-layoffs-160812304.html?src=rss
- Digg shuts down for a 'hard reset' because it was flooded with bots
Digg has shut down, for now, just a few months after its open beta launched. Justin Mezzell, the company’s CEO, has explained on the home page that it noticed hours after the beta launched that it was already being targeted by SEO spammers. “The internet is now populated, in meaningful part, by sophisticated AI agents and automated accounts,” he wrote. Apparently, the Digg team wasn’t ready for the scale and the speed at which bots found and started flooding the website.
Mezzell said Digg banned thousands of accounts and deployed both internal tools and external solutions, but they weren’t enough. He admitted that the votes and the comments on the website couldn’t be trusted due to the amount of bot activity it got. While Digg has decided to significantly downsize its team, a small number of staff members has stayed to rebuild it completely. He said it wasn’t enough to present Digg as an alternative to current social networks and community-based websites. “What comes next needs to be genuinely different,” he added.
The CEO didn’t explain how Digg will reinvent itself, but he did announce that its founder, Kevin Rose, is joining the company full time. Rose bought back Digg last year in partnership with Reddit co-founder Alexis Ohanian. Back then, they said they had “a fresh vision to restore the spirit of discovery and genuine community that made the early web a fun and exciting place to be.” Based on what happened to Digg, that’s now harder to achieve with the state of the internet today.
This article originally appeared on Engadget at https://www.engadget.com/social-media/digg-shuts-down-for-a-hard-reset-because-it-was-flooded-with-bots-153848094.html?src=rss
- Ball x Pit on mobile, Piece by Piece x2 and other new indie games worth checking out
Welcome to our latest roundup of what's going on in the indie game space. A bunch of intriguing games arrived this week, including a mobile port of one of the most absorbing things I’ve played in years and two completely different titles with the same name. Let’s get things started with a look at a few projects that were featured in the latest edition of the Future Games Show.
Hyperwired (from SidralGames and publisher SelectaPlay) is a 2D roguelike shooter with an interesting resource-management twist. To recharge your weapons and systems, you have to plug a cable that trails behind your spaceship into a socket. While you're plugged in, your movement is restricted by the length of the tether, but you gain more firepower.
There are a whole bunch of upgrades and bullet modifiers to play around with here, including a slow-motion system you can activate at almost any time. Hyperwired is slated to hit Steam, PS4, PS5, Xbox One, Xbox Series X/S and Nintendo Switch this summer.
In Clean Up Earth, you and other players can work together to restore polluted environments. You can play solo if you like, but on the larger maps you'll need to team up with others to handle large bits of junk. One particularly neat aspect of Clean Up Earth is that in-game actions will automatically trigger micro-donations from developer Magic Pockets and its partners to environmental organizations.
Clean Up Earth is coming to Steam, Epic Games Store, PS5, and Xbox Series X/S on April 2. A Nintendo Switch 2 version is on the way in the future. There's a demo available on Steam as well.
Mr. Magpie’s Harmless Card Game is a minesweeper-style riff on the likes of Inscryption and Buckshot Roulette. As with some other roguelike deckbuilders, you're trapped in a creepy situation and the only way to escape alive is to gamble and earn enough money in time to meet quotas. To do that, you'll need to twist the odds in your favor by building multipliers and synergies. You can boost your deck with powerful cards you can buy from a shop.
However, there are dangerous JERRY cards on the board that could spell doom if you flip them over. You can use hints and strategies to try to figure out where those cards are and avoid them.
There's no release date as yet for Mr. Magpie’s Harmless Card Game, which is from Giant Light Studios. However, you can request access to a playtest on Steam.
A press release described Herdles as "Spyro meets Breath of the Wild, with a dog." I'm immediately sold.
Playing as a magical version of creative director Christian Hübel’s own dog, Snoopy, you'll "restore balance to a fracturing world" in this open-world platformer. On your journey, you'll rescue Herdles, or corrupted creatures. Doing so will unlock new powers, such as being able to glide, bust through walls and swim up waterfalls.
There's no combat or death in this game, which seems to be largely about solving puzzles, experimenting with physics-based abilities and exploring. It's said to have "deep accessibility and customization options" too. Fire Sword Studios and One More Journey are behind Herdles, which does not have a release window, though the Steam page is live.
New releases
I took an earlier-than-usual lunch break on Thursday to check out the OhSnap's MCON or the Backbone Pro works better for me.
A bunch more people will be able to enjoy Ball x Pit now that it's on iOS and Android. You can play the first level for free and it costs $10 to unlock the full game.
It's a pretty good week for folks who are into brick-breaking roguelites, because here's another one. ITER-8 (from fluckyMachine and publisher Fireshine Games) blends mining and tower defense. It's a bit like Dome Keeper.
You're tasked with acquiring resources from an enormous monolith that's above your base. You'll need to drag these items back to your base so you can upgrade your character, ship, shield and weapon. There are relics to find and you can swap these for installations like lasers, barriers and cannons. There are also puzzle-based sections that sees your character leave their ship for some in-person mining and upgrade collecting, temporarily switching from 2D to 3D action.
After a while, the monolith starts to thrum with an ominous sound. That means it's time to race back to base (with the help of a fast-travel system) to fend off waves of alien enemies.
The two sides of ITER-8 work fairly well together and I've enjoyed my time with it so far. I actually find it pretty relaxing overall, though the tower-defense aspect could have been designed a bit more elegantly. Switching aim from one side of the base to the other doesn’t feel snappy enough. ITER-8 is available on Steam for $13. There's a 25 percent launch discount available until March 23.
Piece by Piece is billed as a cozy repair shop game from Gamkat and publisher No More Robots. It looks cute!
You can decorate your shop and make it homely by cleaning, keeping the log fire burning and making sure the cookie jar is full. Of course, you'll be fixing up heirlooms and antiques for customers too. It's out now on Steam for $12, with a 20 percent discount until March 25.
Piece by Piece is a puzzle platformer in the most literal sense. You manipulate levels by moving puzzle pieces around. It's a great idea from Neon Polygons and I'm keen to check this one out on Steam. It typically costs $13, but there's a 15 percent discount until March 27.
Wait a second here... Two games called Piece by Piece that were released in the same week? That's a heck of a coincidence. Thankfully, the teams behind both games saw the funny side. They've even created a bundle of both games so you can buy them both for an extra 10 percent off.
Here's another puzzle-forward game, albeit one that's more of an adventure. In Rhell: Warped Worlds & Troubled Times, you'll discover and combine spells in creative ways to solve riddles in similar fashion to games like Baba Is You. There are said to be more than a million ways to combine the magical keywords. Since every spell works on any object in the game, there are more than 102 million possible configurations. Neat!
Solo developer Alice Jarratt from SlugGlove spent three years making Rhell: Warped Worlds & Troubled Times and drew more than 10,000 frames of animation for it. The game is available on Steam for $15, with a 20 percent launch discount until March 26. A demo is available too.
Upcoming
I've had Hoa on my wishlist for forever, so it's probably time for me to check out that puzzle platformer before the sequel arrives later this year. Hoa 2 (from Skrollcat Studio and publisher PM Studios) sticks with the hand-painted art of the original game but it’s a 3D game this time.
It begins a long, long time after the end of Hoa, with the eponymous fairy returning to a world that's been transformed by time. But many of her old friends have passed away, so Hoa seeks a new purpose.
Along with platforming and spatial puzzles, Hoa 2 features secrets and mini-games. It's coming to Steam, PS5, Xbox Series X/S and Nintendo Switch 2.
I dig what I've seen of MotorSlice, which seems to have Mirror's Edge-style parkour action but in a much grittier-looking world. The developers also took inspiration from the Prince of Persia series and Shadow of the Colossus here — perhaps not too surprising in the latter case given that you'll be scaling huge bosses. This action adventure sees you on a mission to destroy every piece of machinery inside a ruined megastructure.
MotorSlice is coming to Steam this spring. A demo for this game from Regular Studio and publisher Top Hat Studios is available now.
Being a lifelong soccer fan is a curse that's punctuated with infrequent moments of the most intense joy you'll ever feel. Plus, every few years, I lose about a month of my life to the most recent version of Football Manager (I gave up on the last one after winning every possible trophy with Borussia Mönchengladbach for three seasons in a row). So, it's safe to say that a game focused on perhaps the least glamourous job in soccer is up my alley.
Kitman — a job you might know of as "equipment manager" — is a sports management game with co-op for up to four people in which you take care of things behind the scenes of a soccer team. You'll clean locker rooms, polish boots, make sure players have the right uniforms and so on, while taking care of details on the fly on match days.
There's a fun twist here in that you can secretly take on some of the manager's duties, such as scouting players and adjusting formations. Maybe that explains what's been happening with Tottenham Hotspur lately.
Kitman, from Outlier, is coming to Steam later this year. In the meantime, you can sign up to take part in a playtest.
If, like me, you offered Trest the chance to bring his game to PS5. Astrolander is also coming to Steam. It's set to arrive later this year.
This article originally appeared on Engadget at https://www.engadget.com/gaming/ball-x-pit-on-mobile-piece-by-piece-x2-and-other-new-indie-games-worth-checking-out-110000319.html?src=rss
- OpenAI reportedly plans to add Sora video generation to ChatGPT
OpenAI plans to add its Sora video generation model directly into ChatGPT, Sora app was seen as a smash hit when it launched alongside Sora 2 in September 2025, but interest in the video generation app has fallen in the time since as users ran into limits on the amount and kinds of videos they could create.
Adding Sora to the ChatGPT could give the model a second life, and ideally grow the ChatGPT app's weekly active users from the 900 million OpenAI reported in February, to a billion or more. According to The Information, the standalone Sora app will stick around after the model is integrated, even though the app has fallen out of the App Store's top 100 free apps and only a small number of users reportedly share their videos publicly in the app.
It’s hard to pin down an exact number for what generating a video costs OpenAI, but the company charges API customers $0.10 per second for a 720p video, and in 2025, it was willing to give away 30 free video generations per account per a day in the Sora app. When you consider the even larger audience that could use the model in the ChatGPT app, things could get expensive fast. That could be one reason The Information reports OpenAI has projected it could spend over $225 billion on inference — the cost of running the company's models — between 2026 and 2030.
The company has attempted to monetize the Sora app by having users pay for credits to generate new videos, and could deploy something similar once the model comes to ChatGPT. Maybe giving customers the ability to generate videos with Disney characters could even get people to pay for more videos once they run out of free generations. Whether or not adding Sora to ChatGPT moves the needle for OpenAI, though, the company will likely be spending even more money than it was before.
This article originally appeared on Engadget at https://www.engadget.com/apps/openai-reportedly-plans-to-add-sora-video-generation-to-chatgpt-222611439.html?src=rss
- Meta is bringing more international news to its AI
Meta AI should soon be better at surfacing international news content thanks to a set of new deals with publishers. The company announced new agreements with international outlets and offered additional details on its recent deal with News Corp.
The latest deals bring French newspaper Le Figaro, Spanish media company Prisa and German newspaper Süddeutsche Zeitung into the fold. Together, along with News Corp, which runs a number of outlets in the UK, these sources should give Meta AI better access to timely info about world events. Meta didn9t disclose terms of the deals — The Wall Street Journal previously reported the News Corp arrangement was worth up to $50 million a year — but it said that it intends to link out to the relevant news sources.
"These integrations will also facilitate easier access to information by linking out to articles, allowing you to visit these partners’ websites for more details while providing value to partners, enabling them to reach new audiences," Meta wrote in an update. The company has a long and sometimes fraught history with publishers as its priorities have shifted over the years. In the past, Meta has struck deals to pay publishers to produce live video and "instant articles" only to change course as news content has become less of a priority for Facebook.
Now, with Meta struggling to compete with its AI rivals, it seems the social media company is once again interested in news content. As the company notes in its blog post, Meta AI isn9t always great at surfacing accurate and timely info. I noted this in 2024 when the company9s assistant was repeatedly unable to accurately answer seemingly simple questions like " who is the Speaker of the House of Representatives."
By striking a bunch of deals with publishers, the company should be better equipped to handle these kinds of queries (and hopefully more complex ones). How much benefit publishers will see from these arrangements, however, is an open question. While Meta says it will link out to the relevant news sources, there are lots of outside data points that raise serious questions about the effect AI search tools are having on web traffic.
This article originally appeared on Engadget at https://www.engadget.com/social-media/meta-is-bringing-more-international-news-to-its-ai-213323713.html?src=rss
- Adobe agrees to pay settlement for making its subscriptions hard to cancel
Adobe has agreed to pay the US government $75 million to settle its lawsuit over the company's allegedly harmful approach to subscriptions. The suit started in 2024, when the US Department of Justice and the Federal Trade Commission filed a joint complaint alleging the company deliberately made it difficult to cancel subscriptions and obscured the frequently expensive "early termination fee" customers have to pay to get out of annual subscriptions that are paid monthly.
"While we disagree with the government’s claims and deny any wrongdoing, we are pleased to resolve this matter," Adobe writes. "We have agreed to provide $75 million worth of free services to customers that qualify. We will proactively reach out to the affected customers once the appropriate filings with the Court are made and accepted. Additionally, we have agreed to a $75 million payment to the Department of Justice."
Adobe's statement also notes that it's made the process of both signing up for and canceling subscriptions "more streamlined and transparent." A major sticking point of the original complaint is that canceling an "annual plan, paid monthly" subscription before completing the first year of service required customers to pay an early termination fee to make up for the value Adobe lost initially offering its software at a discount. Adobe currently allows plans to be refunded if they're canceled within 14 days after signing up, but canceling an "annual plan, paid monthly" subscription after those first 14 days requires paying a hefty fee (as outlined in the company's detailed support page).
A court will have to approve Adobe's proposed settlement before the lawsuit can be totally resolved, but the timing is at least a little ironic. Shantanu Narayen, Adobe's CEO for the last 18 years and the executive who oversaw the company's transition from traditional software business to software-as-a-service business, recently announced plans to retire.
This article originally appeared on Engadget at https://www.engadget.com/big-tech/adobe-agrees-to-pay-settlement-for-making-its-subscriptions-hard-to-cancel-210336635.html?src=rss
- Nothing updates its AI app with semantic search and a new way to track events
In the mad dash many companies have made to incorporate AI features into their phones, Nothing arrived at one of the better ideas with Essential Space on the Nothing Phone 3a in 2025. The AI-powered app turns screenshots and voice recordings into actionable to-do lists and transcriptions, and now Nothing is rolling out an update to make the app easier to search and capable of recognizing new kinds of content.
As part of the update, Essential Space now recognizes "Events," displaying them in their own card with fields for the date, time and location. That means, for example, if you add a photo of a flyer for pottery class to the app, Essential Space will be able to pull the details of when and where it9s happening, and track it in much the same way it does tasks or to-dos. Nothing foresees events being such a big part of how people will use Essential Space that it9s also changing the layout of the app9s interface and listing things like Events and Tasks in a new For You page you see when you open the app.
To make everything you9ve stored in Essential Space easier to find, the app now also supports semantic search, surfacing results that don9t just match the text you9ve entered, but try to match the meaning of what you9re looking for. Semantic search should be particularly useful when you9re looking for an image, because you can enter a description of what you9re looking for and Essential Space should still be able to surface it.
Sorting and indexing digital ephemera like voice notes and screenshots with AI is a popular use for the technology. Google offers Pixel Screenshots, and even Apple gave iOS and iPadOS the ability to automatically recognize events in images and add them to your calendar. Essential Space might be less unique now, but the fact that Nothing continues to update it bodes well for its future.
Nothing9s new Essential Space update is available starting today on "all 2025–2026 Nothing and CMF phones that support Essential Key," the company says. Essential Space should automatically update, but you also manually update the app in the Google Play Store.
This article originally appeared on Engadget at https://www.engadget.com/apps/nothing-updates-its-ai-app-with-semantic-search-and-a-new-way-to-track-events-202500495.html?src=rss
- The MacBook Neo is Apple's most repairable laptop
Apple's cheapest laptop is also its most repairable. iFixit gave the new MacBook Neo a 6/10 repairability score. Although that number would only be mediocre for, say, a game review or final exam grade, it's the MacBook line's highest iFixit score in about 14 years.
As always, iFixit goes into great detail about the product's repairability, but a few points stand out. First, the MacBook Neo's battery is screwed down rather than glued — moving it from "this might burn the house down" to "routine repair" territory. The laptop also has a flat disassembly tree. That means its battery, speakers, ports and trackpad are all immediately accessible after opening the back case.
In other areas, a simplified antenna assembly helps the screen come away cleanly. Keyboard repair is still a bit tedious (41 screws and tape), but at least it isn't riveted to the top case like on other models. (The screwed-not-glued battery helps here, too.) Apple's decision to forego a Force Touch trackpad and return to a mechanical style improves repairability as well. And in a nice touch, all the machine's Torx Plus screw sizes are clearly labeled inside the case.
 Apple Apple
Several other encouraging signs carry over from recent MacBooks. iFixit found that Apple's Repair Assistant accepted all replacement parts it tried without a fuss. And its USB-C ports and headphone jack are modular, so replacing either doesn't "turn into logic board work."
Not everything is peachy. As expected, the Neo still has soldered RAM and storage, so there's no upgrade path there. iFixit describes Apple's pentalobe screws on the bottom case as an "annoying" choice. And while the device's speakers are easy to remove, they, well, just aren't very good. (Had to cut that cost somewhere.)
While iFixit describes the Neo's repairability as "a real comeback," it's premature to assume higher-end MacBooks will follow suit. After all, with this $599 device ($499 for schools), Apple is targeting the educational sector, where repairability could mean more bulk orders. Until Apple is convinced that the MacBook Air or Pro would sell better with similar serviceability, this kind of score may be limited to the budget model.
This article originally appeared on Engadget at https://www.engadget.com/computing/laptops/the-macbook-neo-is-apples-most-repairable-laptop-200923202.html?src=rss
- Meta is killing end-to-end encryption in Instagram DMs
Meta is killing end-to-end encryption in Instagram DMs. The feature will "no longer be supported after May 8, 2026," the company wrote in an update on its support page. Unlike WhatsApp, Meta never made encryption available to all Instagram users and it was never a default setting. Instead, users in "some areas" had the ability to opt-in to encryption on a per-chat basis.
In a statement, a Meta spokesperson said the feature was being retired due to low adoption. "Very few people were opting in to end-to-end encrypted messaging in DMs, so we're removing this option from Instagram in the coming months," the spokesperson said. "Anyone who wants to keep messaging with end-to-end encryption can easily do that on WhatsApp.”
Interestingly, Meta's statement doesn't mention the status of encryption on Messenger. The company began turning on end-to-end encryption as a default setting in 2023 after years of work on the feature. A support page for Messenger currently states that the company "is in the process of securing personal messages with end-to-end encryption by default."
Meta's approach to encrypted messaging has changed several times over the years. It started encrypting WhatsApp chats in 2016. In 2019, Mark Zuckerberg outlined a "privacy-focused" revamp of the company's apps, saying at the time that "implementing end-to-end encryption for all private communications is the right thing to do." In 2021, the company's head of safety said that Meta was delaying its encryption work until 2023 in order to create stronger safety features.
Meta’s use of encryption has been repeatedly criticized by law enforcement and some child safety organizations that say the feature makes it harder to catch predators who target children on social media. Recently, the topic has been raised numerous times during a trial in New Mexico over child safety. Internal documents that have surfaced as part of the trial show Meta executives and researchers debating the trade-offs between safety and privacy as it relates to encryption.
In testimony that was broadcast during the trial, Zuckerberg said that safety issues were "a large part of the reason why it took so long" to bring encryption to Messenger. "There's been debate about this, but I think the majority of folks, from people who use our products to people who are involved in security overall, believe that strong encryption is positive," he said.
This article originally appeared on Engadget at https://www.engadget.com/social-media/meta-is-killing-end-to-end-encryption-in-instagram-dms-195207421.html?src=rss
- You'll now have to fork out for an additional subscription if you want to watch 4K content on Prime Video
Amazon is raising the price of its ad-free Prime Video subscription and locking 4K UHD streaming behind this new tier. Starting April 10 for US customers, a rebranded Prime Video Ultra subscription will cost $5 per month, up from $3 per month.
For that extra $2, you get a download capacity increase from 25 to 100, and you can now run five streams concurrently instead of three. Whether those "Ultra" upgrades are worth the $24 annual hike will probably depend on how many boxsets you like to plough through on a long flight, or how many devices are using your Prime Video account.
The changes are most galling for Prime members who automatically qualify for Prime Video with ads through their membership, as Amazon has decided to remove 4K streaming from the standard tier. That means that, despite already paying $15 per month or $139 per year for Amazon Prime, you’ll be stuck with 1080p shows and movies unless you sign up to Prime Video Ultra.
Amazon has thrown in Dolby Vision support for the first time, as well as upping the concurrent stream and download count on its free tier as well, but you’re losing the privilege of UHD content that has been available to all Prime Video members for years. Dolby Atmos remains exclusive to the $5 tier too.
Amazon is the latest streamer to put its prices up, following similar recent hikes to Apple TV, Disney+ and HBO Max. If you don’t want to give the company any more of your hard-earned, you have just under a month to binge your way through the second season of Fallout in all of its irradiated UHD glory.
This article originally appeared on Engadget at https://www.engadget.com/entertainment/streaming/youll-now-have-to-fork-out-for-an-additional-subscription-if-you-want-to-watch-4k-content-on-prime-video-174028064.html?src=rss
- Parallels Desktop creators say MacBook Neo does indeed have enough muscle to run Windows apps
Parallels, the company best known for making the virtualization software that enables you to run Windows and other operating systems on a Mac, has confirmed that Parallels Desktop is compatible with the MacBook Neo.
At launch it was unclear if Apple9s new $600 laptop possessed the under-the-hood heft to run Windows apps, but in a recently updated post on its website, Parallels said that initial tests show its software running "stably," although performance is still being assessed.
The MacBook Neo uses an A18 Pro chip, which debuted in the iPhone 16 Pro. However, as this chip is based on the same ARM architecture as M-series chips for Mac, it’s still capable of running Parallels’ Windows virtual machine.
But there is a caveat to all this. Just because you can do something, it doesn’t necessarily mean you should. While Parallels Desktop could theoretically be a viable option for Neo owners who are only interested in light Windows use, anything that puts a significant strain on the CPU or GPU is going to present a problem.
This is because the MacBook Neo only ships with 8GB of RAM, and as Parallels highlights, Windows 11 requires a minimum of 4GB of RAM to run. That leaves a very small amount of remaining headroom for macOS and your Mac apps to run alongside Windows, which is going to noticeably hurt the laptop’s performance. Add to that the lack of a cooling fan, meaning the chip will reduce clock speeds when it detects a heavy CPU or GPU load, and this definitely isn’t a device for power users.
If you really want to dabble with Windows on a Mac, Parallels recommends picking up an Apple laptop with 16GB of unified memory or more, like the new MacBook Air M5 or a MacBook Pro. And for those content with macOS and looking to save some money, we dubbed the MacBook Neo the best $600 laptop we’ve ever used in our recently published review.
This article originally appeared on Engadget at https://www.engadget.com/computing/laptops/parallels-desktop-creators-say-macbook-neo-does-indeed-have-enough-muscle-to-run-windows-apps-164525546.html?src=rss
- X could be breaching US sanctions on Iran, watchdog warns
The newly verified X account for Iran's supreme leader could be putting the company on the wrong side of US sanctions, according to a watchdog group. The Tech Transparency Project, which last month published a report on X granting premium perks to sanctioned officials in Iran, now says that the verified account for the country's new leader raises fresh questions about the issue.
The TTP notes that the X account for Iran's new supreme leader, Mojtaba Khamenei, appears to be paying for an X premium subscription despite being on the US government's list of sanctioned individuals since 2019. As the group points out, the Iran-based account was created this month and currently bears a blue checkmark, which typically indicates the account holder is paying for a subscription.
Last month, TTP found that X was providing premium subscriptions to Iranian officials sanctioned by @USTreasury, a transaction that may violate sanctions.
It didn't end there.
An account for Iran's new supreme leader created this month also carries the blue premium checkmark.🧵 pic.twitter.com/5K9Ss1Sex8
— Tech Transparency Project (@TTP_updates) March 12, 2026
The account belonging to Mojtaba Khamenei has been boosted by other state-linked accounts in Iran, including the one that previously belonged to Khamenei's father. That account has had a gray checkmark, which indicates it belongs to a verified government official. Verified accounts on X are rewarded with extra visibility on the platform, along with other perks. The younger Khamenei's verified account has already gained more than 20,000 new followers in the hours since TTP first posted about it.
"The new Supreme Leader's account is just the latest account for a sanctioned entity apparently paying X for premium services," TTP director Katie Paul said in a statement to Engadget. "TTP has identified dozens of accounts, many linked to designated terrorists, that subscribed to X premium over the past three years. What's more concerning than the blatant disregard for U.S. sanctions law is the fact that Musk's companies have a contract with the Pentagon while X is actively profiting from U.S. adversaries."
As Paul notes, this isn't the first time TTP has raised questions about whether X is running afoul of US sanctions via its premium service. In 2024, the group published a report noting that X was accepting paid verification from more than two dozen sanctioned individuals and groups. The company said at the time that it had a "a robust and secure approach in place for our monetization features."
X didn't respond to a request for comment. But in the hours after Engadget reached out about Khamenei’s account, the blue checkmark was removed. The company also removed blue checks from a handful of Iran-based accounts flagged by TTP last month following reporting from Wired.
Update, March 13, 2026, 9:08AM PT: This story was updated to reflect changes made to Khamenei’s account following publication.
This article originally appeared on Engadget at https://www.engadget.com/social-media/x-could-be-breaching-us-sanctions-on-iran-watchdog-warns-213550284.html?src=rss
- How to clean and organize your Mac
Inevitably, the more you use something — your Mac included — the more dirty and cluttered it’s likely to become. At that point, you can buy a new machine, but the more economical move is to make what you have already work better. To help your computer feel new, or at least a little cleaner and less chaotic, we put together this guide with techniques and useful apps that have helped us maintain a more organized computer. I’ve been using these tips since before I first published this guide in 2021, and they’ve helped keep my 2018 MacBook Air looking and running (almost) like brand new.
How to clean your Mac’s screen and body
While there are many products out there from manufacturers claiming their one does it best, my advice is to keep things simple. It’s also the one Apple recommends. To start, you will need some water in a spray bottle and a clean microfiber cloth. You can use regular water from the tap but I9ve found distilled water works best; it’s far less likely to leave residue behind on your Mac, particularly on the display. You can buy distilled water at a grocery store or make it yourself with some simple cookware. Either way, it’s more affordable than dedicated cleaning solutions. If you don’t already own any microfiber towels, Amazon sells affordable 24-packs you can get for about $10.
One other product I would recommend is a Giottos Rocket Blower. I can’t say enough good things about this little tool. It will save you from buying expensive and wasteful cans of compressed air.
As for the actual process of cleaning your Mac, remember to start with a clean cloth (that’s part of the reason we recommend buying them in bulk). You’ll save yourself time and frustration this way. Begin by turning off your computer and unplugging it. If you bought a Rocket Blower, use it now to remove any dust. If not, take a dry microfiber cloth and go over your computer. Take special care around the keys, particularly if you own an older Mac with a butterfly keyboard.
Next, dampen one side of your cleaning cloth with water. Never spray any liquid directly on your computer. You’ll have more control this way and you’ll avoid getting any moisture into your Mac’s internals. I always clean the display first since the last thing I want to do is create more work for myself by transferring dirt from some other part of my computer to the screen.
The last step is to buff and polish your computer with the dry side of the cloth. Be gentle here as you don’t want to scratch the screen or any other part of. That’s it. Your Mac should be looking clean again.
How to organize your hard drive Igor Bonifacic / Engadget
One of the trickiest parts of cleaning your Mac’s hard drive is knowing where to start; most of us have apps on our computers we don’t even remember installing in the first place. Thankfully, macOS comes with a tool to help you with that exact issue.
Navigate to System Settings > General > Storage. Here you’ll find a tool that separates your storage into broad categories like "Applications," "Documents," "Music," "Photos" and so on. Either double-click on an item in the list or click the circled i icon to see the last time you used an app and how much space it’s taking up. You can delete the apps from the same window.
The applications section is particularly helpful since you can see the last time you used a program, as well as if it’s no longer supported by the operating system or if it’s outdated thanks to a more recent release.
You don’t need me to tell you to uninstall programs you don’t use, but what you might not know is that there’s a better way to erase them than simply dragging them to the trash can. A free program calledAppCleaner will help you track down any files and folders that would get left behind if you were just to delete an application.
Igor Bonifacic / Engadget
After deleting any apps you don’t need, move to the Documents section. The name is somewhat misleading here since you’ll find more than just text files and Keynote spreadsheets. In this case, documents turns out to be the tool’s catch-all term for a variety of files, including ones that take up a large amount of space. You can also safely delete any DMGs (disc image files with the extension .dmg) for which you’ve installed the related app.
The other sections in the storage space are self-explanatory. The only other thing I’ll mention is if you’ve been using an iPhone for a while, there’s a good chance you’ll have old iOS backups stored on your computer. You can safely delete those, too.
Tips and tricks for keeping a neat Desktop and Finder Igor Bonifacic
Let’s start with the menu bar. It may not technically be part of the desktop, but a tidy one can go a long way toward making everything else look less cluttered. My recommendation here is to download an app calledBartender. At first glance, it’s a simple program allowing you to hide unwanted menu bar items behind a three-dots icon, but the strength of Bartender is that you get a lot of customization options. For example, you can set a trigger that will automatically move the battery status icon out from hiding when your computer isn’t connected to a power outlet.
While we’re on the subject of the menu bar, take a second to navigate to System Settings > General > Login Items & Extensions and look at all the apps that launch when you boot up your system. You can speed up your system by paring down this list to only the programs you use frequently.
When it comes to the desktop itself, less is more. Nothing will make your computer look like a cluttered mess more than a busy desktop. Folders and stacks can help, but for most people, I suspect part of the problem is they use their desktop as a way to quickly and easily find files that are important to them.
If you’ve ever struggled to find a specific file or folder on your computer, try using your Mac’s tagging capabilities instead. Start by opening the Finder Settings menu (Command + ,) and click the Tags tab. You can use the default ones provided by macOS or make your own. Drag the ones you think you’ll use most often to the favorites areas at the bottom of the preferences window. This will make it so that they’re easily accessible when you want to use them. To append a tag to a file or folder, click on it while holding the ctrl key and select the one you want from the dropdown menu. You can also tag a file while working on it within an app. Keep in mind you can apply multiple tags to a single file or folder, and you can even apply them to applications.
Igor Bonifacic / Engadget
What makes tags so useful in macOS is that they can appear in the sidebar of the Finder window, and are easily searchable either directly with Finder or using Siri. As long as you have a system for organizing your files, even a simple one, you’ll find it easier to keep track of them. As one example, I like to apply an Engadget tag to any files related to my work. I’ll add an “Important” tag if it’s something that’s critical and I want to find quickly.
One tool that can help supercharge your Finder experience isAlfred. It’s effectively a more powerful version of Apple’s Spotlight feature. Among other things, you can use Alfred to find and launch apps quickly. There’s a bit of a learning curve, but once you get a hang of it, Alfred will change how you use your Mac for the better.
How to organize your windows and tabs Igor Bonifacic / Engadget
If you’ve used both macOS and Windows 10, you’ll know that Apple’s operating system doesn’t come with the best window management tools. You can click and hold on the green full-screen button to tile a window to either the left or right side of your screen, but that’s about it and the feature has always felt less precise than its Windows counterpart.
My suggestion is to download an app that replicates Windows 10’s snapping feature. You have several competing options that more or less offer the same functionality. My go-to is a $5 program calledMagnet. If you want a free alternative, check outRectangle. Another option isBetterSnapTool, which offers more functionality than Magnet but doesn’t have as clean of an interface. All three apps give you far more ways to configure your windows than what you get through the built-in tool in macOS. They also come with shortcut support, which means you can quickly set up your windows and get to work.
Check out more from our spring cleaning guide.
This article originally appeared on Engadget at https://www.engadget.com/computing/how-to-clean-your-mac-macbook-cleaning-supplies-digital-organization-153007592.html?src=rss
- Samsung Galaxy S26 review: The smartphone status quo
It's already smartphone season. Samsung's annual deluge encompasses three new phones for 2026: the frontier-pushing S26 Ultra ($1,300) with its innovative Privacy Screen, the S26 ($899) and the S26+ ($999). The smaller flagships, yet again, are iterative versions of what came before, with the major differences centering on bigger batteries and brighter screens.
I'm getting waves of deja vu as I review the Galaxy S26, because at times I was writing exactly what I wrote last year��� including the part about it being a little too similar to what came before.
Hardware Image by Mat Smith for Engadget
Let's focus on the changes. The Galaxy S26's screen size is a little bigger than its predecessor's; 6.3 inches, up from 6.2 inches on the S25. However, it still has the same FHD+ (2,340 x 1,080) resolution. Given the slight size difference, there's no particular drop in sharpness. The screen can also go slightly brighter, topping out at 3,000 nits, which is always welcome — especially when Samsung has increased the battery to 4,300mAh from the S25's 4,000mAh. (The S25 already impressed us with its battery longevity.)
The design, however, is largely unchanged. The camera trio now sits on a unified circular island and, well, that's all I really have to say. Once again, it's premium Samsung hardware, but otherwise I'd just be reiterating what I said last year��� and our review from the year before that.
Inside, Samsung increased the base RAM to 12GB and the storage to 256GB on the S26, doubling the space found on the S25. With the S26's processor, Samsung split the device into two different builds depending on region. In the US, you'll get the Snapdragon 8 Elite Gen 5 for Galaxy, like the S26 Ultra. Elsewhere, including my review device in the UK, the S26 and (S26+) have the in-house Exynos 2600.
Samsung's Exynos 2600 SoC is its first 2nm chip and should offer power-efficiency improvements over larger alternatives. This year's S26 didn't struggle with any of the games I played or video-editing tasks. Samsung says its new chip delivers around 50 percent better performance across single- and multicore tasks. The Exynos 2600 includes a new Xclipse 960 GPU, which casubtlenuan deliver double the graphical performance of the Exynos 2500.
On Geekbench 6, the Exynos S26 scored 3151 on single-core tests and 10,664 on multicore tests (not far behind the Snapdragon-powered S26 Ultra). Similarly, the GPU score (24425) didn't lag far behind — all pleasant surprises. There is a but coming.
Comparing battery rundown tests between a Snapdragon S26 and my Exynos version revealed a gap. Watching a looped video at 50 percent brightness, the Exynos iteration lasted almost 28 hours, while the Snapdragon 8 Elite S26 lasted nearly 30 hours. Sure, that's great longevity regardless of which S26 model you get. But this year's flagship does have a bigger battery, so why is the Exynos-powered version only matching last year's phone?
Cameras Image by Mat Smith for Engadget
Not much has changed in the composition (or resolution) of the camera trio: there's a 50-megapixel main, a 12MP ultrawide and a 10MP telephoto. That means that any improvements in photos and video are subtle, to put it kindly.
It's hard to discern the improvements this year without really scrutinizing dark shots and zooming right in. The S26 does seem a little faster at capturing bursts and high-res video. And while I prefer the no-nonsense shooting of the Pixel 10a, the S26 offers a little more versatility with its zoom and ultrawide cameras. Cropped zoom, for example, lets you get closer to subjects beyond the 3X optical zoom, though more detail is lost than with the S26 Ultra and its larger resolution sensors.
Image by Mat Smith for Engadget
Once you've taken the shot, Samsung's bundle of AI tools can take over. Photo Assist attempts to corral all of these editing features into one place, offering quick ways to reduce reflections or edit out photobombers. You can now use natural language text prompts to guide your photo editing.
For example, I attempted to adjust the lighting more evenly on a photo of me taken outdoors with a flash. I could do it with my rudimentary photo-editing skills, but Samsung's tools are fast and, crucially, very easy to use. It's a feature where natural language interfaces really make sense.
With the front-facing camera, Samsung has added its Object Aware Engine, promising better, more accurate rendering of skin tones and hair, as well as an improved portrait mode. But again, I noticed marginal differences. The S26 seemed to have better color accuracy than its predecessor, resulting in slightly warmer selfies.
For videos, Samsung Super Steady mode is now more versatile, maintaining a consistent horizontal lock no matter how much you move around. As I mentioned during my hands-on, it's an interesting addition, the kind of feature you typically see on action cams and gimbals. It works well, too, although the footage does pick up a bit of focus-pumping as it fights to stabilize everything.
Rounding out the new additions is an Autoframing mode that crops in on your tracked subject as they move around. There's a degree of auto-detection for faces and pets, but you can tap to apply tracking to anything, to which it locks on well. It works particularly well with tripods, but there is a slight floating effect as the S26 tries to keep up with the phone's movement. I also noticed warping at the edge of the lens when the camera app kept my subject centered in the frame.
Software Image by Mat Smith for Engadget
Samsung's S26 launch event suggested this was the era of agentic AI, with assistants now positioned to connect the dots between tasks themselves. We're not quite there, though.
The company has slightly expanded many of the features introduced last year. Now Brief is capable of pulling data from more apps to generate more comprehensive daily summaries, but I mostly saw the usual suspects: weather, calendar reminders and not much else.
Across the S26, a new Now Nudge feature will suggest actions with an unobtrusive icon, based on what's happening on screen, such as sharing contact numbers with someone or suggesting calendar times while dealing with work emails.
Perplexity is an interesting addition. The S26 series is in a curious spot where it has hooks into no fewer than three AI assistants: Gemini, Bixby (bless its heart) and now Perplexity.
You do have to install the Perplexity app (and log in to use it), but you can then choose to make it your primary AI assistant. Odd things are missing: Samsung said Perplexity integration would work across the phone, including its own Browser app — something I was excited to test. Perplexity's own browser, Comet, has a slick feature that lets it browse and summarize multiple tabs. I was in the middle of deciding where to eat during my recent trip to Barcelona, so I thought this was a great use case. However, that feature isn't available in Samsung's browser for now. According to Perplexity, Samsung will "integrate Perplexity's APIs into the Samsung Browser, with agentic browser capabilities."
Voice commands of "Hey Plex" also went unanswered. I found I had to manually grant permissions to the Perplexity app for it to work like Google's Gemini. This could just be teething issues with a pre-release device and software, but Perplexity, for now, doesn't offer enough utility beyond what I was already used to with Gemini.
Wrap-up Image by Mat Smith for Engadget
The Galaxy S26 is a solid phone, with upgraded battery capacity and more base storage. Whether you get the Exynos or the Snapdragon S26, there's fortunately no performance gulf as has happened in the past. However, the shorter battery life is a disappointing discovery from Samsung's first 2nm chip.
For Samsung's smallest flagships over the last three years, it's all been very samey. Is the company now focused on its true flagship Ultra phone and foldables to generate buzz and make things exciting? That's what it feels like. There's nothing wrong with this safe, solid Android phone, but you could pick up last year's S25 and get an experience that's 99 percent the same for $99 less.
This article originally appeared on Engadget at https://www.engadget.com/mobile/smartphones/samsung-galaxy-s26-review-the-smartphone-status-quo-143033391.html?src=rss
- Engadget Podcast: Apple's $599 MacBook Neo is astounding
Somehow, Apple made a $599 laptop that's actually a joy to use. In this episode, Devindra and Deputy Editor Nathan Ingraham chat about what makes the MacBook Neo so great. And they also dive into the new M4 iPad Air, M5 MacBook Air and M5 Pro/Max MacBook Pros. Also, Roberto Baldwin, SAE International's Sustainability Editor, joins us to chat about the state of EVs today as gas prices explode.
Subscribe!
iTunes
Spotify
Pocket Casts
Stitcher
Google Podcasts
Topic
MacBook Neo review: Apple puts $600 Windows PCs to shame – 1:47
iPad Air M4 remains Apple’s best overall tablet – 18:05
Whistleblower claims ex-DOGE employee illegally took social security info on 500 million Americans to their new job – 33:37
Valve clarifies their outlook on the Steam Machine, it’ll launch in 2026, still no word on price – 36:08
Grammerly hit with a class action lawsuit for using reporters’ names in an editing ‘expert’ tool – 40:29
A new study claims every major AI chatbot will help users plan a hate attack or political assassination – 44:03
What to look for in a used EV with SAE International sustainability editor Roberto Baldwin – 48:31
Around Engadget – 1:21:04
Credits
Hosts: Devindra Hardawar and Nathan Ingraham
Guest: Roberto Baldwin
Producer: Ben Ellman
Music: Dale North and Terrence O’Brien
This article originally appeared on Engadget at https://www.engadget.com/computing/laptops/engadget-podcast-apples-599-macbook-neo-is-astounding-140402521.html?src=rss
- Apple is reducing its App Store commission fees in China
Apple is lowering its developer fees in China following discussions with the Chinese regulator. From March 15, the commission rate for standard in-app purchases (IAPs) will be reduced from 30 percent to 25 percent on its mainland China App Store storefront for both iOS and iPadOS.
In a Developer blog, Apple also said that developers belonging to its App Store Small Business or Mini Apps programmes will also have their fees reduced by 3 percent, from 15 to 12 percent. This applies to the commission rate for IAPs and in-app subscription renewals after the first year.
"We strive for iOS and iPadOS to be the best app ecosystem and a great business opportunity for developers in China," Apple said in the post. "We are committed to terms that remain fair and transparent to all developers, and to always offering competitive App Store rates to developers distributing apps in China that are no higher than overall rates in other markets."
Apple says developers are not required to agree to the terms by March 15 to start receiving their benefits, seemingly making the transition as smooth as possible to avoid further regulatory intervention. It will no doubt be taken as a significant win for Chinese businesses, and comes a year after reports that a state watchdog was investigating the fees Apple enforces on developers it hosts on the App Store.
This article originally appeared on Engadget at https://www.engadget.com/apps/apple-is-reducing-its-app-store-commission-fees-in-china-131221192.html?src=rss
- The Morning After: Our verdict on Apple’s $600 Macbook Neo
Apple9s new family of laptops might have a cringeworthy name, but don9t let it fool you. Despite the MacBook Neo running on a built-for-iPhone A-series processor and being limited to 8GB of RAM, it delivers on what Macs do best. It has a capable screen, keyboardand trackpadand its overall build quality should embarrass other laptop-making rivals that have compromised on those areas with their $600 laptops.
Neo review by Devindra Hardawar – surely you9re intrigued by the idea of a $600 MacBook?
— Mat Smith
The other big stories (and deals) this morning
Bumble is the latest dating app to add an AI assistant
Alexa+ can now swear
I guess this wasn9t an Xbox after all
RAMaggedon is not expected to ease this year as IDC cuts 2026 PC market forecast again.
Rabbit teases its modern take on the netbook, built for vibe codersI don9t have to like the Cyberdeck name.Microsoft9s Project Helix consoles will head to game studios in 2027Xbox wants a do-over.
In a bid to distract from corporate reshuffles, fears of generative AI game slop and a pretty poor showing against the PS5, Microsoft is getting ahead of its rival. At GDC 2026, the company said that it planned to get Project Helix dev consoles in the hands of game devs as soon as 2027.
Jason Ronald, vice-president of next generation for Xbox, reiterated that the new system would be capable of playing both Xbox console games and PC games. (Sony9s decision to halt porting its games across to PC makes more sense. ) Ronald said it would incorporate a custom AMD-made system-on-a-chip, offering "a magnitude leap in ray tracing performance and capability".
Meta bought another social networkFilled with bots, but on purpose.
The owners of Facebook are buying Moltbook, the hyped Reddit-like social network for AI agents that has only been around since January. The company hasn9t disclosed the terms of the deal, but Moltbook and its creators will be joining Meta Superintelligence Labs (MSL) when the deal closes.
And that definitely doesn9t sound like a cabal of comic book villains that fights the Justice League.
Continue reading.
This article originally appeared on Engadget at https://www.engadget.com/general/the-morning-after-engadget-newsletter-120553713.html?src=rss
- The 5 best meditation apps for 2026
Meditation is often touted as a mental cure-all, purported to help with stress, sleep, mood, focus and even certain medical conditions. I’ve been meditating most of my adult life. I’ve done silent retreats. I’ve been formally trained in various techniques. I’ve had someone in my contacts list who I referred to as a “guru.” So I feel I’m relatively qualified to give some bad news: Meditation won’t fix your life,despite what David Lynch says. However, there’s also some good news: Despite not actually being a cure-all for everything bad in the universe, meditation can certainly take the edge off.
This is where meditation apps can come into play. Of course, practicing mindfulness doesn’t require an app; people have been doing it for thousands of years, with nary a smartphone in sight. But mindfulness apps can be useful in a number of ways. They provide access to all kinds of guided meditations to suit different styles. Some even offer social connections, which can motivate you to keep up your practice via the magic of peer pressure. They are also particularly well-suited to beginners, with many of them offering a free trial. With all of this in mind, I downloaded some of the most popular meditation apps and set about sitting calmly on a comfortable chair to test them out. What follows is a comparison aimed at real people just looking to squeeze a bit more joy and relaxation out of daily life.
Best meditation apps
Other meditation gear we tested
Brain-tracking wearables have been around for years, but there are some newer devices that have been tailor-made for meditators. These gadgets track the brain during meditations and offer real-time feedback. It’s a real boon for the data-obsessed, but also a real bank account drainer, with some gadgets costing thousands of dollars. I took two of the more-popular options for a spin to see what they’d make of my brain.
Sens.ai Neurofeedback System
Sens.ai is a weird contraption that not only claims to track brainwaves, but gives real-time feedback to “teach” people how to meditate and enter a flow state. The device involves a giant headset that’s stuffed with brainwave sensors that detect beta, alpha, theta and gamma waves, in addition to heart-rate sensors. It also comes with a truly bizarre companion gadget that uses light stimulation (transcranial photobiomodulation) to keep an eye on focus and attention levels. The whole thing is combined with an app that keeps track of dozens of data metrics and allows access to various guided meditations.
I’m as surprised as you to say that this thing appears to work, with some caveats. It’s uncanny how well it monitors the brain during meditations. If I got lost in a thought spiral about lasagna at six minutes in, sure enough, there would be a dip in analytics at the six-minute mark. It’s also fairly easy to use, despite a process that involves wetting a number of electrodes. As magical as the accurate brain-tracking seems to be, however, I wasn’t as keen on the actual training portion, which often involves staring at a screen throughout the entirety of the practice. It’s also not for the financial faint of heart, as the Sens.ai device costs $1,500.
NeoRhythm Omnipemf
NeoRhythm’s Omnipemf is another wearable to help people get into that ever-elusive flow state. It doesn’t track your brain, but rather floods it with electromagnetic fields at specific frequencies to make it more susceptible to meditation and focus. This is supposed to prime your brain for the meditative state and, in theory, make it easier to capture that zen. However, I didn’t get much from it, other than a placebo-esque buzzing in my head.
To use it, you simply pop on the wearable and go about your day. You aren’t tied to an app, so you can meditate in whatever way you like. There are multiple modes that go beyond meditation, as this thing is supposed to help with focus, pain relief and sleep. I’d wait for some peer-reviewed studies, however, before buying this.
How we tested meditation apps
Every brain is different, so I did not rate these apps based on if they sync up with my preferred meditation style. First and foremost, I looked for apps that cater to various methods and those that offer guided meditations that go beyond what’s free on YouTube. All of the items on this list are available on both Android and iOS, so you won’t have to worry about something being only for iPhone owners.
Of course, there’s lots of free stuff out there, from podcasts and videos on YouTube to audio tracks on streaming services. You can even find guided breathing sessions on an Apple Watch or Fitbit, as well as meditations in Fitness+, Samsung Health or any number of workout video providers. For this guide, I focused on apps that stood out in some way. I liked apps with huge libraries of guided meditations and those that offer additional mindfulness activities, like yoga routines. I also looked for easy-to-use apps with well-designed layouts. You don’t want to start your meditation journey with a clunky app that actually increases anxiety.
The most important thing with meditation is to keep doing it, so I awarded points for clever gamification elements, simple social network integration and anything else that encourages repeat visits. Finally, I considered extra features that set an app apart from the glut of competitors out there. For example, some meditation apps offer novel ways to track your progress, access to yoga routines and a whole lot more.
At the end of the day, each of these apps has its strengths. But if installing an app or using a device is not how you prefer to meditate, you can always turn off your phone and find a quiet room or environment. For those of us who need a little help from a digital guru, though, here are our favorite apps for meditation.
Check out more from our spring cleaning guide.
This article originally appeared on Engadget at https://www.engadget.com/apps/best-meditation-app-140047993.html?src=rss
- Uber robotaxi rides are now available for passengers in Las Vegas
Uber’s and Motional9s Hyundai Ioniq 5 autonomous EVs will start appearing as an option for riders in Las Vegas. Passengers requesting for an UberX, Uber Electric, Uber Comfort or Uber Comfort Electric ride may be matched with a Motional robotaxi. They will not be forced to take it, though, and will be notified and given the option to decline and choose a regular ride instead. But if they want to try it, they can boost their chances of getting matched with a robotaxi ride by opting in via the Ride Preferences section under Settings.
Riders who get on autonomous rides will be able to unlock the vehicle through the Uber app. Inside, they’ll hear audio cues reminding them to close the door and fasten their seatbelt. They’ll also be able to access human support through the Uber app in case they need help. The companies started piloting the robotaxi service in Las Vegas in 2022 after establishing a 10-year partnership. Motional’s Hyundai AVs were also tested by Uber Eats for autonomous deliveries in the same year.
The first autonomous rides under the partnership will still have safety drivers behind the wheel to monitor the roads. They will also be only available, for now, at designated locations along Las Vegas Boulevard, “including rideshare zones at the Resorts World Las Vegas and Encore at the Wynn Las Vegas — plus Westgate Las Vegas Resort & Casino and curbside in Downtown Las Vegas and throughout the Town Square shopping district near the airport.” By the end of the year, the companies expect to start offering fully autonomous rides with no human operators. They have plans to expand the rides’ availability throughout the city, as well.
Uber has also just announced that it’s piloting a robotaxi service in Tokyo in late 2026 in partnership with UK self-driving car startup Wayve and Nissan. In addition, the Uber-backed Nuro will test its own autonomous vehicles in the Japanese metropolis soon.
This article originally appeared on Engadget at https://www.engadget.com/transportation/uber-robotaxi-rides-are-now-available-for-passengers-in-las-vegas-120030395.html?src=rss
- MacBook Air M5 review: Same but faster
It’s hard to believe that it’s been almost four years since Apple gave the MacBook Air a serious glow-up. The 2022 model was a total redesign that bumped its performance with the M2 chip and also improved a number of key components. It was also the first MacBook Air to drop the signature tapered design, and Apple added a 15-inch model one year later to boot. Since then, Apple’s primarily focused on making sure it has a new chip every year — we’re already up to the M5, if you can believe it.
As such, the latest MacBook Air is an expected update that doesn’t change the game. Not that it needed changing: it’s been our favorite ultraportable laptop for years now. But the Air’s place in Apple’s lineup has changed with the simultaneous introduction of the $599 MacBook Neo. And unfortunately, Apple didn’t keep the $999 price that last year’s M4 MacBook Air hit; it’s back up to $1,099, the same price as the M2 and M3 models. Now that there’s the new, inexpensive MacBook Neo out there, who is the MacBook Air for? While I haven’t used the Neo yet, I’m pretty comfortable answering that question: it’s still for almost anyone.
The essentials haven’t changed
While the latest MacBook Air is physically unchanged from its 2022 revision, I don’t have a problem with that. I find the Air to be the Platonic ideal of a laptop that most people will be hard-pressed to find issues with. The 13.6-inch (or 15.3-inch, if you opt for the bigger size) display isn’t the most cutting edge screen out there, but it’s still sharp, bright and colorful. It’s stuck at a 60Hz refresh rate at a time when many PC manufacturers are using faster screens, but for the Air’s audience I don’t think that’s a problem. I may be miffed that the iPad Air similarly only has a pedestrian 60Hz refresh rate — but I think it’s less crucial on a Mac, where you’re not literally touching the screen (at least for now).
Other minor quibbles include the fact that Apple still hasn’t put a USB-C port on the right side of the computer in addition to those on the left, and the screen notch is still weird if you focus on it too much. But other than that, I can’t really come up with any issues here. At 2.7 pounds, the Air isn’t the lightest laptop out there, but I’ll take the extremely solid feel of the unibody aluminum case over a lighter and possibly flimsier plastic.
 MacBook Air M5 Nathan Ingraham for Engadget MacBook Air M5 Nathan Ingraham for Engadget
The keyboard and trackpad remain delightful, as well. My main laptop is a 14-inch MacBook Pro, and I can perceive the Air’s comparatively thinner case when typing on it. It’s not bad at all, it just feels slightly different. But after a short adjustment period, I really didn’t think about it and typed away without a care in the world. It’s baffling to me that a company that made a keyboard this good also made the horrific butterfly keyboards of yore, but fortunately that era is far in the past. The haptic-powered trackpad is huge, smooth and responsive, just like the ones on all other recent Mac laptops. Altogether, the input experience is great, and I rarely find myself really feeling like I need an external keyboard or mouse. I know people have strong feelings about that, so do as you wish, but it’s not really something I think about anymore.
The MacBook Air’s speakers and webcam are also still excellent. Last year, Apple upgraded the 1080p webcam in the Air to a 12-megapixel Center Stage model that can follow your movements to keep you in frame or switch to a “desk view” that shows a top-down viewpoint of the area in front of the laptop. The old 1080p webcam was already pretty solid, and while this one doesn’t magically repair your wrinkles, it’s definitely more versatile and detailed. The speakers, meanwhile, remain one of those things that Apple has absolutely nailed with this generation of its laptops. They’re relatively loud and well-balanced, providing far better sound than I’d expect from such a thin enclosure.
 MacBook Air M5 Nathan Ingraham for Engadget Enough power to last for years MacBook Air M5 Nathan Ingraham for Engadget Enough power to last for years
All of this is well-known, though. The big change this year is the M5 chip, which has been available for a while already in the MacBook Pro and iPad Pro. So, we have a good idea of what to expect here as well. I’m testing the 13-inch model with 16GB of RAM and 1TB of storage that costs $1,299. It’s hard to perceive a difference between the M5 and last year’s M4 in my normal routine (dozens of tabs, Slack, Lightroom, Apple Music streaming and a bunch of lightweight apps like Bear notes, Todoist and so on). And based on my history with Apple’s M-series chips, the M5 will be a great performer for years to come. My work-issued MacBook Pro with an M1 Pro chip still runs like a champ almost five years after it was released, for example.
That said, users who do more than the basics with their laptop and have one with a chip older than 2022’s M2 will likely find the M5 Air to be a nice upgrade. Geekbench 6 benchmarks show the M5 is 11 percent and 17 percent faster than the M4 Air in single-core and multi-core tests (both with 16GB of RAM and 1TB SSDs). There were bigger GPU gains this year, with the M5 scoring 31 percent higher than the M4.
Few people out there are likely looking to upgrade from an M4 Air. But the M5 could be a noteworthy upgrade from the M3, depending of course on your workload. The M5 is 31 percent and 43 percent faster than the M3 in single- and multi-core testing. And the GPU is a whopping 56 percent faster as well. If you’re interested in doing things like video editing, music creation, gaming or AI tasks, you’ll definitely appreciate these performance gains.
 MacBook Air M5 Nathan Ingraham for Engadget MacBook Air M5 Nathan Ingraham for Engadget
Finally, these benchmarks illustrate the gap between the MacBook Neo and the Air. The M5 is about 24 percent faster than the A18 Pro in the single-core test, but it demolishes the Neo’s chip in multi-core (105 percent) and GPU (144 percent) performance. This just reiterates what we already know — the Neo is best-suited for basic tasks, while the Air should have more than enough power until you get into more specialized use cases.
And while no one will mistake the MacBook Air for a gaming laptop, Apple has had increasing success at getting developers to bring big titles to the Mac. Games like Assassin’s Creed Shadows, Cyberpunk 2077, Lies of P, Control and Resident Evil Village, along with indies like Neva, Stray and Balatro, are available here. That’s not to mention the many quality games worth checking out on Apple Arcade. All this is to say that Macs may still not be the premiere gaming platform, but people who don’t have access to a PlayStation, Xbox or more powerful gaming PC can still try a lot of great games on the platform.
Thanks to the M5, these games play pretty well to boot. I tried Cyberpunk 2077, one of the more notoriously demanding games out there, and had a stutter-free experience. Most graphically intense Mac games default to a “for this Mac” setting so you don’t really need to worry about optimizing settings. Cyberpunk 2077 stayed pretty well locked at 30 fps in my experience — obviously not as good as what you’ll get on a high-end PC or PlayStation 5, but I never felt like I was having a degraded experience. It was smooth, responsive and looked gorgeous. Getting that kind of performance from an ultraportable like the MacBook Air is hard to complain about.
Finally, battery life was close to Apple’s expectations. The company promises 18 hours of streaming video playback or 15 hours of web browsing. In my test, I looped a locally-stored 4K video file with my screen at half brightness and got… exactly 18 hours of playback before the laptop died. I’m sure it would have been less if I was streaming the video, but still. Under my usual working conditions running a variety of apps, I got more in the 10-hour range, which is more than good enough for me.
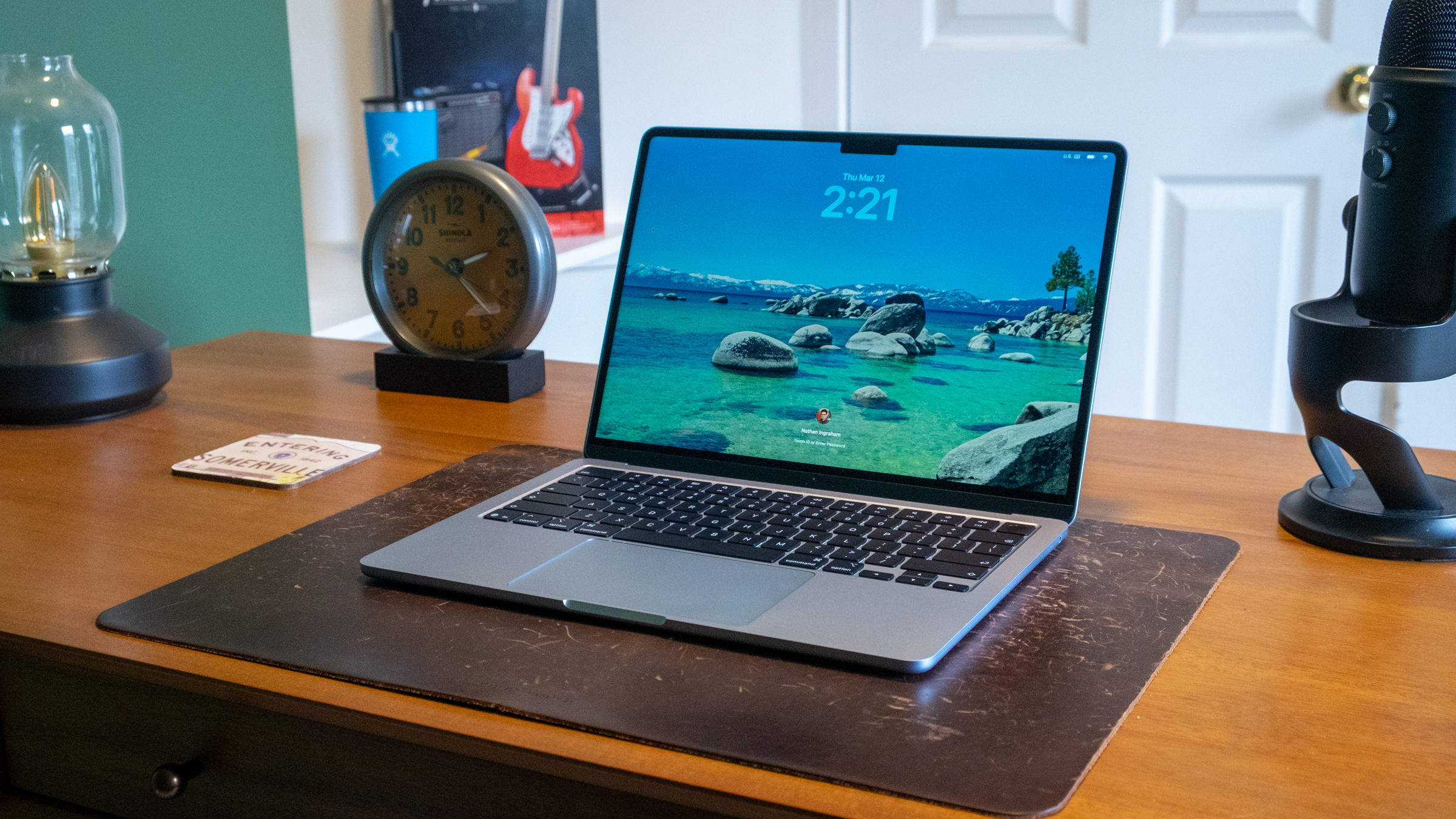 MacBook Air M5 Nathan Ingraham for Engadget Wrap-up MacBook Air M5 Nathan Ingraham for Engadget Wrap-up
Even with the MacBook Neo showing its chops despite its relatively humble hardware, I think the MacBook Air is by far the best Apple laptop for most people. Sure, Apple’s continued insistence on limiting screens with higher refresh rates to its most expensive hardware is increasingly frustrating. But other than that, the MacBook Air punches above its weight in just about every aspect — particularly when it comes to performance. The M5 is extremely powerful now and should make this year’s Air a useful computer for five years or even longer, depending on what you do with it. The MacBook Air is so mature and well-engineered at this point that it’s not the most exciting thing to review. But if you use one for a bit, it’s easy to appreciate just how good of a laptop it is.
This article originally appeared on Engadget at https://www.engadget.com/computing/laptops/macbook-air-m5-review-same-but-faster-120000685.html?src=rss
- Little Nightmares VR: Altered Echoes arrives in April
Bandai Namco has announced a new Little Nightmares game, this time for virtual reality. Little Nightmares VR: Altered Echoes is developed by Iconik and not by Tarsier Studios, but it’s still connected to the beloved titles Little Nightmares I and II. Remember Dark Six, the protagonist Six’s dark doppelganger from the previous games? Well, in this installment, you will control her as she goes on a journey to reunite with the actual Six in order to reunited with her and become whole.
The adventure horror puzzle game promises an “eerie, atmospheric universe” with an immersive first-person perspective. It features new locations within Nowhere, a nightmarish world only accessible through dreams filled with dangerous creatures, such as the human-like Residents. The Thin Man, the antagonist of the franchise’s second installment, is also back.
Little Nightmares VR: Altered Echoes is optimized for the PSVR2, the Meta Quest 2, 3 and 3s, the Oculus Rift and Rift S, the Pico 4, the Valve Index and the HTC Vive. However, it also works with other PC VR headsets. It will be available on April 24, 2026, and you can add it to your Wishlist right now on the PlayStation, Steam and Meta stores.
This article originally appeared on Engadget at https://www.engadget.com/gaming/little-nightmares-vr-altered-echoes-arrives-in-april-101626370.html?src=rss
- This web app lets you 'channel surf' YouTube like a '90s kid watching cable
Many of us remember the halcyon days of being a kid in the ‘90s, spending a weekend afternoon with remote control in hand and a seemingly endless well of stuff to watch on TV. Now you can relive the experience thanks to the appropriately named Channel Surfer web app. It9s essentially a YouTube discovery tool that surfaces interesting videos, but presented in a retro homage to the cable channel screen.
Channel Surfer is the work of developer Steven Irby. He has 40 channels on the app right now, mostly grouping content by theme. There are channels for typical cable fare like news and sports, but also music, movies and a number of more tailored tech subjects like AI, gaming, gadgets and space.
"I built Channel Surfer because I’m tired of the algorithms and indecision fatigue," he told posted on X that the number of views he9s getting for Channel Surfer already broke 10,000 on its first day.
OMG this blew up overnight! I got over 10,000 views on day 1. 🤯 pic.twitter.com/fY20ZVB3Xl
— Steven Irby (@StevenIrby) March 12, 2026
This article originally appeared on Engadget at https://www.engadget.com/entertainment/youtube/this-web-app-lets-you-channel-surf-youtube-like-a-90s-kid-watching-cable-220651107.html?src=rss
- Teamsters urge DOJ to block Paramount's Warner Bros. merger
The International Brotherhood of Teamsters, the union that covers warehouse workers, drivers and a diverse collection of other laborers, has come out against Paramount Skydance's merger with Warner Bros. Discovery. In a press release, the Teamsters announced that it has submitted a report to the US Department of Justice's Antitrust Division outlining its concerns about the impact of the deal, and is urging the DOJ to intervene in the merger.
"This merger threatens the livelihoods of the very workers who built these studios into industry giants," Teamsters General President Sean M. O’Brien said in a statement. "We've seen what happens when corporations consolidate power: jobs disappear, production leaves American communities and workers pay the price. The DOJ has a responsibility to stop deals that eliminate competition and harm working families. Unless Paramount and Warner Bros. can guarantee enforceable protections for domestic production and labor standards, this merger can’t be allowed to move forward."
The Teamsters are primarily concerned with how merging the two companies will consolidate power, and eliminate jobs in the process. "Previous mergers have a well-documented track record of harming workers — Disney’s 2019 acquisition of 20th Century Fox resulted in eliminated production units, significant job losses and canceled projects," the union says. Motion Picture Teamsters, the division of the union concentrated in Hollywood that transports the equipment, props and crew members that make productions possible, stand to be most impacted.
The high likelihood the merger impacts competition in the market is why the Teamsters expect the DOJ to step in, or in the case Paramount and Warner Bros. aren't able to provide "enforceable commitments to increasing and maintaining domestic production, strong labor standards and guarantees against layoffs and erosion of union jobs," block the deal entirely.
Engadget has asked the Teamsters union what it plans to do if the Department of Justice doesn't intervene. We'll update this article if we hear back.
If it's allowed to eat Warner Bros., Paramount Skydance has committed to producing 30 theatrical films annually, evenly split across the two studios’ slates. The larger issue is that the company's offer to acquire the studio is predicated on the idea it will quickly pass the muster of government regulators. Paramount Skydance CEO David Ellison is the son of Oracle co-founder Larry Ellison, who's known to have close ties with President Donald Trump, and has already benefited from favorable treatment from the administration. There's a real possibility that Paramount's new merger could similarly sail through, regardless of the Teamsters' concerns.
This article originally appeared on Engadget at https://www.engadget.com/entertainment/teamsters-urge-doj-to-block-paramounts-warner-bros-merger-215115721.html?src=rss
- Adobe CEO Shantanu Narayen plans to step down after 18 years
Adobe9s long-time CEO has shared that he plans to step down. Shantanu Narayen has been the chief exec at the tech company for 18 years, a tenure where he led Adobe in the major shift to become a software-as-a-service provider. The exact timeline for his exit is still up in the air, as Narayen will depart when the board of directors names his successor. He will remain on the board as its chair after leaving the CEO post.
While Adobe was not the first to take the SaaS route, it was one of the first major tech operations to do so. Software such as Photoshop, Illustrator, Premiere and Lightroom from the brand have been mainstays in creative fields for years, so the launch of the Creative Suite subscription, which is now called Creative Cloud, was a pretty revolutionary change for its customers.
In an memo to employees, Narayen reflected on his nearly two decades at the helm. Adobe has grown from about 3,000 employees to more than 30,000, while its financial performance has leapt, revenue skyrocketing from less than $1 billion to more than $25 billion. He also looked toward the future and the seemingly-inevitable presence of artificial intelligence.
"The next era of creativity is being written right now — shaped by AI, by new workflows and by entirely new forms of expression," he wrote. "Adobe has never waited for the future to arrive. We’ve anticipated it. We’ve built it. And we’ve led it. What gives me the greatest confidence isn’t just our technology — it’s our people. Your ingenuity, resilience and commitment to customers are what will define this moment."
This article originally appeared on Engadget at https://www.engadget.com/big-tech/adobe-ceo-shantanu-narayen-plans-to-step-down-after-18-years-212705623.html?src=rss
- NASA will try its Artemis II launch again in early April
NASA will soon give it another go on April Fools9 Day. On Thursday, NASA said it9s targeting April 1 at 6:24 PM ET for the Artemis II mission9s next launch attempt.
In case that date doesn9t pan out, NASA added April 2 at 7:22 PM as a secondary launch opportunity. If necessary, the agency foresees several more openings between April 1 and 6 to get the Orion rocket into space. "Within those six days between the first and the sixth, we can9t always turn around every day for an attempt," NASA acting associate administrator Lori Glaze said at a press conference. "We would anticipate […] about four opportunities within that six-day period."
In preparation, NASA is targeting March 19 (a week from today) to roll Artemis II back out to the launch pad. However, it warned that further setbacks could occur. "While I am comfortable and the agency is comfortable with targeting April 1 as our first opportunity, just keep in mind we still have work to go," Glaze said. "There are still things that need to be done within the [Vehicle Assembly Building] and out at the pad. As always, we9ll be guided by what the hardware is telling us, and we will launch when we9re ready."
Lori Glaze, acting associate administrator, and John Honeycutt, Artemis II Mission Management Team chair (Photo by Gregg Newton / AFP via Getty Images)GREGG NEWTON via Getty Images
Artemis II is set to be NASA9s first crewed lunar mission since the early 1970s. The 10-day mission will carry four astronauts around the Moon and back to the Earth. It9s set to be the first crewed mission of the Orion spacecraft, and an important step toward the ultimate goal of a Moon landing.
Initially targeted for early February, the launch was pushed back to March after several issues arose during a wet dress rehearsal. Then, 18 days later, it was delayed again (and moved off the launch pad) when NASA discovered a helium flow blockage in the rocket9s upper stage. And it’s all happening against the backdrop of Administrator Jared Isaacman’s overhaul of the Artemis program, which includes postponing a scheduled Moon landing until 2028.
This article originally appeared on Engadget at https://www.engadget.com/science/space/nasa-will-try-its-artemis-ii-launch-again-in-early-april-205714288.html?src=rss
- RAMaggedon not expected to ease this year as IDC cuts 2026 PC market forecast again
We9ve been seeing all sorts of warnings about how RAMaggedon is nigh. The latest horseman signalling a disaster is the International Data Corporation, which had already cautioned that things were looking bad at the end of 2025. Today, the organization further cut its forecasts for the PC market in 2026, anticipating that global shipments would fall 11.6 percent. The previous report projected that this year would see a falloff of up to 8.9 percent due to ongoing memory shortages. And the new figure was set before the escalation of conflicts in Iran and across the Middle East, which could further deflate computing and other industries.
"Memory shortages will persist well into 2027," Jitesh Ubrani, research manager for IDC’s Worldwide Mobile Device Trackers, said in the latest forecast. "While we anticipate some easing of prices beginning in 2028, the market is unlikely to return to the pricing levels seen in 2025."
This market report echoes price changes and official statements from all corners of the tech and computing sector. So far this year, we9ve already seen surging memory costs impacting HP, Samsung, Valve and Framework. Don9t be surprised if many other major players follow suit.
This article originally appeared on Engadget at https://www.engadget.com/computing/ramaggedon-not-expected-to-ease-this-year-as-idc-cuts-2026-pc-market-forecast-again-200000498.html?src=rss
- KPop Demon Hunters is officially getting a sequel
KPop Demon Hunters is getting a sequel, Netflix and Sony have announced. Sony Pictures Animation handed the rights to the film to Netflix in 2021 as part of a larger licensing deal, but neither company could have expected how much of a hit it would ultimately become. Besides being Netflix's "most-watched movie of all time," KPop Demon Hunters is also nominated for Best Animated Feature and Best Original Song at the 98th Academy Awards, and stands a good chance of winning.
Maggie Kang and Chris Appelhans, the directors of the first film, are returning to direct the sequel. The project will be the first in the duo's new "exclusive multiyear writing and directing partnership" with Netflix, which is focused on animation. "I feel immense pride as a Korean filmmaker that the audience wants more from this Korean story and our Korean characters," Kang said in a statement. "There's so much more to this world we have built, and I'm excited to show you. This is only the beginning."
IT'S OFFICIAL HUNTERS 💫 KPOP DEMON HUNTERS will return for a sequel written and directed by Maggie Kang and Chris Appelhans.
“I feel immense pride as a Korean filmmaker that the audience wants more from this Korean story and our Korean characters. There’s so much more to this… pic.twitter.com/QjxD9CV4Hw
— Netflix (@netflix) March 12, 2026
"These characters are like family to us, their world has become our second home," Appelhans said. "We're excited to write their next chapter, challenge them, and watch them evolve — and continue pushing the boundaries of how music, animation, and story can come together."
To put KPop Demon Hunters popularity into perspective, the film had such a wide reach that Netflix was willing to set aside its aversion to theatrical releases and put it in theaters after it premiered on streaming. KPop Demon Hunters reportedly made over $19 million during its initial two-day theatrical run in August 2025, and Netflix has brought it back to theaters multiple times since then. That's on top of the more than 500 million views the film racked up on Netflix itself. Not making a sequel would essentially be leaving money on the table.
expanded their film licensing partnership in January, a deal that reportedly cost the streaming service over $7 billion to secure.
This article originally appeared on Engadget at https://www.engadget.com/entertainment/streaming/kpop-demon-hunters-is-officially-getting-a-sequel-195038954.html?src=rss
- Meta is testing clickable links in Instagram captions for verified subscribers
Instagram has long limited users' ability to share links, restricting link-sharing to Stories, Reels and user profiles. But that might now be changing. The company has started to test clickable links inside of post captions for subscribers to Meta Verified.
The new feature, which has been a long-requested update from creators, was spotted by blogger Andrea Valeria, who posted screenshots of a clickable Substack link she was able to add to an Instagram post. According to Valeria, an in-app message indicated she could share up to 10 links a month.
Meta confirmed to Engadget that it's testing links in captions for subscribers to Meta Verified, but didn't provide details on how many people have access to the feature or if it will be widely available. It does seem to be somewhat limited, however, as the link on Valeria's post appears on Instagram's mobile app, but now when viewing the same post on Instagram's website.
Instagram's restrictions on link-sharing have been a notable part of the platform since its early days. The limitation helped kickstart an entire industry of "link in bio" platforms like Linktree, which help creators direct followers to off-platform websites based on what they share on Instagram. If Meta begins implementing the feature widely, it could drastically change how creators are able to interact with their followers (although a 10-link per month limit would likely still require "link in bio" solutions).
The test is also the latest way that Meta has experimented with making link-sharing a paid feature. The company has also recently tested restricting creators' ability to share links on Facebook by requiring a Meta Verified subscription. Meta Verified for creators starts at $14.99 a month, with the most expensive plans costing $499.99 a month.
This article originally appeared on Engadget at https://www.engadget.com/social-media/meta-is-testing-clickable-links-in-instagram-captions-for-verified-subscribers-184555406.html?src=rss
- PEGI ratings for game releases in Europe will be age-restricted if they contain loot boxes
European regulators are continuing to crack down on loot boxes and gaming features it classifies as "interactive risk categories." The Pan-European Game Information, better known as PEGI, is rolling out new rulesthat will apply age ratings based on the presence of loot boxes and other in-game purchases or systems that could be tied to gambling or addictive behavior. The exact policies are as follows:
Purchases of in-game content: games with time-limited or quantity-limited offers will be classified with a PEGI 12, games with NFTs or blockchain-related mechanisms will be PEGI 18.
Paid random items: the default rating will be PEGI 16 if the game contains paid random items (and in some cases they can be a PEGI 18).
Play-by-appointment: mechanisms that reward returning to the game (e.g. daily quests) will get a PEGI 7. If these mechanisms punish players for not returning (e.g. by losing content or reducing progress) they will become PEGI 12.
Safe online gameplay: if games contain entirely unrestricted communication features (e.g. no blocking or reporting), they will be PEGI 18.
These changes will apply to newly submitted games beginning in June 2026. The messaging from the ratings body is that these rules are aimed at helping parents direct their children9s online safety. "With the updated set of age rating criteria, PEGI aims to make parents aware that certain features in games should be carefully assessed, and that parental tools can be a very helpful assistant when doing that," PEGI Council Chair Beate Våje said.
Many titles may see an impact from the new policy, some more drastic than others. Online shooters might seen a bump from PEGI 12 to PEGI 16, but a franchise like EA Sports FC would leap to at least PEGI 16 from its current installment’s rating of PEGI 3.
Loot boxes have a history of causing strife among regulators. In 2018, Belgium determined that loot boxes were a form of gambling and made them illegal. Other nations have taken similar measures to restrict or prohibit this game mechanic, which has already led some game studios to limit access to their titles. For instance, Blizzard9s free-to-play Diablo Immortaldidn9t launch in Belgium or the Netherlands due to their laws connecting loot boxes and gambling. Stateside, there has been a renewed push against the concept, with the New York attorney general suing Valve over loot boxes.
This article originally appeared on Engadget at https://www.engadget.com/gaming/pegi-ratings-for-game-releases-in-europe-will-be-age-restricted-if-they-contain-loot-boxes-184325819.html?src=rss
- Bumble is the latest dating app to add an AI assistant
Bumble is testing an AI dating assistant called "Bee" that it hopes will get users on dates without them having to swipe through profiles, fourth quarter earnings, and intends to use the AI in a new experience it calls "Dates."
When a user opts in to Bumble9s Dates feature, Bee performs an onboarding chat where it learns about the users9 "values, relationship goals, communications style, lifestyle and dating intentions," and then attempts to find other users who share some or all of those traits. Once Bee finds someone compatible, both users are notified in the app that they could be a great match, and receive a summary generated by Bee explaining why. From there, they can chat and see if things lead to a real-life date.
As is often the case with pie-in-the-sky AI features, Bumble has even bigger plans for how Bee could be used in its app, including as a tool for collecting anonymous feedback from user9s previous matches or as a way to receive suggestions for dates ideas. AI will also apparently enable Bumble to move away from binary yes or no swipes on profiles and towards a system where users connect over "chapter-based" profiles that are more reflective of their life story.
Bumble is testing Bee internally and plans to launch the AI and its Dates feature in beta soon. The company is far from the only dating app experimenting with integrating AI recommendations and summaries. Tinder uses AI to recommend profile pictures to users, and now offers another feature called "Chemistry" that combines insights gained from personal questions and access to users9 Camera Roll to make more informed matches. Meanwhile, Grindr9s "Edge" subscription tier offers AI summaries of past chats and connections, and stats on whether a user is actually compatible with a new match.
It9s too early to tell whether AI makes a meaningful difference in the dating experience for users, but if it keeps them using an app or paying for a subscription, it9s likely a worthwhile experiment for Bumble, Tinder and Grindr.
This article originally appeared on Engadget at https://www.engadget.com/apps/bumble-is-the-latest-dating-app-to-add-an-ai-assistant-181729994.html?src=rss
- Soundcore Nebula P1i projector review: An affordable option with accurate color and loud sound
Anker’s Soundcore projectors have become an attractive option for buyers thanks to models like the P1 and Nebula X1 that combine performance and portability. Now, the company has added "affordability" to that equation with its latest model, the $369 P1i. Instead of being detachable like on the P1, its speakers fold out toward listeners, promising better and louder sound than most cheap projectors.
The P1i also delivers 1080p video, Google TV for streaming and the same easy screen fit setup as other Anker projectors. However, unlike some portable models, it lacks a built-in battery for true portability. Overall brightness is lower as well at 380 lumens compared to 650 on the P1. Despite those issues, the P1i is an outstanding budget projector that’s ideal for impromptu indoor screenings and outdoor party use.
Features and design
With its relatively small size (8.9 x 7.2 x 8.0 inches) and slight five pound weight, the Soundcore Nebula P1i can be perched nearly anywhere and is easily toted around by the soft handle on top. It’s almost too light, as even a slight bump can displace it and ruin the picture. It does have a tripod mount, though, which makes it easy to set up outside or install on your ceiling.
Fortunately, the P1i is perhaps the easiest projector in this price range to align with your wall or screen. It has Anker’s Smart Instant Setup that automatically adjusts the autofocus, keystone correction, screen fit and obstacle avoidance. For my 120-inch roll down screen, I just had to set the P1i about 11 feet from the wall, make sure it was fairly level and then tilt the stand so it pointed at the screen. Then, I just ran the smart setup which instantly gave me a correctly set-up image.
The P1i is not a laser projector but its LED light source lasts even longer, rated for over 30,000 hours. It runs fairly cool compared to a bulb or laser model, but it still has a fan that kicks on from time to time. One annoyance is that the fan seemed to engage even when the projector was turned off, so I found I had to unplug it to stop that.
Steve Dent for Engadget
Connectivity-wise, the P1i has a single HDMI 2.0 port with ARC (Audio Return Channel), along with a USB-A port for external media and a 3.5mm auxiliary audio output. The projector allows for a maximum input of 4K at 60 fps (it outputs 1080p at 60 fps), so it’s only good for light gaming. Plus, you’ll want to keep in mind that if you do any keystone correction, gaming latency quadruples from 20ms to 80ms. It also supports Wi-Fi 5 for streaming and Bluetooth 5.1 to connect extra speakers.
Google TV is built in for streaming and projector control, which is a nice feature for a projector under $400. It provides a large library of apps via Google Play along with a familiar interface. You also get Netflix’s official application with support for 4K Dolby Vision without the need to plug in a streaming device, plus there’s Chromecast support and Google Assistant for voice control. The downside is that the interface can occasionally be sluggish. As for those foldable speakers, you can aim them up, down, forward or backwards, and they support Dolby Audio at 10 watts each.
Image quality
Image quality is decent but not outstanding, about what you’d expect for a projector at this price. While it’s very sharp in the center, the edges are fuzzier, particularly if you’re tilting the projector up or down and using plenty of keystone correction. With just 380 lumens of brightness (I measured it at just over 300 lumens in standard mode), it’s best to use the P1i in a dark room or at night — if there’s any ambient light, you won’t be able to see much detail.
The P1i offers multiple picture profiles, including Standard, Vivid, Sports, Movies and Games, along with a Conference mode for maximum brightness. I found that the “Vivid” setting gave me the best mix of color accuracy and brightness.
Steve Dent for Engadget
Color accuracy is a strong point, with natural looking, nicely saturated hues. Surprisingly, the P1i supports 10-bit HDR to help improve color accuracy and max out what little brightness there is, though it’s a gigantic stretch calling a 380 lumen image (around 50 nits) "HDR." I tested the P1i on my usual roster of content, including Once Upon a Time in Hollywood, Andor, Dune 2 and Spider-Man: No Way Home, and found the colors to be pleasing and realistic. If they’re not quite to your liking, you can make fine adjustments manually.
Sound
The primary selling point of the Nebula P1I is those fold out speakers. However, considering Soundcore’s reputation for solid audio performance (take the Nebula X1 Pro for example), sound quality was a bit disappointing. It’s relatively tinny with very little bass, providing a less-than-theatrical experience. Those speakers can go pretty loud, though, and midrange sounds like voices are very clear.
Fortunately, there are a couple of solutions. The P1i has multiple EQ settings, including Movies (with enhanced bass and treble), Music for the most natural sound and Outdoors to ensure clarity in open and noisy spaces. The best of those, I found, was Movies, as it mildly improves the lows and highs. There’s also a “custom” mode that lets you fine-tune the equalization. I was able to get acceptable sound quality when I boosted the bass to nearly the maximum level.
The other option, of course, is to pair the P1i to some Bluetooth speakers. I did just that with Soundcore’s external speakers sold as an option with the Nebula X1 and the sound quality was much improved. Of course, that would remove much of its convenience and increase the price for better sound.
Wrap-up Steve Dent for Engadget
Anker’s $400 Soundcore Nebula P1i is an excellent option for buyers looking for a portable projector to use outdoors or in the place of a second TV, though it suffers from subpar sound and picture quality. Competitors like XGIMI’s MoGo 2 Pro offer similar brightness, built-in speakers and Google TV. And if you have a bit more in your budget, Anker’s $800 Nebula P1 is brighter and easier to set up. Finally, for those looking for battery portability for camping or other activities, take a look at XGIMI’s $500 Halo+ or the $530 Anker Nebula Capsule.
The P1i is great for simple nighttime movie screenings outdoors. If you feel like watching a movie or series in bed, you can bring it into your room, project the picture onto a wall and enjoy your streaming service of choice. You may not be disappointed with the overall picture quality, though you may wish for slightly better sound.
This article originally appeared on Engadget at https://www.engadget.com/home/home-theater/soundcore-nebula-p1i-projector-review-an-affordable-option-with-accurate-color-and-loud-sound-180034925.html?src=rss
- Another longtime Microsoft executive is retiring
It’s already been a busy year for high-profile Microsoft departures, with longtime Xbox chief Phil Spencer bowing out last month alongside his expected successor Sarah Bond. Today it’s the turn of Microsoft's head of Experiences + Devices, Rajesh Jha, who leaves after more than 35 years at the company.
Jha, who oversaw some of Microsoft’s most important products and services, including Windows, Office and Teams, said in a press release that he’s been planning for his succession alongside CEO Satya Nadella for a while. Rather than bringing in a direct replacement, four members of his team will be promoted to executive vice president and report directly to Nadella.
Taking up these new more senior roles are Office EVP and LinkedIn CEO Ryan Roslanksky, Windows and Surface president Pavan Davuluri, president of business and industry Copilot (BIC) Charles Lamanna, and Microsoft 365 Core chief Perry Clarke. The outgoing Jha, who said his long career at Microsoft had been "an incredible privilege," will officially transition out of Microsoft on July 1, after which he’ll remain in an advisory role.
"When I think about the pantheon of leaders who have truly shaped this company, Rajesh stands firmly among them," Nadella said in a statement, adding that Jha had been a "constant" during his own time at the company. "He embodies the commitment that helped build and transform Microsoft into the company it is today, and it is on the strength of that foundation that we will continue to move forward."
This article originally appeared on Engadget at https://www.engadget.com/computing/another-longtime-microsoft-executive-is-retiring-174453788.html?src=rss
- Alexa+ can now swear, thanks to a new personality style
Amazon just unveiled a new personality type for Alexa+. The "sassy" option is reserved for adults and the company claims it will throw out censored curse words from time to time. Amazon describes this option as a combination of "unfiltered personality" and "razor-sharp wit, playful sarcasm and occasional censored profanity."
We aren9t yet sure how the chatbot handles the censoring. Does it use a garden variety bleep or a replacement word like fudge or something? I managed to get it to say "damn" and "hell", but couldn9t force anything more profane than that.
In any event, adult users have to jump through a couple of hoops to activate this mode. It won9t work if there9s an enabled Amazon Kids profile on the account and it requires additional security checks, like face scans. The company also warns people upon being selected that the new tone could contain "mature subject matter." I9m more afraid of the bot using "clever comebacks" to absolutely shred my buying habits. Yes, I buy bagged popcorn when I have plenty of uncooked kernels in the pantry. I9m working on it.
This is still Alexa+, despite the ability to drop colorful language every now and again. It9s not an adult AI companion like the anime-inspired weirdness Grok recently trotted out or whatever erotica-infused nonsense OpenAI has been working on. Also, Amazon says the bot won9t get involved with hate speech, illegal activities, personal attacks or anything that could cause harm.
Amazon
This is just the latest personality type that the company has introduced for the chatbot. Users can also choose from sweet, brief or chill, with the last one resembling a surfer archetype. Alexa+ is an updated version of the company9s long-standing chatbot that prioritizes natural-sounding conversation. It9s fine, more or less, but I still use it primarily for alarms and weather.
This article originally appeared on Engadget at https://www.engadget.com/ai/alexa-can-now-swear-thanks-to-a-new-personality-style-172106310.html?src=rss
- BallotGuessr is Geoguessr for budding political pundits
Fancy yourself as one of those folks who stands in front of an expensive touchscreen display on a news network on election night, zooming in and out of counties while bleating about polling and voting data? If so, you might get a kick out of GeoGuessr that tasks you with guessing how a county voted in the 2024 presidential election. All you have to go on to figure out the identity of each county are contextual clues from Google Street View images. You can move around the environment a bit, but unless you get lucky, you9ll need to have a good sense of politics and geography to do well here.
Once you think you have an idea of where the county is, you move a slider to guess whether residents voted for the Democrat or Republican ticket and by how many points. In the daily challenge mode, you only have 30 seconds to make your guess in each of five rounds. I9m bad at it, but it9s a fun take on GeoGuessr all the same.
BallotGuessr features 2,845 curated Google Street View locations from all 50 states, with a maximum of 15 locations for each county. Its creator plans to expand the game with data for the 2022 midterms and 2020 presidential election, as well as recent elections in France, Germany and the United Kingdom.
This article originally appeared on Engadget at https://www.engadget.com/gaming/ballotguessr-is-geoguessr-for-budding-political-pundits-170028894.html?src=rss
- Ukraine allows allies to train AI models on its battlefield data
Ukraine's four-year war with Russia has made it the world leader in battlefield drone technology. One byproduct of that is that the data it collects has become one of the country's most valuable assets. On Thursday, Ukraine played that card, saying it will begin sharing its battlefield data with allies to train drone AI software.
"In modern warfare, we must defeat Russia in every technological cycle," Ukraine Defense Minister Mykhailo Fedorov wrote on Telegram (translated from Ukrainian). "Artificial intelligence is one of the key areas of this competition."
Fedorov previewed the move when he took his post in January. At the time, the tech-savvy cabinet member pledged to "more actively" bring allies into projects. Foreign allies and companies have sought access to the country's data as, for better or worse, AI increasingly becomes an integral element of warfare.
Fedorov says Ukraine has a platform that will safely train partners' AI models without providing sensitive data. The system is said to provide continually updating datasets, including large volumes of photos and videos.
"For us, this is the next step in the development of win-win cooperation," Fedorov wrote. "Partners get the opportunity to train their AI models on real data from modern warfare. And [for] Ukraine: faster development of autonomous systems and new technological solutions for the front."
Last year, Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy warned global leaders of a dangerous escalation tied to drone tech and AI. “We are now living through the most destructive arms race in human history,” he said at a meeting of the UN General Assembly in September. However, given the ugly realities in his country, Zelenskyy reiterated his need for armaments. “The only guarantee of security is friends and weapons,” he said.
This article originally appeared on Engadget at https://www.engadget.com/ai/ukraine-allows-allies-to-train-ai-models-on-its-battlefield-data-165104853.html?src=rss
- Former Overwatch director Jeff Kaplan returns with a Western survival shooter
After spending many years as the public face of Overwatch, Jeff Kaplan stayed well out of the limelight after leaving Blizzard in 2021. Five years later, the former Blizzard vice president and Overwatch lead director is back with his own studio and a new game, which you might be able to play pretty soon.
The Legend of California is billed as an open-world, action-survival shooter. It looks like a mix of Red Dead Redemption and Rust (Rust Dead Redemption, if you will). It9s set during the gold rush era, but Kaplan says he and his team at Kintsugiyama were not aiming for historical accuracy. For one thing, this version of California is an island. Still, the developers wanted to make the game feel authentic to the time period.
There are cowboys and prospectors, and you9ll be able to go hunting, build mines and stables, craft tools and weapons, build out your homestead and raid hostile camps. There are "challenging" player vs. environment encounters (Kaplan says there are four difficulty tiers available to start with) and optional player vs. player battles. You9ll be able to form a company with up to three other players and share progress, resources, buildings and other things with them.
Kaplan says his 34-strong team hand-crafted the world, though there9s a degree of randomization at play. A certain biome (say, the game9s version of the Mojave Desert) might be the easiest, most beginner-friendly area of the game on one server, and the endgame, tier four section on another. The points of interest might pop up in unexpected spots too — an Alcatraz-inspired structure will appear in a Bay Area-style region in some world seeds, and in snowy mountains in others.
The Legend of California is being published by Blizzard co-founder and former CEO Mike Morhaime9s company Dreamhaven. It9s slated to enter early access on Steam and the Epic Games Store later this year, with closed alpha playtests expected to start soon.
Kaplan announced The Legend of California in unusual fashion. Not during a splashy showcase, but in a five-hour appearance on Lex Fridman9s podcast. Kaplan discussed his life and career, including his work on World of Warcraft, the ill-fated Overwatch League and Overwatch 2 played a part in his departure, but the final straw came in 2020 during a meeting with Blizzard9s then-chief financial officer. Kaplan says he was told that if Overwatch didn9t reach certain revenue targets, the publisher would lay off 1,000 people and that would be on Kaplan9s shoulders.
This article originally appeared on Engadget at https://www.engadget.com/gaming/former-overwatch-director-jeff-kaplan-returns-with-a-western-survival-shooter-161221852.html?src=rss
- Claude can now generate charts and diagrams
With Claude enjoying a moment of newfound popularity among regular people, Anthropic is previewing an update designed to make its chatbot better at explaining some concepts. Starting today, Claude can generate charts and diagrams as part of its responses, either when asked directly or when it decides visuals might be helpful to the user.
For example, try asking Claude what9s the best way to fold a paper plane. Where previously it was limited to text, now it can show you step by step how to fold a Nakamura lock plane. Anthropic is quick to point out what it9s introducing today isn9t image generation. When producing visual aids, Claude will use HTML code and XML vector graphics. Anthropic likens it to giving Claude access to its own whiteboard.
The new feature is available to all Claude users, regardless of whether you pay for one of Anthropic9s subscriptions. However, the company does warn it9s releasing beta software, so expect some quirks along the way. The feature also isn’t available on mobile just yet. This release comes just days after OpenAI made ChatGPT capable of generating interactive visuals when explaining science and math concepts.
This article originally appeared on Engadget at https://www.engadget.com/ai/claude-can-now-generate-charts-and-diagrams-160000369.html?src=rss
- Honda cancels three EVs that were months away from US production
Honda has announced it is canceling three electric vehicles it was months from starting production on at its EV Hub in Ohio. The Honda 0 SUV, the Honda 0 sedan and the Acura RSX are all being wound down. The company showed off all three models, and touted them as in near-production form at CES 2025. Unlike the Honda Prologue and Acura ZDX, which run on GM's Ultium platform, the scrapped models were built on Honda's own Zero platform and would have been its first fully in-house EVs.
Honda in part blamed the elimination of federal EV tax credits, eased fossil fuel regulations and US tariffs for the decision. The company said US demand for electric vehicles had slowed because of the policy changes. In China, it admitted it could not match the value offered by newer manufacturers building software-driven vehicles on shorter production cycles. CEO Toshihiro Mibe said at a press conference that the demand shift had made EV profitability "very difficult," according to Hyundai, Kia, Volkswagen, Porsche and Ford having all scrapped or delayed major US EV projects since federal policy shifted.
The total restructuring of its EV business could cost Honda up to 2.5 trillion yen ($15.7 billion), with the company set to lose money for the first time since going public in 1957. Mibe and Executive Vice President Noriya Kaihara will forgo 30 percent of their compensation for three months, with other senior executives giving up 20 percent. Honda said it plans to share a detailed long-term strategy at a press conference in May.
This article originally appeared on Engadget at https://www.engadget.com/transportation/evs/honda-cancels-three-evs-that-were-months-away-from-us-production-155523384.html?src=rss
- Google built a flash-flood prediction tool using Gemini and old news reports
Flash floods are March 12, 2026
Google tasked Gemini with sorting through 5 million news articles from around the world and isolating flood reports. It transformed this data into a geo-tagged series of chronological events. Next, researchers trained a model to ingest current weather forecasts and leverage the Groundsource data to determine the likelihood of a flash flood in a given area.
We don9t have any concrete information as to how accurate Google9s forecast model is, though that should come over time. One trial user did say it helped his organization respond quicker to localized weather events. For now, the company is highlighting risks for urban areas in 150 countries via its Flood Hub platform. Google is also sharing its data with emergency response agencies in these locations.
Google
There are some limitations here. The model can only identify risk across a 20-square-kilometer area. It9s also not quite as precise as the US National Weather Service9s flood alert system, because Google9s model doesn9t integrate local radar data. This data typically enables real-time tracking of precipitation. However, the platform9s been designed to work in areas that don9t typically have access to that kind of weather-sensing infrastructure.
Juliet Rothenberg, a program manager on Google9s Resilience team, hopes that this technology can eventually be used to predict other tricky phenomena. This includes stuff like heat waves and mudslides.
"We’re aggregating millions of reports,” she told reporters this week. "It enables us to extrapolate to other regions where there isn’t as much information."
This is Google9s first use of a language model for weather forecasts, but not its first time it has relied on AI for this type of thing. The company9s DeepMind WeatherNext 2 forecasting model has proven to be extremely accurate.
This article originally appeared on Engadget at https://www.engadget.com/ai/google-built-a-flash-flood-prediction-tool-using-gemini-and-old-news-reports-154542963.html?src=rss
- Microsoft's Copilot Health can use AI to turn your fitness data and medical records 'into a coherent story'
Microsoft has unveiled Copilot Health, an AI-powered tool it claims can help make sense of your medical records, health history and fitness data from wearables, should you grant it access to that information. The company said it will be in a "separate, secure space" in the Copilot app and that the idea is to help provide you with more context and insights so you can ask your doctor the right questions when you see them.
Copilot Health is designed to help you better understand your medical information as a whole, Microsoft says. It is not "intended to diagnose, treat or prevent diseases or other conditions and is not a substitute for professional medical advice," the company pointed out in a blog post.
The tool can pull in activity, fitness and sleep data from more than 50 devices, including Apple Watch, Oura and Fitbit. Through HealthEx, it can access health records that include visit summaries, medication details and test results from more than 50,000 hospitals and provider organizations in the US. It can tap into lab test results from Function, should you allow it to do so.
Copilot Health can take all those details and apply "intelligence to turn them into a coherent story," such as helping you pinpoint the reasons why you don't sleep too well, the company suggested. It can access real-time provider directories in the US to help users find clinicians based on factors like location, specialty, spoken languages and insurance coverage.
Microsoft says that, across AI-powered consumer products like Copilot and Bing, users ask more than 50 million health-related questions every day. "We’ve improved the quality and reliability of answers by elevating information from credible health organizations across 50 countries, as verified by our clinical team using principles independently established by the National Academy of Medicine," the blog post states. "Responses include clear citations with easy links to source material, alongside expert‑written answer cards from Harvard Health."
As far as privacy is concerned, Microsoft says Copilot Health data and conversations are siloed from the broader Copilot app and there are extra access and safety controls in place, including "encryption at rest and in transit." You can delete your information and cut off the app's access to health records and wearable data at any time. Microsoft also notes that it won't use your Copilot Health information to train its models.
The company explained that Copilot Health was informed by its responsible AI principles. Microsoft built the tool in collaboration with its own clinical team and with the expertise and feedback of more than 230 physicians from dozens of countries. "Copilot Health has achieved ISO/IEC 42001 certification, the world’s first standard for AI management systems, meaning an independent third party has verified how we build, govern and continuously improve the AI behind this service," it noted.
Microsoft has opened up a waitlist for those interested in trying Copilot Health. The tool will initially be available in English in the US for those aged 18 and over. The company is working on adding support for more language and voice options and it will announce availability for those and other territories down the line.
While users will be able to try Copilot Health for free at first, Microsoft plans to charge for access via a subscription, according to Health AI tool beyond One Medical. It's now available on the Amazon website and app. Prime members in the US have the option to chat about certain conditions with a One Medical provider via direct message at no extra cost. Earlier this year, OpenAI announced that it was testing ChatGPT Health. Anthropic has healthcare tools as well.
Given how tough it is for many folks to access affordable healthcare and the fact their data and health records are often spread across a number of providers, some might believe there are benefits of using such tools from AI companies.
However, there's a big difference between tracking your sleep or calling your doctor after an Apple Watch detects signs of atrial fibrillation and entrusting all of your medical information to a chatbot. There are also issues like AI hallucinations and chatbots providing users with straight-up bad advice, as well as the possibility that an LLM-based tool might downplay or exaggerate potential risks.
This article originally appeared on Engadget at https://www.engadget.com/ai/microsofts-copilot-health-can-use-ai-to-turn-your-fitness-data-and-medical-records-into-a-coherent-story-152000621.html?src=rss
- Uber is shooting for even more upscale clientele with Uber Elite
Uber has launched a new invite-only luxury ride experience called Uber Elite. Aimed at "executives, frequent travelers, and riders looking for a more elevated experience," it sounds like an upgraded version of Uber Black for the, well, uber-rich.
A ride booked through Uber Elite will be operated by a professional chauffeur driving a new-model luxury vehicle less than three years old. An Elite-only "Meet and Greet" feature allows riders to pre-arrange to be picked up in the airport terminal they arrive at from a flight, with their chauffeur dutifully awaiting them at baggage claim.
Uber says all Elite rides include chargers, bottled water, mints and premium hand wipes. If those perks are deemed too basic by the customer, they can also request sparkling water or champagne in the app ahead of their ride, and Uber says it’ll work with its partners to accommodate them "where feasible." Once an Uber Elite trip is booked, the rider can also take advantage of round-the-clock phone support.
The new luxury service is available through the Uber app, as well as via Uber Reserve and Uber for Business. Rides can be booked one hour in advance or up to 90 days ahead.
Uber Elite is launching first in Los Angeles and San Francisco, with New York to follow soon, and then other cities in the US and internationally. Invitations will first be extended to frequent Uber Black and Uber for Business users, before the service is eventually made available to all riders. If you think you’re important enough, you can join a waitlist right now.
This article originally appeared on Engadget at https://www.engadget.com/transportation/uber-is-shooting-for-even-more-upscale-clientele-with-uber-elite-150620441.html?src=rss
- Rivian's R2 EV arrives this spring with a $58,000 price tag
Ahead of its official release later this spring, today Rivan is announcing full pricing and trim levels for its long-awaited R2 electric SUV.
The rollout for the company9s first mid-size (two-row) offering will be similar to its previous vehicles, with more expensive premium models hitting the road first this spring, followed by more affordable configurations becoming available later this year and into 2027. This timeline is especially important for anyone hoping to snag the $45,000 base model of the R2, which isn9t expected to go on sale until sometime in late 2027. The R2 Performance with Launch Package and R2 Premium trims will arrive initially as model year 2027 vehicles, followed by the R2 Standard (MY 2028) next year.
 The new R2 with Rivian9s Black Crater interiorRivian The new R2 with Rivian9s Black Crater interiorRivian
Some features that will be standard on every R2 are a native NACS charging port and Autonomy+ hardware. However, for the latter, while new vehicles will come with a free 60-day trial of Autonomy+, once that expires, owners will need to choose between a one-time fee or a monthly subscription to continue using Rivian9s enhanced hands-free driving tech.
Regardless of which trim or performance package you prefer, the arrival of the R2 is a huge deal for Rivian as it represents the company9s first true mass-market vehicle that looks to bring a lot of the tech and engineering used in the R1T and R1S to a more affordable price point.
For a closer look at the R29s trim levels and pricing, see the breakdown below.
R2 Performance with Launch Package
Available Spring 2026 starting at $57,990
Features a dual-motor AWD setup with 656 horsepower and 609 lb-ft of torque
EPA-estimated range of up to 330 miles
0 to 60 time of up to 3.6 seconds
Notably, the Launch Package will include a free lifetime subscription to Autonomy+, along with 20-inch Black Sand all-terrain wheels, a limited Rivian Green anodized key fob, exclusive Launch Green exterior paint option (which will be a paid upgrade) and a tow package that supports up to 4,440 pounds of towing capacity.
Other inclusions on the Performance trim include an Esker Silver exterior, semi-active suspension, Compass Yellow brake calipers and rear drop glass. This config also features Rivian9s Matrix LED headlights with adaptive high beams, integrated tow hooks, a flashlight that can be stowed inside the driver door and 21-inch tungsten all-season wheels.
The interior features birch wood accents with a Black Crater color scheme along with heated and ventilated front readers, heated steering wheel, heated rear outboard seats and 12-way adjustment with lumbar support for the driver and front passenger.
R2 Premium
Available late 2026 starting at $53,990
Features a dual-motor AWD setup with 450 horsepower and 537 lb-ft of torque
EPA-estimated range of up to 330 miles
0 to 60 time of up to 4.6 seconds
The premium trim includes many of the same features as the Performance model, but with smaller 20-inch bicolor carbon all-season wheels and fewer drive modes (there9s no option for rally, soft sand and launch).
R2 Standard (aka the RWD Long Range configuration)
Available first half of 2027 starting at $48,490
Features a single motor RWD setup with 350 horsepower and 355 lb-ft of torque
Rivian-estimated range of up to 345 miles
0 to 60 time of 5.9 seconds
Finally, the R2 Standard variant features a slightly more spartan kit consisting of heated front seats, a heated steering wheel, 12-way seats (but only for the driver) and 19-inch machine graphite wheels.
R2 Standard (aka the base model)
Available late 2027 starting at $45,000
Rivian-estimated range of 265+ miles
More detailed info will be released closer to launch
This article originally appeared on Engadget at https://www.engadget.com/transportation/evs/rivians-r2-ev-arrives-this-spring-with-a-58000-price-tag-150000363.html?src=rss
- Disney+ gets its own time-sucking vertical video section
It’s not just the major social platforms that know how effective an endless scroll of short videos is at hijacking your dopamine system. Disney+ is adding Verts, a selection of short vertical clips you can scroll through to keep your brain chemistry happy when you are in the bathroom so inclined. The company says it’s a “dynamic feed” to help users “quickly find their next favorite watch,” letting you jump straight in to see the full movie or TV show the clip hails from. Not to mention the side benefit of elbowing out those social platforms, many of which use cut-down clips of Disney-owned content anyway.
Disney said it would be adding vertical video to its premiere streaming platform back in January, and it also launched Verts on the ESPN app last year. Today, it said the addition of vertical clips drove “additional engagement,” but neglected to mention by how much. It9s worth noting Disney9s not an outlier here — Netflix announced a similar pivot back in January as well.
The company does say, however, that its recommendation engine has an “advanced algorithm” to ensure the clips are relevant to each user. Naturally, Disney is happy to lean on the century or more of content in its library, but also said Verts could broaden out to include “content from creators that reflects our fandoms.” Which you could (and should) take as a plan to at least try to put a tank or two on YouTube’s front lawn.
This article originally appeared on Engadget at https://www.engadget.com/entertainment/streaming/disney-gets-its-own-time-sucking-vertical-video-section-133308487.html?src=rss
- Starfleet Academy is the best first season of a Star Trek show ever
The first season of a TV show is a tricky thing. It has to convince people to watch it and justify the show’s existence to the network (or streaming service) execs. It has to deal with actors and writers who may not have fully dialed into the characters and world yet. There are some shows with absolutely stellar first seasons — Stranger Things, Veronica Mars and Ted Lasso are a few — but many other hit shows stumbled out of the gate, like The Office and Supernatural.
Star Trek is not immune to this phenomenon. The Original Series had a decent first season, with classic episodes like “The City on the Edge of Forever.” But the next four shows all have rather weak beginnings, with even fan-favorite The Next Generation stumbling badly with episodes like “Code of Honor.” That show picked up in season three, beginning a trend called “Growing the Beard,” in reference to how Commander Riker’s new beard coincided with the uptick in quality.
This trend unfortunately continued into the current era, with 2017’s Star Trek: Discovery delivering a first season with an overwhelmingly dour tone and a lot of franchise changes that didn’t sit well with fans. The show made some tweaks in season two (including a change in setting that involved traveling 900 years into the future), and showed a lot of improvement with season three. Picard also floundered horribly, with an uneven first season that killed off some fan-favorite characters and also turned the title character into an android.
Things started looking up after that, with shows like Strange New Worlds all posting strong outings with their first go-arounds. While episodes like “A Quality of Mercy” and “Lift Us Where Suffering Cannot Reach” may not make the list of all-time classics, there are no outright stinkers. It seemed like the franchise as a whole was finally finding its footing in this new streaming era.
 L-R: Tatiana Maslany as Anisha, Sandro Rosta as Caleb, Kerrice Brooks as SAM, Bella Shepard as Genesis, and George Hawkins as Darem in season 1, episode 9, of Star Trek: Starfleet Academy streaming on Paramount+.Michael Gibson/Paramount+ L-R: Tatiana Maslany as Anisha, Sandro Rosta as Caleb, Kerrice Brooks as SAM, Bella Shepard as Genesis, and George Hawkins as Darem in season 1, episode 9, of Star Trek: Starfleet Academy streaming on Paramount+.Michael Gibson/Paramount+
That leads us to Starfleet Academy, which debuted in January on Paramount+. Prior to its premiere, the internet was full of people deriding it as “CW Trek” and declaring that they don’t want to watch a show about “teenyboppers” that wasn’t “real” Star Trek. Now that the show has finished its first season… the internet is still full of people complaining. But many folks who were wary of it at the beginning have been pleasantly surprised — every day there seems to be multiple posts on various Star Trek subreddits along the lines of “Starfleet Academy is actually good?!?��� I personally didn’t enjoy the first episode, but episode two turned me around rather quickly, and it seemed that every week brought new converts.
Granted, 10 episodes is a short amount of time to make an impact, but Starfleet Academy did a lot with that number. Four of the episodes are dedicated to the ongoing villainy of Nus Braka, a murderous pirate played with scene-chewing delight by Paul Giamatti. These have all been pretty straightforward adventure stories, which also did a good job of fleshing out not only Braka, but cadet Caleb Mir, whose mother went to prison because of Braka.
The emphasis on Caleb in the first episode made it seem like the show would focus on him, much in the way Discovery focused on Michael Burnham, but he took a back seat as the show explored the other characters as well as its setting. Episode two, “Beta Test,” focused on diplomacy, a long-standing theme of Star Trek, and even shook up the status quo by moving the Federation headquarters from Earth to Betazed.
 Paul Giamatti as Nus Braka and Holly Hunter as Captain Nahla Ake in season 1, episode 6, of Star Trek: Starfleet Academy streaming on Paramount+.Brooke Palmer/Paramount+ Paul Giamatti as Nus Braka and Holly Hunter as Captain Nahla Ake in season 1, episode 6, of Star Trek: Starfleet Academy streaming on Paramount+.Brooke Palmer/Paramount+
Episodes four and five were more personal stories, with “Vox in Excelso” focusing on soft boy Klingon character Jay-Den as well as the fate of his race in general after hundreds of years, while “Series Acclimation Mil” also gave us characterization of photonic being Sam along with some heartfelt fan service for the Deep Space Nine fandom. Sam would also shine once more in “The Life of the Stars,” an episode that dealt with trauma, but also (again) delivered fan service in a way that didn’t feel like pandering because of how it was used to develop not just Sam, but also the Doctor, a legacy character from Voyager.
It’s not that every episode in season one of Starfleet Academy is a masterpiece – “Vitus Reflux” and “Ko’Zeine” are somewhat weak – but none of them are outright bad, making the batting average of the season rather high. That bodes well for word-of-mouth, as it9s easier to recommend a show when you don9t have to couch it with excuses about how it gets good “eventually.”
It will need that word-of-mouth if it wants to get through a complete four seasons of schooling; season two just finished filming so we9re guaranteed at least that, but there9s a lot up in the air for not just the show, but the entire franchise. Strange New Worlds season four will debut later this year, and then we have an abbreviated season five to look forward to. But past that, nothing firm is on the horizon: Starfleet Academy hasn9t been renewed yet, and projects like the Tawny Newsome-helmed comedy show are still in development with nothing tangible revealed yet.
Newsome played Beckett Mariner on Lower Decks and worked in the writers room for Starfleet Academy — she9s an example of how Paramount has been building up a roster of talent behind the scenes for the franchise who, even when a show is new, understand the universe and, more importantly, how to work together to make good TV. And that9s going to be important in the next year or so, as Paramount makes decisions about the future of the franchise in the shadow of the recent Skydance merger and the upcoming Warner Bros. purchase. Star Trek has an uphill battle ahead of it, but at least Starfleet Academy’s first season has made it an easier climb.
This article originally appeared on Engadget at https://www.engadget.com/entertainment/starfleet-academy-is-the-best-first-season-of-a-star-trek-show-ever-133000945.html?src=rss

- Understanding SMF properties in Solaris-based operating systems
SMF is the illumos system for managing traditional Unix services (long-lived background processes, usually). It’s quite rich in order to correctly accommodate a lot of different use cases. But it sometimes exposes that complexity to users even when they’re trying to do something simple. In this post, I’ll walk through an example using a demo service and the svcprop(1) tool to show the details. ↫ Dave Pacheco Soalris� system management facility or SMF is effectively Solaris� systemd, and this article provides a deeper insight into one of its features: properties. While using SMF and its suite of tools and commands for basic tasks is rather elementary and easy to get into � even I can do it � once you start to dive deeper into what is can do, things get complex and capable very fast.
- Chrome comes to Linux on ARM64
Google has announced that it will release Chrome for Linux on ARM64 in the second quarter of this year. Launching Chrome for ARM64 Linux devices allows more users to enjoy the seamless integration of Google’s most helpful services into their browser. This move addresses the growing demand for a browsing experience that combines the benefits of the open-source Chromium project with the Google ecosystem of apps and features. This release represents a significant undertaking to ensure that ARM64 Linux users receive the same secure, stable, and rich Chrome experience found on other platforms. ↫ The Chromium Blog While the idea of running Linux on Arm, only to defile it with something as unpleasant as Chrome seem entirely foreign to me, most normal people do actually use Google�s browser. Having it available on Linux for Arm makes perfect sense, and might convince a few people to buy an Arm machine for Linux, assuming the platform can get its act together.
- Just try Plan 9 already
I will not pass up an opportunity to make you talk about Plan 9, so let�s focus on Acme. Acme is remarkable for what it represents: a class of application that leverages a simple, text-based GUI to create a compelling model of interacting with all of the tools available in the Unix (or Plan 9) environment. Cox calls it an “integrating development environment,” distinguishing it from the more hermetic “integrated development environment” developers will be familiar with. The simplicity of its interface is important. It is what has allowed Acme to age gracefully over the past 30 or so years, without the constant churn of adding support for new languages, compilers, terminals, or color schemes. ↫ Daniel Moch While the article mentions you can use Acme on UNIX, to really appreciate it you have to use it on Plan 9, which today most likely means 9front. Now, I am not the kind of person who can live and breathe inside 9front � you need to be of a certain mindset to be able to do so � but even then I find that messing around with Plan 9 has given me a different outlook on UNIX. In fact, I think it has helped me understand UNIX and UNIX-like systems better and more thoroughly. If you�re not sure if Plan 9 is something that suits you, the only real way to find out is to just use it. Fire up a VM, read the excellent documentation at 9front, and just dive into it. Most of you will just end up confused and disoriented, but a small few of you will magically discover you possess the right mindset. Just do it.
- Hello, world! in Z80 assembly language
I�m feeling kind of nostalgic today so I thought I�d write Hello, world! in Z80 assembly for the ZX Spectrum! The last time I wrote any Z80 assembly was when I was 14 so around 36 years ago! I may be a little rusty! ↫ Old Man By the Sea It�s easy to tell the world hello in BASIC, but a bit more involved in Z80 assembly.
- Fedora struggles bringing its RISC-V variant online due to slow build times
Red Hat developer Marcin Juszkiewicz is working on the RISC-V port of Fedora Linux, and after a few months of working on it, published a blog post about just how incredibly slow RISC-V seems to be. This is a real problem, as in Fedora, build results are only released once all architectures have completed their builds. There is no point of going for inclusion with slow builders as this will make package maintainers complain. You see, in Fedora build results are released into repositories only when all architectures finish. And we had maintainers complaining about lack of speed of AArch64 builders in the past. Some developers may start excluding RISC-V architecture from their packages to not have to`wait. And any future builders need to be rackable and manageable like any other boring server (put in a rack, connect cables, install, do not touch any more). Because no one will go into a data centre to manually reboot an SBC-based`builder. Without systems fulfilling both requirements, we can not even plan for the RISC-V 64-bit architecture to became one of official, primary architectures in Fedora`Linux. ↫ Marcin Juszkiewicz RISC-V really seems to have hit some sort of ceiling over the past few years, with performance improvements stalling and no real performance-oriented chips and boards becoming available. Everybody seems to want RISC-V to succeed and become an architecture that can stand its own against x86 and Arm, but the way things are going, that just doesn�t seem likely any time soon. There�s always some magical unicorn chip or board just around the corner, but when you actually turn that corner, it�s just another slow SBC only marginally faster than the previous one. Fedora is not the first distribution struggling with bringing RISC-V online. Chimera Linux faced a similar issue about a year ago, but managed to eventually get by because someone from the Adélie Linux team granted remote access to an unused Milk-V Pioneer, which proved enough for Chimera for now. My hope is still that eventually we�re going to see performant, capable RISC-V machines, because I would absolutely jump for joy if I could have a proper RISC-V workstation.
- Amazon enters find out! phase
Now let�s go live to Amazon for the latest updates about this developing story. Amazon’s ecommerce business has summoned a large group of engineers to a meeting on Tuesday for a “deep dive” into a spate of outages, including incidents tied to the use of AI coding tools. The online retail giant said there had been a “trend of incidents” in recent months, characterized by a “high blast radius” and “Gen-AI assisted changes” among other factors, according to a briefing note for the meeting seen by the FT. Under “contributing factors” the note included “novel GenAI usage for which best practices and safeguards are not yet fully established.” ↫ Rafe Rosner-Uddin at Ars Technica Oh boy.
- You�re supposed to replace the stock photos in new picture frames
Back in 2023, John Earnest created a fun drawing application called WigglyPaint. The thing that makes WigglyPaint unique is that it automatically applies what artists call the line boil effect to anything you draw, making it seem as if everything is wiggling (hence the name). Even if you�re not aware of the line boil effect, you�ve surely encountered it several times in your life. The tool may seem simple at first glance, but as Earnest details, he�s put quite a lot of thought into the little tool. WigglyPaint was well-received, but mostly remained a curiosity � that is, until artists in Asia picked up on it, and the popularity of WigglyPaint positively exploded from a few hundred into the millions. The problem, though, is that basically nobody is actually using WigglyPaint: they�re all using slopcoded copycats. The sites are slop; slapdash imitations pieced together with the help of so-called “Large Language Models” (LLMs). The closer you look at them, the stranger they appear, full of vague, repetitive claims, outright false information, and plenty of unattributed (stolen) art. This is what LLMs are best at: quickly fabricating plausible simulacra of real objects to mislead the unwary. It is no surprise that the same people who have total contempt for authorship find LLMs useful; every LLM and generative model today is constructed by consuming almost unimaginably massive quantities of human creative work- writing, drawings, code, music- and then regurgitating them piecemeal without attribution, just different enough to hide where it came from (usually). LLMs are sharp tools in the hands of plagiarists, con-men, spammers, and everyone who believes that creative expression is worthless. People who extract from the world instead of contributing to it. It is humiliating and infuriating to see my work stolen by slop enthusiasts, and worse, used to mislead artists into paying scammers for something that ought to be free. ↫ John Earnest There�s a huge amount of slopcoded WrigglyPaint ripoffs out there, and it goes far beyond websites, too. People are putting slopcoded ripoffs in basic webviews, and uploading them en masse to the Play Store and App Store. None of these slopcoded ripoffs actually build upon WrigglyPaint with new ideas or approaches, there�s no creativity or innovation; it�s just trash barfed up by glorified autocomplete built upon mass plagiarism and theft, made! by bottom feeders who despise creativity, art, and originality. You know how when you go to IKEA or whatever other similar store to buy picture frames, they have these stock photos of random people in them? I wonder if AI! enthusiasts understand you�re supposed to replace those with pictures that actually have meaning to you.
- Redox bans code regurgitated by AI!
Redox, the rapidly improving general purpose operating system written in Rust, has amended its contribution policy to explicitly ban code regurgitated by AI!. Redox OS does not accept contributions generated by LLMs (Large Language Models), sometimes also referred to as AI!. This policy is not open to discussion, any content submitted that is clearly labelled as LLM-generated (including issues, merge requests, and merge request descriptions) will be immediately closed, and any attempt to bypass this policy will result in a ban from the project. ↫ Redox� contribution policy Excellent news.
- FreeBSD 14.4 released
While FreeBSD 15.x may be getting all the attention, the FreeBSD 14.x branch continues to be updated for the more conservative users among us. FreeBSD 14.4 has been released today, and brings with it updated versions of OpenSSH, OpenZFS, and Bhyve virtual machines can now share files with their host over 9pfs � among other things, of course.
- ArcaOS 5.1.2 released
While IBM�s OS/2 technically did die, its development was picked up again much later, first through eComStation, and later, after money issues at its parent company Mensys, through ArcaOS. eComStation development stalled because of the money issues and has been dead for years; ArcaOS picked up where it left off and has been making steady progress since its first release in 2017. Regardless, the developers behind both projects develop OS/2 under license from IBM, but it�s unclear just how much they can change or alter, and what the terms of the agreement are. Anyway, ArcaOS 5.1.2 has just been released, and it seems to be a rather minor release. It further refines ArcaOS� support for UEFI and GPT-based disks, the tentpole feature of ArcaOS 5.1 which allows the operating system to be installed on a much more modern systems without having to fiddle with BIOS compatibility modes. Looking at the list of changes, there�s the usual list of updated components from both Arca Noae and the wider OS/2 community. You�ll find the latest versions of of the Panorama graphics drivers, ACPI, USB, and NVMe drivers, improved localisation, newer versions of the VNC server and viewer, and much more. If you have an active Support 8 Maintenance subscription for ArcaOS 5.1, this update is free, and it�s also available at discounted prices as upgrades for earlier versions. A brand new copy of ArcaOS 5.1.x will set you back $139, which isn�t cheap, but considering this price is probably a consequence of what must be some onerous licensing terms and other agreements with IBM, I doubt there�s much Arca Noae can do about it.
- AI! translations are ruining Wikipedia
Oh boy. Wikipedia editors have implemented new policies and restricted a number of contributors who were paid to use AI to translate existing Wikipedia articles into other languages after they discovered these AI translations added AI “hallucinations,” or errors, to the resulting article. ↫ Emanuel Maiberg at 404 Media There seems to be this pervasive conviction among Silicon Valley techbro types, and many programmers and developers in general, that translation and localisation are nothing more than basic find/replace tasks that you can automate away. At first, we just needed to make corpora of two different languages kiss and smooch, and surely that would automate translation and localisation away if the corpora were large enough. When this didn�t turn out to work very well, they figured that if we made the words in the corpora tumble down a few pachinko machines and then made them kiss and smooch, yes, then we�d surely have automated translation and localisation. Nothing could be further from the truth. As someone who has not only worked as a professional translator for over 15 years, but who also holds two university degrees in the subject, I keep reiterating that translation isn�t just a dumb substitution task; it�s a real craft, a real art, one you can have talent for, one you need to train for, and study for. You�d think anyone with sufficient knowledge in two languages can translate effectively between the two, but without a much deeper understanding of language in general and the languages involved in particular, as well as a deep understanding of the cultures in which the translation is going to be used, and a level of reading and text comprehension that go well beyond that of most, you�re going to deliver shit translations. Trust me, I�ve seen them. I�ve been paid good money to correct, fix, and mangle something usable out of other people�s translations. You wouldn�t believe the shit I�ve seen. Translation involves the kinds of intricacies, nuances, and context AI! isn�t just bad at, but simply cannot work with in any way, shape, or form. I�ve said it before, but it won�t be long before people start getting seriously injured � or worse � because of the cost-cutting in the translation industry, and the effects that�s going to have on, I don�t know, the instruction manuals for complex tools, or the leaflet in your grandmother�s medications. Because some dumbass bean counter kills the budget for proper, qualified, trained, and experienced translators, people are going to die.
- I don’t know what is Apple’s endgame for the Fn/Globe key, and I’m not sure Apple knows either!
Every modifier key starts simple and humble, with a specific task and a nice matching name. This never lasts. The tasks become larger and more convoluted, and the labels grow obsolete. Shift no longer shifts a carriage, Control doesn’t send control codes, Alt isn’t for alternate nerdy terminal functions. Fn is the newest popular modifier key, and it feels we’re speedrunning it through all the challenges without having learned any of the lessons. ↫ Marcin Wichary Grab a blanket, curl up on the couch with some coffee or tea, and enjoy.
- MenuetOS 1.59.20 released
MenuetOS, the operating system written in x86-64 assembly, has released two new versions since we last talked about it roughly two months ago. In fact, I�m not actually sure it�s just two, or more, or fewer, since it seems sometimes releases disappear entirely from the changelog, making things a bit unclear. Anyway, since the last time we talked about MenuetOS, it got improvements to videocalling, networking, and HDA audio drivers, and a few other small tidbits.
- Haiku inches closer to next beta release
And when a Redox monthly progress report is here, Haiku�s monthly report is never far behind (or vice versa, depending on the month). Haiku�s February was definitely a busy month, but there�s no major tentpole changes or new features, highlighting just how close Haiku is to a new regular beta release. The OpenBSD drivers have been synchronised wit upstream to draw in some bugfixes, there�s a ton of smaller fixes to various applications like StyledEdit, Mail, and many more, as well a surprisingly long list of various file system fixes, improving the drivers for file systems like NTFS, Btrfs, XFS, and others. There�s more, of course, so just like with Redox, head on over to pore over the list of smaller changes, fixes, and improvements. Just like last month, I�d like to mention once again that you really don�t need to wait for the beta release to try out Haiku. The operating system has been in a fairly stable and solid condition for a long time now, and whatever�s the latest nightly will generally work just fine, and can be updated without reinstallation.
- Redox gets NodeJS, COSMIC�s compositor, and much more
February has been a busy month for Redox, the general purpose operating system written in Rust. For instance, the COSMIC compositor can now run on Redox as a winit window, the first step towards fully porting the compositor from COSMIC to Redox. Similarly, COSMIC Settings now also runs on Redox, albeit with only a very small number of available settings as Redox-specific settings panels haven�t been made yet. It�s clear the effort to get the new COSMIC desktop environment from System76 running on Redox is in full swing. Furthermore, Vulkan software can now run on Redox, thanks to enabling Lavapipe in Mesa3D. There�s also a ton of fixes related to the boot process, the reliability of multithreading has been improved, and there�s the usual long list of kernel, driver, and Relibc improvements as well. A major port comes in the form of NodeJS, which now runs on Redox, and helped in uncovering a number of bugs that needed to be fixed. Of course, there�s way more in this month�s progress report, so be sure to head on over and read the whole thing.
- Hardware hotplug events on Linux, the gory details
One day, I suddenly wondered how to detect when a USB device is plugged or unplugged from a computer running Linux. For most users, this would be solved by relying on libusb. However, the use case I was investigating might not actually want to do so, and so this led me down a poorly-documented rabbit hole. ↫ ArcaneNibble (or R) And ArcaneNibble (or R) is taking you down with them.

- EU OS: A Bold Step Toward Digital Sovereignty for Europe
Image 
A new initiative, called "EU OS," has been launched to develop a Linux-based operating system tailored specifically for the public sector organizations of the European Union (EU). This community-driven project aims to address the EU's unique needs and challenges, focusing on fostering digital sovereignty, reducing dependency on external vendors, and building a secure, self-sufficient digital ecosystem.
What Is EU OS?
EU OS is not an entirely novel operating system. Instead, it builds upon a Linux foundation derived from Fedora, with the KDE Plasma desktop environment. It draws inspiration from previous efforts such as France's GendBuntu and Munich's LiMux, which aimed to provide Linux-based systems for public sector use. The goal remains the same: to create a standardized Linux distribution that can be adapted to different regional, national, and sector-specific needs within the EU.
Rather than reinventing the wheel, EU OS focuses on standardization, offering a solid Linux foundation that can be customized according to the unique requirements of various organizations. This approach makes EU OS a practical choice for the public sector, ensuring broad compatibility and ease of implementation across diverse environments.
The Vision Behind EU OS
The guiding principle of EU OS is the concept of "public money – public code," ensuring that taxpayer money is used transparently and effectively. By adopting an open-source model, EU OS eliminates licensing fees, which not only lowers costs but also reduces the dependency on a select group of software vendors. This provides the EU’s public sector organizations with greater flexibility and control over their IT infrastructure, free from the constraints of vendor lock-in.
Additionally, EU OS offers flexibility in terms of software migration and hardware upgrades. Organizations can adapt to new technologies and manage their IT evolution at a manageable cost, both in terms of finances and time.
However, there are some concerns about the choice of Fedora as the base for EU OS. While Fedora is a solid and reliable distribution, it is backed by the United States-based Red Hat. Some argue that using European-backed projects such as openSUSE or KDE's upcoming distribution might have aligned better with the EU's goal of strengthening digital sovereignty.
Conclusion
EU OS marks a significant step towards Europe's digital independence by providing a robust, standardized Linux distribution for the public sector. By reducing reliance on proprietary software and vendors, it paves the way for a more flexible, cost-effective, and secure digital ecosystem. While the choice of Fedora as the base for the project has raised some questions, the overall vision of EU OS offers a promising future for Europe's public sector in the digital age.
Source: It's FOSS
European Union
- Linus Torvalds Acknowledges Missed Release of Linux 6.14 Due to Oversight
Linus Torvalds Acknowledges Missed Release of Linux 6.14 Due to Oversight
Linux kernel lead developer Linus Torvalds has admitted to forgetting to release version 6.14, attributing the oversight to his own lapse in memory. Torvalds is known for releasing new Linux kernel candidates and final versions on Sunday afternoons, typically accompanied by a post detailing the release. If he is unavailable due to travel or other commitments, he usually informs the community ahead of time, so users don’t worry if there’s a delay.
In his post on March 16, Torvalds gave no indication that the release might be delayed, instead stating, “I expect to release the final 6.14 next weekend unless something very surprising happens.” However, Sunday, March 23rd passed without any announcement.
On March 24th, Torvalds wrote in a follow-up message, “I’d love to have some good excuse for why I didn’t do the 6.14 release yesterday on my regular Sunday afternoon schedule,” adding, “But no. It’s just pure incompetence.” He further explained that while he had been clearing up unrelated tasks, he simply forgot to finalize the release. “D'oh,” he joked.
Despite this minor delay, Torvalds’ track record of successfully managing the Linux kernel’s development process over the years remains strong. A single day’s delay is not critical, especially since most Linux users don't urgently need the very latest version.
The new 6.14 release introduces several important features, including enhanced support for writing drivers in Rust—an ongoing topic of discussion among developers—support for Qualcomm’s Snapdragon 8 Elite mobile chip, a fix for the GhostWrite vulnerability in certain RISC-V processors from Alibaba’s T-Head Semiconductor, and a completed NTSYNC driver update that improves the WINE emulator’s ability to run Windows applications, particularly games, on Linux.
Although the 6.14 release went smoothly aside from the delay, Torvalds expressed that version 6.15 may present more challenges due to the volume of pending pull requests. “Judging by my pending pile of pull requests, 6.15 will be much busier,” he noted.
You can download the latest kernel here.
Linus Torvalds kernel
- AerynOS 2025.03 Alpha Released with GNOME 48, Mesa 25, and Linux Kernel 6.13.8
Image 
AerynOS 2025.03 has officially been released, introducing a variety of exciting features for Linux users. The release includes the highly anticipated GNOME 48 desktop environment, which comes with significant improvements like HDR support, dynamic triple buffering, and a Wayland color management protocol. Other updates include a battery charge limiting feature and a Wellbeing option aimed at improving user experience.
This release, while still in alpha, incorporates Linux kernel 6.13.8 and the updated Mesa 25.0.2 graphics stack, alongside tools like LLVM 19.1.7 and Vulkan SDK 1.4.309.0. Additionally, the Moss package manager now integrates os-info to generate more detailed OS metadata via a JSON file.
Future plans for AerynOS include automated package updates, easier rollback management, improved disk handling with Rust, and fractional scaling enabled by default. The installer has also been revamped to support full disk wipes and dynamic partitioning.
Although still considered an alpha release, AerynOS 2025.03 can be downloaded and tested right now from its official website.
Source: 9to5Linux
AerynOS
- Xojo 2025r1: Big Updates for Developers with Linux ARM Support, Web Drag and Drop, and Direct App Store Publishing
Image 
Xojo has just rolled out its latest release, Xojo 2025 Release 1, and it’s packed with features that developers have been eagerly waiting for. This major update introduces support for running Xojo on Linux ARM, including Raspberry Pi, brings drag-and-drop functionality to the Web framework, and simplifies app deployment with the ability to directly submit apps to the macOS and iOS App Stores.
Here’s a quick overview of what’s new in Xojo 2025r1:
1. Linux ARM IDE Support
Xojo 2025r1 now allows developers to run the Xojo IDE on Linux ARM devices, including popular platforms like Raspberry Pi. This opens up a whole new world of possibilities for developers who want to create apps for ARM-based devices without the usual complexity. Whether you’re building for a Raspberry Pi or other ARM devices, this update makes it easier than ever to get started.
2. Web Drag and Drop
One of the standout features in this release is the addition of drag-and-drop support for web applications. Now, developers can easily drag and drop visual controls in their web projects, making it simpler to create interactive, user-friendly web applications. Plus, the WebListBox has been enhanced with support for editable cells, checkboxes, and row reordering via dragging. No JavaScript required!
3. Direct App Store Publishing
Xojo has also streamlined the process of publishing apps. With this update, developers can now directly submit macOS and iOS apps to App Store Connect right from the Xojo IDE. This eliminates the need for multiple steps and makes it much easier to get apps into the App Store, saving valuable time during the development process.
4. New Desktop and Mobile Features
This release isn’t just about web and Linux updates. Xojo 2025r1 brings some great improvements for desktop and mobile apps as well. On the desktop side, all projects now include a default window menu for macOS apps. On the mobile side, Xojo has introduced new features for Android and iOS, including support for ColorGroup and Dark Mode on Android, and a new MobileColorPicker for iOS to simplify color selection.
5. Performance and IDE Enhancements
Xojo’s IDE has also been improved in several key areas. There’s now an option to hide toolbar captions, and the toolbar has been made smaller on Windows. The IDE on Windows and Linux now features modern Bootstrap icons, and the Documentation window toolbar is more compact. In the code editor, developers can now quickly navigate to variable declarations with a simple Cmd/Ctrl + Double-click. Plus, performance for complex container layouts in the Layout Editor has been enhanced.
What Does This Mean for Developers?
Xojo 2025r1 brings significant improvements across all the platforms that Xojo supports, from desktop and mobile to web and Linux. The added Linux ARM support opens up new opportunities for Raspberry Pi and ARM-based device development, while the drag-and-drop functionality for web projects will make it easier to create modern, interactive web apps. The ability to publish directly to the App Store is a game-changer for macOS and iOS developers, reducing the friction of app distribution.
How to Get Started
Xojo is free for learning and development, as well as for building apps for Linux and Raspberry Pi. If you’re ready to dive into cross-platform development, paid licenses start at $99 for a single-platform desktop license, and $399 for cross-platform desktop, mobile, or web development. For professional developers who need additional resources and support, Xojo Pro and Pro Plus licenses start at $799. You can also find special pricing for educators and students.
Download Xojo 2025r1 today at xojo.com.
Final Thoughts
With each new release, Xojo continues to make cross-platform development more accessible and efficient. The 2025r1 release is no exception, delivering key updates that simplify the development process and open up new possibilities for developers working on a variety of platforms. Whether you’re a Raspberry Pi enthusiast or a mobile app developer, Xojo 2025r1 has something for you.
Xojo ARM
- New 'Mirrored' Network Mode Introduced in Windows Subsystem for Linux
Microsoft's Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) continues to evolve with the release of WSL 2 version 0.0.2. This update introduces a set of opt-in preview features designed to enhance performance and compatibility.
Key additions include "Automatic memory reclaim" which dynamically optimizes WSL's memory footprint, and "Sparse VHD" to shrink the size of the virtual hard disk file. These improvements aim to streamline resource usage.
Additionally, a new "mirrored networking mode" brings expanded networking capabilities like IPv6 and multicast support. Microsoft claims this will improve VPN and LAN connectivity from both the Windows host and Linux guest.
Complementing this is a new "DNS Tunneling" feature that changes how DNS queries are resolved to avoid compatibility issues with certain network setups. According to Microsoft, this should reduce problems connecting to the internet or local network resources within WSL.
Advanced firewall configuration options are also now available through Hyper-V integration. The new "autoProxy" feature ensures WSL seamlessly utilizes the Windows system proxy configuration.
Microsoft states these features are currently rolling out to Windows Insiders running Windows 11 22H2 Build 22621.2359 or later. They remain opt-in previews to allow testing before final integration into WSL.
By expanding WSL 2 with compelling new capabilities in areas like resource efficiency, networking, and security, Microsoft aims to make Linux on Windows more performant and compatible. This evolutionary approach based on user feedback highlights Microsoft's commitment to WSL as a key part of the Windows ecosystem.
Windows
- Linux Threat Report: Earth Lusca Deploys Novel SprySOCKS Backdoor in Attacks on Government Entities
The threat actor Earth Lusca, linked to Chinese state-sponsored hacking groups, has been observed utilizing a new Linux backdoor dubbed SprySOCKS to target government organizations globally.
As initially reported in January 2022 by Trend Micro, Earth Lusca has been active since at least 2021 conducting cyber espionage campaigns against public and private sector targets in Asia, Australia, Europe, and North America. Their tactics include spear-phishing and watering hole attacks to gain initial access. Some of Earth Lusca's activities overlap with another Chinese threat cluster known as RedHotel.
In new research, Trend Micro reveals Earth Lusca remains highly active, even expanding operations in the first half of 2023. Primary victims are government departments focused on foreign affairs, technology, and telecommunications. Attacks concentrate in Southeast Asia, Central Asia, and the Balkans regions.
After breaching internet-facing systems by exploiting flaws in Fortinet, GitLab, Microsoft Exchange, Telerik UI, and Zimbra software, Earth Lusca uses web shells and Cobalt Strike to move laterally. Their goal is exfiltrating documents and credentials, while also installing additional backdoors like ShadowPad and Winnti for long-term spying.
The Command and Control server delivering Cobalt Strike was also found hosting SprySOCKS - an advanced backdoor not previously publicly reported. With roots in the Windows malware Trochilus, SprySOCKS contains reconnaissance, remote shell, proxy, and file operation capabilities. It communicates over TCP mimicking patterns used by a Windows trojan called RedLeaves, itself built on Trochilus.
At least two SprySOCKS versions have been identified, indicating ongoing development. This novel Linux backdoor deployed by Earth Lusca highlights the increasing sophistication of Chinese state-sponsored threats. Robust patching, access controls, monitoring for unusual activities, and other proactive defenses remain essential to counter this advanced malware.
The Trend Micro researchers emphasize that organizations must minimize attack surfaces, regularly update systems, and ensure robust security hygiene to interrupt the tactics, techniques, and procedures of relentless threat groups like Earth Lusca.
Security
- Linux Kernel Faces Reduction in Long-Term Support Due to Maintenance Challenges
The Linux kernel is undergoing major changes that will shape its future development and adoption, according to Jonathan Corbet, Linux kernel developer and executive editor of Linux Weekly News. Speaking at the Open Source Summit Europe, Corbet provided an update on the latest Linux kernel developments and a glimpse of what's to come.
A major change on the horizon is a reduction in long-term support (LTS) for kernel versions from six years to just two years. Corbet explained that maintaining old kernel branches indefinitely is unsustainable and most users have migrated to newer versions, so there's little point in continuing six years of support. While some may grumble about shortened support lifecycles, the reality is that constantly backporting fixes to ancient kernels strains maintainers.
This maintainer burnout poses a serious threat, as Corbet highlighted. Maintaining Linux is largely a volunteer effort, with only about 200 of the 2,000+ developers paid for their contributions. The endless demands on maintainers' time from fuzz testing, fixing minor bugs, and reviewing contributions takes a toll. Prominent maintainers have warned they need help to avoid collapse. Companies relying on Linux must realize giving back financially is in their interest to sustain this vital ecosystem.
The Linux kernel is also wading into waters new with the introduction of Rust code. While Rust solves many problems, it also introduces new complexities around language integration, evolving standards, and maintainer expertise. Corbet believes Rust will pass the point of no return when core features depend on it, which may occur soon with additions like Apple M1 GPU drivers. Despite skepticism in some corners, Rust's benefits likely outweigh any transition costs.
On the distro front, Red Hat's decision to restrict RHEL cloning sparked community backlash. While business considerations were at play, Corbet noted technical factors too. Using older kernels with backported fixes, as RHEL does, risks creating divergent, vendor-specific branches. The Android model of tracking mainline kernel dev more closely has shown security benefits. Ultimately, Linux works best when aligned with the broader community.
In closing, Corbet recalled the saying "Linux is free like a puppy is free." Using open source seems easy at first, but sustaining it long-term requires significant care and feeding. As Linux is incorporated into more critical systems, that maintenance becomes ever more crucial. The kernel changes ahead are aimed at keeping Linux healthy and vibrant for the next generation of users, businesses, and developers.
kernel
- Linux Celebrates 32 Years with the Release of 6.6-rc2 Version
Today marks the 32nd anniversary of Linus Torvalds introducing the inaugural Linux 0.01 kernel version, and celebrating this milestone, Torvalds has launched the Linux 6.6-rc2. Among the noteworthy updates are the inclusion of a feature catering to the ASUS ROG Flow X16 tablet's mode handling and the renaming of the new GenPD subsystem to pmdomain.
The Linux 6.6 edition is progressing well, brimming with exciting new features that promise to enhance user experience. Early benchmarks are indicating promising results, especially on high-core-count servers, pointing to a potentially robust and efficient update in the Linux series.
Here is what Linus Torvalds had to say in today's announcement:
Another week, another -rc.I think the most notable thing about 6.6-rc2 is simply that it'sexactly 32 years to the day since the 0.01 release. And that's a roundnumber if you are a computer person.Because other than the random date, I don't see anything that reallystands out here. We've got random fixes all over, and none of it looksparticularly strange. The genpd -> pmdomain rename shows up in thediffstat, but there's no actual code changes involved (make sure touse "git diff -M" to see them as zero-line renames).And other than that, things look very normal. Sure, the architecturefixes happen to be mostly parisc this week, which isn't exactly theusual pattern, but it's also not exactly a huge amount of changes.Most of the (small) changes here are in drivers, with some tracingfixes and just random things. The shortlog below is short enough toscroll through and get a taste of what's been going on. Linus Torvalds
- Introducing Bavarder: A User-Friendly Linux Desktop App for Quick ChatGPT Interaction
Want to interact with ChatGPT from your Linux desktop without using a web browser?
Bavarder, a new app, allows you to do just that.
Developed with Python and GTK4/libadwaita, Bavarder offers a simple concept: pose a question to ChatGPT, receive a response, and promptly copy the answer (or your inquiry) to the clipboard for pasting elsewhere.
With an incredibly user-friendly interface, you won't require AI expertise (or a novice blogger) to comprehend it. Type your question in the top box, click the blue send button, and wait for a generated response to appear at the bottom. You can edit or modify your message and repeat the process as needed.
During our evaluation, Bavarder employed BAI Chat, a GPT-3.5/ChatGPT API-based chatbot that's free and doesn't require signups or API keys. Future app versions will incorporate support for alternative backends, such as ChatGPT 4 and Hugging Chat, and allow users to input an API key to utilize ChatGPT3.
At present, there's no option to regenerate a response (though you can resend the same question for a potentially different answer). Due to the lack of a "conversation" view, tracking a dialogue or following up on answers can be challenging — but Bavarder excels for rapid-fire questions.
As with any AI, standard disclaimers apply. Responses might seem plausible but could contain inaccurate or false information. Additionally, it's relatively easy to lead these models into irrational loops, like convincing them that 2 + 2 equals 106 — so stay alert!
Overall, Bavarder is an attractive app with a well-defined purpose. If you enjoy ChatGPT and similar technologies, it's worth exploring.
ChatGPT AI
- LibreOffice 7.5.3 Released: Third Maintenance Update Brings 119 Bug Fixes to Popular Open-Source Office Suite
Today, The Document Foundation unveiled the release and widespread availability of LibreOffice 7.5.3, which serves as the third maintenance update to the current LibreOffice 7.5 open-source and complimentary office suite series.
Approximately five weeks after the launch of LibreOffice 7.5.2, LibreOffice 7.5.3 arrives with a new set of bug fixes for those who have successfully updated their GNU/Linux system to the LibreOffice 7.5 series.
LibreOffice 7.5.3 addresses a total of 119 bugs identified by users or uncovered by LibreOffice developers. For a more comprehensive understanding of these bug fixes, consult the RC1 and RC2 changelogs.
You can download LibreOffice 7.5.3 directly from the LibreOffice website��or from SourceForge as binary installers for DEB or RPM-based GNU/Linux distributions. A source tarball is also accessible for individuals who prefer to compile the software from sources or for system integrators.
All users operating the LibreOffice 7.5 office suite series should promptly update their installations to the new point release, which will soon appear in the stable software repositories of your GNU/Linux distributions.
In early February 2023, LibreOffice 7.5 debuted as a substantial upgrade to the widely-used open-source office suite, introducing numerous features and improvements. These enhancements encompass major upgrades to dark mode support, new application and MIME-type icons, a refined Single Toolbar UI, enhanced PDF Export, and more.
Seven maintenance updates will support LibreOffice 7.5 until November 30th, 2023. The next point release, LibreOffice 7.5.4, is scheduled for early June and will include additional bug fixes.
The Document Foundation once again emphasizes that the LibreOffice office suite's "Community" edition is maintained by volunteers and members of the Open Source community. For enterprise implementations, they suggest using the LibreOffice Enterprise family of applications from ecosystem partners.
LibreOffice

- Keep Android Open
Google has announced that, soon, anyone looking to develop Android apps will have to first register centrally with Google.
- Kernel 7.0 Now in Testing
Linus Torvalds has announced the first Release Candidate (RC) for the 7.x kernel is available for those who want to test it.
- LibreOffice 26.2 Now Available
With new features, improvements, and bug fixes, LibreOffice 26.2 delivers a modern, polished office suite without compromise.
- Photoshop on Linux?
A developer has patched Wine so that it'll run specific versions of Photoshop that depend on Adobe Creative Cloud.
|