|
1825 Monetary Lane Suite #104 Carrollton, TX
Do a presentation at NTLUG.
What is the Linux Installation Project?
Real companies using Linux!
Not just for business anymore.
Providing ready to run platforms on Linux
|
Show Descriptions... (Show All/All+Images)
(Single Column)

- Debian 8 imagemagick Important Info Leak DoS CVE-2026-24481 DSA-6158-1
Multiple security vulnerabilities were discovered in imagemagick, a software suite used for editing and manipulating digital images, which could lead to information leaks, bypass of security policies, denial of service or arbitrary code execution. For the stable distribution (trixie), these problems have been fixed in

- [$] Inspecting and modifying Python types during type checking
Python has aunique approach to static typing. Python programs can contain typeannotations, and even access those annotations at run time, but the annotationsaren't evaluated by default. Instead, it is up to external programs to ascribemeaning to those annotations. The annotations themselves can be arbitrary Pythonexpressions, but in practice usually involve using helpers from the built-inPEP 827 ("Type Manipulation")aims to add additionalcapabilities to Python's type system to fix this, butdiscussionof the PEP has been of mixed sentiment.
- digiKam 9.0.0 released
Version9.0.0 of the digiKam photo-management system has beenreleased. "This major version introduces groundbreakingimprovements in performance, usability, and workflow efficiency, witha strong focus on modernizing the user interface, enhancing metadatamanagement, and expanding support for new camera models and fileformats." Some of the changes include anew survey tool, more advanced search and sorting options, as wellas bulkediting of geolocation coordinates.
- Security updates for Monday
Security updates have been issued by AlmaLinux (delve, git-lfs, and postgresql16), Fedora (cef, chezmoi, chromium, coturn, erlang-hex_core, firefox, gh, gimp, k9s, keylime, keylime-agent-rust, libsixel, microcode_ctl, nextcloud, nss, perl-Crypt-URandom, pgadmin4, php-zumba-json-serializer, postgresql16-anonymizer, prometheus, python-asyncmy, python3.10, python3.11, python3.9, staticcheck, valkey, and vim), SUSE (chromedriver, chromium, coredns, expat, freetype2-devel, gitea-tea, go1.24-openssl, go1.25-openssl, grpc, gstreamer-rtsp-server, gstreamer-plugins-ugly,, helm, jetty-annotations, kubeshark-cli, libaec, libblkid-devel, libsoup, libxml2, libxslt, NetworkManager-applet-strongswan, podman, python-joserfc, python-Markdown, python-pypdf2, python-tornado, python-uv, python311-Django, python311-joserfc, python311-nltk, roundcubemail, and valkey), and Ubuntu (python3.4, python3.5, python3.6, python3.7, python3.8, python3.9, python3.10, python3.11, python3.12, python3.13, python3.14).
- Kernel prepatch 7.0-rc3
Linus has released 7.0-rc3 for testing."So it's still pretty early in the release cycle, and it just feels abit busier than I'd like. But nothing particularly stands out or looksbad."
- Huston: Revisiting time
Geoff Huston looks at the networktime protocol, and efforts to secure it, in detail.
NTP operates in the clear, and it is often the case that the servers used by a client are not local. This provides an opportunity for an adversary to disrupt an NTP session, by masquerading as a NTP server, or altering NTP payloads in an effort to disrupt a client's time-of-day clock. Many application-level protocols are time sensitive, including TLS, HTTPS, DNSSEC and NFS. Most Cloud applications rely on a coordinated time to determine the most recent version of a data object. Disrupting time can cause significant chaos in distributed network environments.
While it can be relatively straightforward to secure a TCP-based protocol by adding an initial TLS handshake and operating a TLS shim between TCP and the application traffic, it's not so straightforward to use TLS in place of a UDP-based protocol for NTP. TLS can add significant jitter to the packet exchange. Where the privacy of the UDP payload is essential, then DTLS might conceivably be considered, but in the case of NTP the privacy of the timestamps is not essential, but the veracity and authenticity of the server is important.
NTS, a secured version of NTP, is designed to address this requirement relating to the veracity and authenticity of packets passed from a NTS server to an NTS client. The protocol adds a NTS Key Establishment protocol (NTS-KE) in additional to a conventional NTPv4 UDP packet exchange (RFC 8915).
- [$] Fedora shares strategy updates and "weird research university" model
In early February, members of the Fedora Council met in Tirana,Albania to discuss and set the strategic direction for the Fedora Project. Thecouncil has publishedsummaries from its strategy summit, and Fedora Project Leader (FPL) Jef Spaleta,as well as some of the council members, held a video meeting to discuss outcomes fromthe summit on February 25. Topics included a plan to experiment with Open Collective to raisefunds for specific Fedora projects, tools to build image-based editions, andmore. Spaleta also explained his model for Fedora governance.
- OpenWrt 25.12.0 released
Version25.12.0 of the OpenWrt router distribution is available; this releasehas been dedicated to the memory of Dave Täht. Changes include a switch tothe apk package manager, the integration of the attendedsysupgrade method, and support for a long list of new targets.
- Security updates for Friday
Security updates have been issued by Debian (chromium), Fedora (freerdp, libsixel, opensips, and yt-dlp), Mageia (python-django, rsync, and vim), Red Hat (go-rpm-macros and osbuild-composer), SUSE (7zip, assertj-core, autogen, c3p0, cockpit-machines, cockpit, cockpit-repos, containerized-data-importer, cpp-httplib, docker, docker-stable, expat, firefox, gnutls, go1.25-openssl, golang-github-prometheus-prometheus, haproxy, ImageMagick, incus, kernel, kubevirt, libsoup, libsoup2, mchange-commons, ocaml, openCryptoki, openvpn, php-composer2, postgresql14, postgresql15, python-Authlib, python-azure-core, python-nltk, python-urllib3_1, python311-Django4, python311-pillow-heif, python311-PyPDF2, python313, python313-Django6, qemu, rhino, roundcubemail, ruby4.0-rubygem-rack, sdbootutil, and wicked2nm), and Ubuntu (less, nss, python-bleach, qtbase-opensource-src, and zutty).
- Rust 1.94.0 released
Version1.94.0 of the Rust language has been released. Changes include arraywindows (an iterator for slices), some Cargo enhancements, and a numberof newly stabilized APIs.
- A GitHub Issue Title Compromised 4,000 Developer Machines (grith.ai)
The grith.ai blog reportson an LLM prompt-injection vulnerability that led to 4,000 installations ofa compromised version of the Cline utility.
For the next eight hours, every developer who installed or updated Cline got OpenClaw - a separate AI agent with full system access - installed globally on their machine without consent. Approximately 4,000 downloads occurred before the package was pulled.
The interesting part is not the payload. It is how the attacker got the npm token in the first place: by injecting a prompt into a GitHub issue title, which an AI triage bot read, interpreted as an instruction, and executed.

- Ubuntu 26.04 LTS Officially Supporting Cloud-Based Authentication With Authd
Canonical for a while has been developing Authd as an authentication service for external cloud-based identity providers. Authd was designed from the ground-up to provide secure management of identity and access for Ubuntu systems while only with next month's Ubuntu 26.04 LTS release is it actually hitting the universe archive...
- MariaDB backs down on Galera removal after community outcry
But questions remain over long-term commitment to clustering tech in open sourceAfter a couple of years of relative calm, the relationship between MariaDB and its open source foundation was ruffled in February, leaving observers with a few unanswered questions.…
- AMD Formally Launches Ryzen AI Embedded P100 Series 8-12 Core Models
AMD announced back at CES the Ryzen AI Embedded P100 series with initially the models up to six Zen 5 cores launching while the eight through twelve core models would be available later in H1. Today AMD formally announced those higher-tier Ryzen AI Embedded P100 series parts...
- NVIDIA 595 Linux Driver Running Well In Early Benchmarks
Last week NVIDIA released the 595.45.04 beta Linux driver as their first public build in the R595 release branch. The NVIDIA R595 Linux driver is bringing a number of Vulkan driver improvements, HDR enhancements, DRI3 v1.2 support, and a variety of other improvements. Benchmarking the NVIDIA 595.45.04 Linux driver the past few days on GeForce RTX 50 "Blackwell" have been showing some nice incremental performance improvements over the current NVIDIA 590 driver stable series.
- Linuxiac Weekly Wrap-Up: Week 10, 2026 (Mar 2 – 8)
Catch up on the latest Linux news: CachyOS, Linux From Scratch 13.0, Nitrux 6.0, NVIDIA 595 Beta Linux Driver, KDE Plasma 6.6.2, early mockups reveal Mozilla exploring a new Nova design for Firefox, and more.

- European Consortium Wants Open-Source Alternative To Google Play Integrity
An anonymous reader quotes a report from Heise: Pay securely with an Android smartphone, completely without Google services: This is the plan being developed by the newly founded industry consortium led by the German Volla Systeme GmbH. It is an open-source alternative to Google Play Integrity. This proprietary interface decides on Android smartphones with Google Play services whether banking, government, or wallet apps are allowed to run on a smartphone. Obstacles and tips for paying with an Android smartphone without official Google services have been highlighted by c't in a comprehensive article. The European industry consortium now wants to address some problems mentioned. To this end, the group, which includes Murena, which develops the hardened custom ROM /e/OS, Iode from France, and Apostrophy (Dot) from Switzerland, in addition to Volla, is developing a so-called "UnifiedAttestation" for Google-free mobile operating systems, primarily based on the Android Open-Source Project (AOSP). According to Volla, a European manufacturer and a leading manufacturer from Asia, as well as European foundations such as the German UBports Foundation, have also expressed interest in supporting it. Furthermore, developers and publishers of government apps from Scandinavia are examining the use of the new procedure as "first movers." In its announcement, Volla explains that Google provides app developers with an interface called Play Integrity, which checks whether an app is running on a device with specific security requirements. This primarily affects applications from "sensitive areas such as identity verification, banking, or digital wallets -- including apps from governments and public administrations". The company criticizes that the certification is exclusively offered for Google's own proprietary "Stock Android" but not for Android versions without Google services, such as /e/OS or similar custom ROMs. "Since this is closely intertwined with Google services and Google data centers, a structural dependency arises -- and for alternative operating systems, a de facto exclusion criterion," the company states. From the consortium's perspective, this also leads to a "security paradox," because "the check of trustworthiness is carried out by precisely that entity whose ecosystem is to be avoided at the same time". The UnifiedAttestation system is built around three main components: an "operating system service" that apps can call to check whether the device's OS meets required security standards, a decentralized validation service that verifies the OS certificate on a device without relying on a single central authority, and an open test suite used to evaluate and certify that a particular operating system works securely on a specific device model. "We don't want to centralize trust, but organize it transparently and publicly verifiable. When companies check competitors' products, we can strengthen that trust," says Dr. Jorg Wurzer, CEO of Volla Systeme GmbH and initiator of the consortium. The goal is to increase digital sovereignty and break free from the control of any one, single U.S. company, he says.
 
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
- Samsung Wants To Let You Vibe Code Your Galaxy Phone Experience
Samsung says it's thinking about bringing "vibe coding" to future Galaxy phones, allowing users to describe apps or interface changes in plain language and have AI generate the code. TechRadar interviewed Won-Joon Choi, Samsung's head of mobile experience, to learn more about the plans. Here's an excerpt from their report: As noted by Won-Joon Choi, the usefulness of vibe coding on smartphones is that it opens up the "possibility of customizing your smartphone experience in new ways, not just your apps but your UX." He added, "Right now we're limited to premade tools, but with vibe coding, users could adjust their favorite apps or make something customized to their needs. So vibe coding is very interesting, and something we're looking into." [...] Samsung recently debuted the Galaxy S26 series of phones and made a point to not call them smartphones -- they're "AI phones" now. This certainly rang true with the majority of upgrades to the devices being AI software-focused, like the new Now Nudge and expanded Audio Eraser tools, with the biggest hardware bump for the base models coming via the 39% improved NPU processing (the processor in charge of on-device AI tasks). It also teased the debut of Perplexity on its phones, joining as an alternative to the Gemini assistant, and teased the possibility of other AI models getting the same treatment in the future.
 
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
- EA Lays Off Staff Across All Battlefield Studios Following Record-Breaking Battlefield 6 Launch
Electronic Arts has laid off staff across multiple Battlefield studios despite Battlefield 6 being the best-selling game in the U.S. in 2025 and the "biggest launch in franchise history." According to IGN, the layoffs include workers at Criterion, Dice, Ripple Effect, and Motive Studios. From the report: Individuals are being informed that the layoffs are taking place as part of a "realignment" across the Battlefield studios, as the team continues its ongoing, live service support for Battlefield 6 following launch. All four studios will remain operational, though the layoffs seem to be impacting a variety of teams across multiple studios and offices. IGN asked EA for comment on total number and types of roles impacted, as well as for the specific reasons for the layoffs. An EA spokesperson told IGN: "We've made select changes within our Battlefield organization to better align our teams around what matters most to our community. Battlefield remains one of our biggest priorities, and we're continuing to invest in the franchise, guided by player feedback and insights from Battlefield Labs."
 
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
- Live Nation Avoids Ticketmaster Breakup By 'Open Sourcing' Their Ticketing Model
Live Nation reached a settlement with the U.S. Department of Justice that avoids breaking up its dominant live events empire with Ticketmaster. Instead, the deal requires changes like "open sourcing" their ticketing model and divesting some venues. NBC News reports: The company and the Justice Department reached a settlement on Monday, following a week of testimony during an antitrust trial that threatened to potentially separate the world's largest live entertainment company. [...] On a background call with reporters Monday, a senior justice official said the deal will drive down prices by giving both artists and consumers more choice. As part of the agreement, Ticketmaster will provide a standalone ticketing system that will allow third-party companies like SeatGeek and StubHub to offer primary tickets through the platform. The senior justice official described it as "open sourcing" their ticketing model. The company will also divest up to 13 amphitheaters and reserve 50% of tickets for nonexclusive venues. Ticketmaster is also prohibited from retaliating against a venue that selects another primary ticket distributor, among other requirements. Although a group of states have joined the DOJ in signing the agreement, other states can continue to press their own claims.
 
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
- How AI Assistants Are Moving the Security Goalposts
An anonymous reader quotes a report from KrebsOnSecurity: AI-based assistants or "agents" -- autonomous programs that have access to the user's computer, files, online services and can automate virtually any task -- are growing in popularity with developers and IT workers. But as so many eyebrow-raising headlines over the past few weeks have shown, these powerful and assertive new tools are rapidly shifting the security priorities for organizations, while blurring the lines between data and code, trusted co-worker and insider threat, ninja hacker and novice code jockey. The new hotness in AI-based assistants -- OpenClaw (formerly known as ClawdBot and Moltbot) -- has seen rapid adoption since its release in November 2025. OpenClaw is an open-source autonomous AI agent designed to run locally on your computer and proactively take actions on your behalf without needing to be prompted. If that sounds like a risky proposition or a dare, consider that OpenClaw is most useful when it has complete access to your entire digital life, where it can then manage your inbox and calendar, execute programs and tools, browse the Internet for information, and integrate with chat apps like Discord, Signal, Teams or WhatsApp. Other more established AI assistants like Anthropic's Claude and Microsoft's Copilot also can do these things, but OpenClaw isn't just a passive digital butler waiting for commands. Rather, it's designed to take the initiative on your behalf based on what it knows about your life and its understanding of what you want done. "The testimonials are remarkable," the AI security firm Snyk observed. "Developers building websites from their phones while putting babies to sleep; users running entire companies through a lobster-themed AI; engineers who've set up autonomous code loops that fix tests, capture errors through webhooks, and open pull requests, all while they're away from their desks." You can probably already see how this experimental technology could go sideways in a hurry. [...] Last month, Meta AI safety director Summer Yue said OpenClaw unexpectedly started mass-deleting messages in her email inbox, despite instructions to confirm those actions first. She wrote: "Nothing humbles you like telling your OpenClaw 'confirm before acting' and watching it speedrun deleting your inbox. I couldn't stop it from my phone. I had to RUN to my Mac mini like I was defusing a bomb." Krebs also noted the many misconfigured OpenClaw installations users had set up, leaving their administrative dashboards publicly accessible online. According to pentester Jamieson O'Reilly, "a cursory search revealed hundreds of such servers exposed online." When those exposed interfaces are accessed, attackers can retrieve the agent's configuration and sensitive credentials. O'Reilly warned attackers could access "every credential the agent uses -- from API keys and bot tokens to OAuth secrets and signing keys." "You can pull the full conversation history across every integrated platform, meaning months of private messages and file attachments, everything the agent has seen," O'Reilly added. And because you control the agent's perception layer, you can manipulate what the human sees. Filter out certain messages. Modify responses before they're displayed."
 
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
- Bluesky CEO Jay Graber Is Stepping Down
Bluesky CEO Jay Graber is stepping down after overseeing the platform's growth from a Twitter research project into a 40-million-user alternative to X. "As Bluesky matures, the company needs a seasoned operator focused on scaling and execution, while I return to what I do best: building new things," Graber wrote in a statement. She will be transitioning to a new Chief Innovation Officer role while Venture capitalist Toni Schneider will serve as interim CEO until the board searches for a permanent replacement. Wired reports: Graber joined Bluesky in 2019, when it was a research project within Twitter focused on developing a decentralized framework for the social web. She became the company's first chief executive officer in 2021, when it spun out into an independent entity. She oversaw the platform's remarkable rise and the growing pains it experienced as it transformed from a quirky Twitter offshoot to a full-fledged alternative to X. Schneider tells WIRED that he intends to help Bluesky "become not just the best open social app, but the foundation for a whole new generation of user-owned networks." Schneider, who will continue working as a partner at the venture capital firm True Ventures while at Bluesky, was previously CEO of the Wordpress parent company, Automattic, from 2006 to 2014. He also served as its CEO again in 2024 while top executive Matt Mullenweg went on a sabbatical. During that time, Schneider met Graber and became an adviser to Bluesky's leadership. In a blog post announcing his new role, Schneider said he plans to emphasize scaling, describing his job as "to help set up Bluesky's next phase of growth." This isn't the end for Graber and Bluesky. She will transition to become the company's chief innovation officer, a role focused on Bluesky's technology stack rather than its business operations. The position was created for her. Graber, who began her career as a software engineer, has always sounded the most enthusiastic when discussing Bluesky's technology rather than its revenue streams. Bluesky's board of directors will appoint the next permanent CEO. The members include Jabber founder Jeremie Miller, crypto-focused VC Kinjal Shah, TechDirt founder Mike Masnick, and Graber. (Twitter founder Jack Dorsey was originally part of the board but quit in 2024.) This means Graber will have input on her successor. The talent search is still in early stages.
 
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
- Qualcomm's New Arduino Ventuno Q Is an AI-Focused Computer Designed For Robotics
Qualcomm and Arduino have unveiled the Arduino Ventuno Q, a new AI-focused single-board computer built for robotics and edge systems. Engadget reports: Called the Arduino Ventuno Q, it uses Qualcomm's Dragonwing IQ8 processor along with a dedicated STM32H5 low-latency microcontroller (MCU). "Ventuno Q is engineered specifically for systems that move, manipulate and respond to the physical world with precision and reliability," the company wrote on the product page. The Ventuno Q is more sophisticated (and expensive) than Arduinio's usual AIO boards, thanks to the Dragonwing IQ8 processor that includes an 8-core ARM Cortex CPU, Adreno Arm Cortex A623 GPU and Hexagon Tensor NPU that can hit up ot 40 TOPs. It also comes with 16GB of LPDDR5 RAM, along with 64GB of eMMC storage and an M.2 NVME Gen.4 slot to expand that. Other features include Wi-Fi 6, Bluetooth 5.3, 2.5Gbps ethernet and USB camera support. The Ventuno Q includes Arudino App Lab, with pre-trained AI models including LLMs, VLMs, ASR, gesture recognition, pose estimation and object tracking, all running offline. It's designed for AI systems that run entirely offline like smart kiosks, healthcare assistants and traffic flow analysis, along with Edge AI vision and sensing systems. It also supports a full robotics stack including vision processing combined with deterministic motor control for precise vision and manipulation. It's also ideal for education and research in areas like computer vision, generative AI and prototyping at the edge, according to Arduino. Further reading: Up Next for Arduino After Qualcomm Acquisition: High-Performance Computing
 
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
- Anthropic Sues the Pentagon After Being Labeled a Threat To National Security
Anthropic is suing the Department of Defense after the Trump administration labeled the company a "supply chain risk" and canceled its government contracts when Anthropic refused to allow its AI model Claude to be used for domestic surveillance or autonomous weapons. Fortune reports: The lawsuit, filed Monday in the U.S. District Court for the Northern District of California, calls the administration's actions "unprecedented and unlawful" and claims they threaten to harm "Anthropic irreparably." The complaint claims that government contracts are already being canceled and that private contracts are also in doubt, putting "hundreds of millions of dollars" at near-term risk. An Anthropic spokesperson told Fortune: "Seeking judicial review does not change our longstanding commitment to harnessing AI to protect our national security, but this is a necessary step to protect our business, our customers, and our partners." "We will continue to pursue every path toward resolution, including dialogue with the government," they added.
 
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
- 'If Lockheed Martin Made a Game Boy, Would You Buy One?'
"If Lockheed Martin made a Game Boy, would you buy one?" That was the [rhetorical] question The Verge's Sean Hollister asked when he reviewed ModRetro's Game Boy-style handheld device back in 2024. He said it "might be the best version of the Game Boy ever made," though the connection to Palmer Luckey and his defense tech startup Anduril left him conflicted. "I don't remember my childhood nostalgia coming with a side of possible guilt and fear about putting money into the pocket of a weapons contractor," he wrote. "Feels weird!" Those conflicted feelings have lingered ever since. TechCrunch recently cited Hollister's review while reporting that ModRetro is now seeking funding at a $1 billion valuation. The company is said to have additional retro-inspired hardware in development, including one designed to replicate the Nintendo 64. As for Anduril? It's reportedly in talks to raise a new funding round that would value the company at around $60 billion.
 
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
- AI Allows Hackers To Identify Anonymous Social Media Accounts, Study Finds
An anonymous reader quotes a report from the Guardian: AI has made it vastly easier for malicious hackers to identify anonymous social media accounts, a new study has warned. In most test scenarios, large language models (LLMs) -- the technology behind platforms such as ChatGPT -- successfully matched anonymous online users with their actual identities on other platforms, based on the information they posted. The AI researchers Simon Lermen and Daniel Paleka said LLMs make it cost effective to perform sophisticated privacy attacks, forcing a "fundamental reassessment of what can be considered private online". In their experiment, the researchers fed anonymous accounts into an AI, and got it to scrape all the information it could. They gave a hypothetical example of a user talking about struggling at school, and walking their dog Biscuit through a "Dolores park." In that hypothetical case, the AI then searched elsewhere for those details and matched @anon_user42 to the known identity with a high degree of confidence. While this example was fictional, the paper's authors highlighted scenarios in which governments use AI to surveil dissidents and activists posting anonymously, or hackers are able to launch "highly personalized" scams.
 
Read more of this story at Slashdot.

- HPE tweaks T&Cs so the price it quotes may not be the price you pay
With memory and storage contributing over half the price of a server, Big Green needs to protect its margins
HPE has changed its terms and conditions in ways that allow it to change hardware prices after it’s issued a quote, due to rampant storage and memory price rises.…
- Anthropic debuts pricey and sluggish automated Code Review tool
First vibe coding, now vibe reviewing ... but the buzz is good as it finds worthy issues
Anthropic has introduced a more extensive – and expensive – way to review source code in hosted repositories, many of which already contain large swaths of AI-generated code.…
- Moody humans should let AI handle bad public feedback first, study finds
Enjoy meltdowns from businesses on Yelp over negative reviews? AI is threatening to take that away
Angry company responses to customer complaints are a favorite topic of internet amusement and outrage, but they're also embarrassing for the employees who post them. Having AI process customer reviews could be a better way. …

- Using OpenTelemetry and the OTel Collector for Logs, Metrics, and Traces
OpenTelemetry (fondly known as OTel) is an open-source project that provides a unified set of APIs, libraries, agents, and instrumentation to capture and export logs, metrics, and traces from applications. The project’s goal is to standardize observability across various services and applications, enabling better monitoring and troubleshooting. Read More at Causely
The post Using OpenTelemetry and the OTel Collector for Logs, Metrics, and Traces appeared first on Linux.com.
- Xen 4.19 is released
Xen Project 4.19 has been officially out since July 31st, 2024, and it brings significant updates. With enhancements in performance, security, and versatility across various architectures like Arm, PPC, RISC-V, and x86, this release is an important milestone for the Xen community. Read more at XCP-ng Blog
The post Xen 4.19 is released appeared first on Linux.com.

- There9s Hope That At Least Colorado9s Age Attestation Bill Could Exclude Open-Source
Last week was a statement by System76 regarding recent age verification laws in California and Colorado among other US states that could have a profound impact on Linux distributions and other open-source software. The Colorado legislation is especially pressing to System76 considering that is where they are based. Fortunately, they aren't taking this lightly and there is some hope that at least in Colorado open-source software could be excluded...
- Ubuntu 26.04 LTS Officially Supporting Cloud-Based Authentication With Authd
Canonical for a while has been developing Authd as an authentication service for external cloud-based identity providers. Authd was designed from the ground-up to provide secure management of identity and access for Ubuntu systems while only with next month's Ubuntu 26.04 LTS release is it actually hitting the universe archive...
- NVIDIA 595 Linux Driver Running Well In Early Benchmarks
Last week NVIDIA released the 595.45.04 beta Linux driver as their first public build in the R595 release branch. The NVIDIA R595 Linux driver is bringing a number of Vulkan driver improvements, HDR enhancements, DRI3 v1.2 support, and a variety of other improvements. Benchmarking the NVIDIA 595.45.04 Linux driver the past few days on GeForce RTX 50 "Blackwell" have been showing some nice incremental performance improvements over the current NVIDIA 590 driver stable series.
- AMD Formally Launches Ryzen AI Embedded P100 Series 8-12 Core Models
AMD announced back at CES the Ryzen AI Embedded P100 series with initially the models up to six Zen 5 cores launching while the eight through twelve core models would be available later in H1. Today AMD formally announced those higher-tier Ryzen AI Embedded P100 series parts...
- New Rust Driver Aims To Improve Upstream Linux On Synology NAS Devices
A set of patches posted to the Linux kernel mailing list last week introduce a new driver for enhancing the upstream/mainline Linux kernel support for Synology network attached storage (NAS) devices. This new driver is Synology Microp and is making use of the Linux kernel's modern Rust programming language support...
- Rode’s Rodecaster Video Core makes livestreaming even cheaper
Rode’s not done releasing trimmed-down versions of its production tools with an eye on budget conscious creators. Today, it’s launching Rodecaster Video Core, an all-in-one studio setup which sits below its flagship Rodecaster Video and its (now) mid-range Video S. It’s aimed at folks who are either dipping a toe into this world, or already have audio gear and just want to broaden out to HD video as well. Arguably, the biggest change is the lack of any controls on the hardware itself, as you’ll be running the show entirely from inside the Rodecaster App.
In terms of connectivity, you’ll find three HDMI-in, one HDMI-out, four USB-C, two 3.5mm and two Neutrik combo ports ‘round back. Connect a compatible video device to a USB-C port and you’ll be able to run up to four sources at a time, and you can even use network cameras via Ethernet. Plus, you’ll be able to use the Rode Capture app to wirelessly connect the feed from an iOS device to your setup. And you’ll even be able to set it up to automatically switch between feeds based on audio inputs, reducing your need to micromanage multi-person feeds.
Rode
And, if you’re already rocking one of Rode’s audio consoles, the Rodecaster Sync app will make your life a lot easier. Essentially, if you’ve got a Rodecaster Pro 2 or Duo, you’ll be able to hook it up to your Video Core, allowing you to set shortcuts directly to your pads. In fact, you can run your audio and video setup from the one desk, hopefully reducing the amount of fiddling you need to do in the middle of your stream.
Core is designed to stream straight to YouTube, Twitch and any other platforms you’d care to use instead. You’ll be able to record your footage to an external drive and, thanks yo a new firmware update across the range, you’ll also be able to output a EDL file for DaVinci Resolve. Oh, and you’ll now be able to import media in non-standard resolutions and aspect ratios — such as square footage from social media — which will be automatically scaled and optimized for your show.
Rodecaster Video Core is available to pre-order now for $599, but there’s no word yet on when the sturdy boxes will start winging their way around the world.
This article originally appeared on Engadget at https://www.engadget.com/entertainment/rodes-rodecaster-video-core-makes-livestreaming-even-cheaper-230053061.html?src=rss
- You can (sort of) block Grok from editing your uploaded photos
People can block the xAI9s Grok chatbot from creating modifications of their uploaded images on social network X. Neither X or xAI, both Elon Musk-owned businesses, have made a public announcement about this feature, which users began noticing on the iOS app within the image/video upload menu over the past few days.
This option is likely a response to Grok9s latest scandal, which began at the start of 2026 when the addition of image generation tools to the chatbot saw about 3 million sexualized or nudified images created. An estimated 23,000 of the images made in that 11-day period contained sexualized images of children, according to the Center for Countering Digital Hate. Grok is now facing two separate investigations by regulators in the EU over the issue.
The positive side of the recent feature addition is that X and xAI have taken a step toward limiting inappropriate uses of Grok. This block is a simple toggle and it hasn9t been buried in the UI. So that9s nice.
The negative side, however, is that this token gesture that doesn9t amount to any serious improvement to how Grok works or can be used. It9s great that the chatbot won9t alter the file uploaded by one person, but as reported by real people in scanty clothing that X announced in January seem to have had only partial success at best. If this additional and narrow use case is all the company offers, then the claims of being a zero-tolerance space for nonconsensual nudity are going to ring hollow. Especially since, as we noted at the time, xAI could stop allowing image generation at all until the issue is properly and thoroughly fixed.
This article originally appeared on Engadget at https://www.engadget.com/ai/you-can-sort-of-block-grok-from-editing-your-uploaded-photos-215356117.html?src=rss
- Bluesky's CEO is stepping down after nearly 5 years
Bluesky CEO Jay Graber, who has led the upstart social platform since 2021, is stepping downfrom her role as its top executive. Toni Schneider, who has been an advisor and investor in Bluesky, will take over the job temporarily while Graber stays on as Chief Innovation Officer.
"As Bluesky matures, the company needs a seasoned operator focused on scaling and execution, while I return to what I do best: building new things," Graber wrote in a blog post. Schneider, who was previously CEO at Wordpress parent Automattic, will be that "experienced operator and leader" while Blueksy's board searches for a permanent CEO, she said.
Graber's history with Bluesky dates back to its early days as a side project at Jack Dorsey's Twitter. She was officially brought on as CEO in 2021 as Bluesky spun off into an independent company (it officially ended its association with Twitter in 2022 and Dorsey cut ties with Bluesky in 2024). She led the company through its launch and early viral success as it grew from an invitation-only platform to the 43 million-user service it is today. During that time, she's become known as an advocate for decentralized social media and for trolling Mark Zuckerberg's t-shirt choices.
Nearly three years since it launched publicly, Bluesky has carved out a small but influential niche in the post-Twitter social landscape. The platform is less than a third of the size of Meta's competitor, Threads, which has also copied some of Bluesky's signature features. Bluesky also has yet to roll out any meaningful monetization features, though it has teased a premium subscription service in the past.
As Chief Innovation Officer, Graber will presumably still be an influential voice at the company going forward. And, as Wired points out, she still has a seat on Bluesky's board so she will get some say in who steps into the role permanently. Until then, Schneider, who is also a partner at VC firm Tre Ventures, will lead the company. "I deeply believe in what this team has built and the open social web they're fighting for," he wrote in a post on Bluesky.
This article originally appeared on Engadget at https://www.engadget.com/social-media/blueskys-ceo-is-stepping-down-after-nearly-5-years-201900960.html?src=rss
- Samsung promises 120 games will be playable via its glasses-free 3D monitor tech by the end of the year
Samsung just announced that 120 games will be playable via its Odyssey 3D Hub platform by the end of the year. This is the platform that provides content for glasses-free 3D monitors like recent Odyssey displays.
The company made this claim at GDC 2026, while also noting that the platform currently offers around 60 playable titles. Samsung has only announced a couple of games headed to the platform this year, which include Cronos: The New Dawn and Hell is Us. These are both solid third-person action games that originally came out last year.
The collection already includes several notable games, including Stellar Blade, Lies of P and Psychonauts 2, among others. It's good to know the library continues to grow, proving that there might still be some life left in 3D display technology after all.
We came away impressed with the technology when we gave it a go last year. We even said that if "3D had been like this all along, people would be much more receptive." The games look great and the displays include head tracking so users don't have to constantly struggle to find the one sweet spot (I'm looking at you, Nintendo 3DS.)
Samsung has quietly been adding to its lineup of glasses-free 3D displays. There are several models to choose from nowadays, with screen sizes up to 32-inches.
The company also used GDC to announce a partnership with game developer CD Projekt Red, but details remain scant. It has something to do with display technology and Samsung's HDR10+ Gaming standard. We do know that CDPR and Samsung are integrating HDR10+ Gaming into Cyberpunk 2077.
This article originally appeared on Engadget at https://www.engadget.com/gaming/samsung-promises-120-games-will-be-playable-via-its-glasses-free-3d-monitor-tech-by-the-end-of-the-year-180102470.html?src=rss
- EA laid off staffers across Battlefield studios to 'better align' its teams
EA axed an undisclosed number of employees across the game studios behind the Battlefield franchise. As first reported by seven million copies sold in the first three days following its release in October. EA even called the latest Battlefield title the "best-selling shooter title of 2025" in its third quarter report for FY26, which disclosed the company's net revenue of more than $1.9 billion for the quarter.
"Battlefield remains one of our biggest priorities, and we’re continuing to invest in the franchise, guided by player feedback and insights from Battlefield Labs," an EA spokesperson also said in a statement.
Despite being one of EA's most popular franchises, Battlefield isn't the only one to suffer staffing cuts. Full Circle, the developer behind the skate. that's also owned by EA, also announced layoffs and "restructuring" in February. However, EA isn't the only company in the industry to look at downsizing its personnel. Ubisoft said it was planning to get rid of up to 200 jobs in its Paris office earlier this year and Microsoft announced it would cut thousands of jobs, including within its Gaming division, in July.
This article originally appeared on Engadget at https://www.engadget.com/gaming/ea-laid-off-staffers-across-battlefield-studios-to-better-align-its-teams-173617672.html?src=rss
- Hyper Light Drifter studio workers form union after rounds of layoffs
Workers at Heart Machine, the independent studio behind Hyper Light Drifter and Solar Ash, have formed a union with Communications Workers of America (CWA) Local 9003. The wall-to-wall unit covers all 13 frontline employees at the studio, which voluntarily recognized the union in February after a supermajority of eligible workers voted for the measure.
The organizing effort follows a rough stretch at Heart Machine, after the studio laid off employees in November 2024, then announced in October 2025 that it would end development on its early access title Hyper Light Breaker and cut further staff.
"I decided to get involved in organizing my studio because I9ve seen so many peers in the industry stand up to protect the craft we all care so deeply about. Watching that momentum grow made me realize that if we love this work, we have to protect it, especially now," said Steph Aligbe, a gameplay tools engineer at the studio.
Heart Machine joining the CWA extends the union9s gaming footprint even further. The union counts thousands of employees at Microsoft subsidiaries among its members, as well as staff at EA, Id Software and others. CWA also runs the United Videogame Workers, a direct-join union that launched in 2025, allowing individual game workers in the US and Canada to sign up on their own without elections or employer consent. Large gaming studios like Ubisoft have been undergoing a seemingly endless string of layoffs, and workers are increasingly demanding to have their voices heard.
This article originally appeared on Engadget at https://www.engadget.com/gaming/hyper-light-drifter-studio-workers-form-union-after-rounds-of-layoffs-165828565.html?src=rss
- Anthropic sues US government over supply chain risk designation
Anthropic has filed a lawsuit to prevent the Pentagon from adding the company it a national security blocklist. This comes days after the Department of Defense sent a letter to Anthropic confirming the company was labeled a supply chain risk; at the time CEO Dario Amodei had all but guaranteed Anthropic would fight back with legal action.
The lawsuit claims the designation is unlawful and violated free speech and due process rights. “These actions are unprecedented and unlawful. The Constitution does not allow the government to wield its enormous power to punish a company for its protected speech," Anthropic said in a pressuring Anthropic to remove certain safeguards from its AI systems, but Amodei made it clear the company would refuse to allow its model to be used for mass surveillance or development of autonomous weapons.
On the February 27 deadline, Amodei refused to budge, leading Hegseth to threaten the company with the supply chain risk designation; he also said the US government would cancel its $200 million contract with the company. The same day, President Trump ordered all federal agencies to cease using Anthropic as well. Despite all this, according to the lawsuit, Anthropic had agreed to “collaborate with the Department on an orderly transition to another AI provider willing to meet its demands.”
Anthropic rival OpenAI stepped into this chaos and quickly made a deal with the Department of Defense. At the time, OpenAI CEO Sam Altman said that two of OpenAI’s most important safety principles are “prohibitions on domestic mass surveillance and human responsibility for the use of force, including for autonomous weapon systems” — the same issues that got Anthropic in hot water. OpenAI then doubled down on the surveillance issue, writing into its contract that “the AI system shall not be intentionally used for domestic surveillance of U.S. persons and nationals.”
Depsite this, OpenAI’s head of robotics hardware resigned from the company this weekend in response to the Defense Department deal. Caitlin Kalinowski wrote on X that “surveillance of Americans without judicial oversight and lethal autonomy without human authorization are lines that deserved more deliberation than they got.”
This article originally appeared on Engadget at https://www.engadget.com/ai/anthropic-sues-us-government-over-supply-chain-risk-designation-152838128.html?src=rss

- ArcaOS 5.1.2 released
While IBM�s OS/2 technically did die, its development was picked up again much later, first through eComStation, and later, after money issues at its parent company Mensys, through ArcaOS. eComStation development stalled because of the money issues and has been dead for years; ArcaOS picked up where it left off and has been making steady progress since its first release in 2017. Regardless, the developers behind both projects develop OS/2 under license from IBM, but it�s unclear just how much they can change or alter, and what the terms of the agreement are. Anyway, ArcaOS 5.1.2 has just been released, and it seems to be a rather minor release. It further refines ArcaOS� support for UEFI and GPT-based disks, the tentpole feature of ArcaOS 5.1 which allows the operating system to be installed on a much more modern systems without having to fiddle with BIOS compatibility modes. Looking at the list of changes, there�s the usual list of updated components from both Arca Noae and the wider OS/2 community. You�ll find the latest versions of of the Panorama graphics drivers, ACPI, USB, and NVMe drivers, improved localisation, newer versions of the VNC server and viewer, and much more. If you have an active Support 8 Maintenance subscription for ArcaOS 5.1, this update is free, and it�s also available at discounted prices as upgrades for earlier versions. A brand new copy of ArcaOS 5.1.x will set you back $139, which isn�t cheap, but considering this price is probably a consequence of what must be some onerous licensing terms and other agreements with IBM, I doubt there�s much Arca Noae can do about it.
- AI! translations are ruining Wikipedia
Oh boy. Wikipedia editors have implemented new policies and restricted a number of contributors who were paid to use AI to translate existing Wikipedia articles into other languages after they discovered these AI translations added AI “hallucinations,” or errors, to the resulting article. ↫ Emanuel Maiberg at 404 Media There seems to be this pervasive conviction among Silicon Valley techbro types, and many programmers and developers in general, that translation and localisation are nothing more than basic find/replace tasks that you can automate away. At first, we just needed to make corpora of two different languages kiss and smooch, and surely that would automate translation and localisation away if the corpora were large enough. When this didn�t turn out to work very well, they figured that if we made the words in the corpora tumble down a few pachinko machines and then made them kiss and smooch, yes, then we�d surely have automated translation and localisation. Nothing could be further from the truth. As someone who has not only worked as a professional translator for over 15 years, but who also holds two university degrees in the subject, I keep reiterating that translation isn�t just a dumb substitution task; it�s a real craft, a real art, one you can have talent for, one you need to train for, and study for. You�d think anyone with sufficient knowledge in two languages can translate effectively between the two, but without a much deeper understanding of language in general and the languages involved in particular, as well as a deep understanding of the cultures in which the translation is going to be used, and a level of reading and text comprehension that go well beyond that of most, you�re going to deliver shit translations. Trust me, I�ve seen them. I�ve been paid good money to correct, fix, and mangle something usable out of other people�s translations. You wouldn�t believe the shit I�ve seen. Translation involves the kinds of intricacies, nuances, and context AI! isn�t just bad at, but simply cannot work with in any way, shape, or form. I�ve said it before, but it won�t be long before people start getting seriously injured � or worse � because of the cost-cutting in the translation industry, and the effects that�s going to have on, I don�t know, the instruction manuals for complex tools, or the leaflet in your grandmother�s medications. Because some dumbass bean counter kills the budget for proper, qualified, trained, and experienced translators, people are going to die.
- I don’t know what is Apple’s endgame for the Fn/Globe key, and I’m not sure Apple knows either!
Every modifier key starts simple and humble, with a specific task and a nice matching name. This never lasts. The tasks become larger and more convoluted, and the labels grow obsolete. Shift no longer shifts a carriage, Control doesn’t send control codes, Alt isn’t for alternate nerdy terminal functions. Fn is the newest popular modifier key, and it feels we’re speedrunning it through all the challenges without having learned any of the lessons. ↫ Marcin Wichary Grab a blanket, curl up on the couch with some coffee or tea, and enjoy.
- MenuetOS 1.59.20 released
MenuetOS, the operating system written in x86-64 assembly, has released two new versions since we last talked about it roughly two months ago. In fact, I�m not actually sure it�s just two, or more, or fewer, since it seems sometimes releases disappear entirely from the changelog, making things a bit unclear. Anyway, since the last time we talked about MenuetOS, it got improvements to videocalling, networking, and HDA audio drivers, and a few other small tidbits.
- Haiku inches closer to next beta release
And when a Redox monthly progress report is here, Haiku�s monthly report is never far behind (or vice versa, depending on the month). Haiku�s February was definitely a busy month, but there�s no major tentpole changes or new features, highlighting just how close Haiku is to a new regular beta release. The OpenBSD drivers have been synchronised wit upstream to draw in some bugfixes, there�s a ton of smaller fixes to various applications like StyledEdit, Mail, and many more, as well a surprisingly long list of various file system fixes, improving the drivers for file systems like NTFS, Btrfs, XFS, and others. There�s more, of course, so just like with Redox, head on over to pore over the list of smaller changes, fixes, and improvements. Just like last month, I�d like to mention once again that you really don�t need to wait for the beta release to try out Haiku. The operating system has been in a fairly stable and solid condition for a long time now, and whatever�s the latest nightly will generally work just fine, and can be updated without reinstallation.
- Redox gets NodeJS, COSMIC�s compositor, and much more
February has been a busy month for Redox, the general purpose operating system written in Rust. For instance, the COSMIC compositor can now run on Redox as a winit window, the first step towards fully porting the compositor from COSMIC to Redox. Similarly, COSMIC Settings now also runs on Redox, albeit with only a very small number of available settings as Redox-specific settings panels haven�t been made yet. It�s clear the effort to get the new COSMIC desktop environment from System76 running on Redox is in full swing. Furthermore, Vulkan software can now run on Redox, thanks to enabling Lavapipe in Mesa3D. There�s also a ton of fixes related to the boot process, the reliability of multithreading has been improved, and there�s the usual long list of kernel, driver, and Relibc improvements as well. A major port comes in the form of NodeJS, which now runs on Redox, and helped in uncovering a number of bugs that needed to be fixed. Of course, there�s way more in this month�s progress report, so be sure to head on over and read the whole thing.
- Hardware hotplug events on Linux, the gory details
One day, I suddenly wondered how to detect when a USB device is plugged or unplugged from a computer running Linux. For most users, this would be solved by relying on libusb. However, the use case I was investigating might not actually want to do so, and so this led me down a poorly-documented rabbit hole. ↫ ArcaneNibble (or R) And ArcaneNibble (or R) is taking you down with them.
- New Oracle Solaris CBE release released
Oracle�s Solaris 11 basically comes in two different flavours: the SRU (Support Repository Update) releases for commercial Oracle customers, and the CBE (Common Build Environment) releases, available to everyone. We�ve covered the last few SRU releases, and now it�s time for a new CBE release. We first introduced the Oracle Solaris CBE in March 2022 and we released an updated version in May 2025. Now, as Oracle Solaris keeps on evolving, we’ve released the latest version of our CBE. With the previous release Alan and Jan had compiled a list to cover all the changes in the three years since the first CBE release. This time, because it’s relatively soon after the last release we are opting to just point you to the what’s new blogs on the feature release SRUs Oracle Solaris 11.4 SRU 84, Oracle Solaris 11.4 SRU 87, and Oracle Solaris 11.4 SRU 90. And of course you can always go to the blogs by Joerg Moellenkamp and Marcel Hofstetter who have excellent series of articles that show how you can use the Oracle Solaris features. ↫ Joost Pronk van Hoogeveen at the Oracle Solaris Blog You can update your existing installation with a pkg update, or do a fresh insrtall with the new CBE images.
- The great license-washing has begun
In the world of open source, relicensing is notoriously difficult. It usually requires the unanimous consent of every person who has ever contributed a line of code, a feat nearly impossible for legacy projects. chardet, a Python character encoding detector used by requests and many others, has sat in that tension for years: as a port of Mozilla’s C++ code it was bound to the LGPL, making it a gray area for corporate users and a headache for its most famous consumer. Recently the maintainers used Claude Code to rewrite the whole codebase and release v7.0.0, relicensing from LGPL to MIT in the process. The original author, a2mark, saw this as a potential GPL violation. ↫ Tuan-Anh Tran Everything about this feels like a license violation, and in general a really shit thing to do. At the same time, though, the actual legal situation, what lawyers and judges care about, is entirely unsettled and incredibly unclear. I�ve been reading a ton of takes on what happened here, and it seems nobody has any conclusive answers, with seemingly valid arguments on both sides. Intuitively, this feels deeply and wholly wrong. This is the license-washing AI! seems to be designed for, so that proprietary vendors can take code under copyleft licenses, feed it into their AI! model, and tell it to regurgitate something that looks just different enough so a new, different license can be applied. Tim takes Jim�s homework. How many individual words does Tim need to change � without adding anything to Jim�s work � before it�s no longer plagiarism? I would argue that no matter how many synonyms and slight sentence structure changes Tim employs, it�s still a plagiarised work. However, what it feels like to me is entirely irrelevant when laws are involved, and even those laws are effectively irrelevant when so much money is riding on the answers to questions like these. The companies who desperately want this to be possible and legal are so wealthy, so powerful, and sucked up to the US government so hard, that whatever they say might very well just become law. AI! is the single-greatest coordinated attack on open source in history, and the open source world would do well to realise that.
- DOS memory management
The memory management in DOS is simple, but that simplicity may be deceptive. There are several rather interesting pitfalls that programming documentation often does not mention. ↫ Michal Necasek at the OS/2 Museum A must-read for people writing software for earlier DOS versions.

- EU OS: A Bold Step Toward Digital Sovereignty for Europe
Image 
A new initiative, called "EU OS," has been launched to develop a Linux-based operating system tailored specifically for the public sector organizations of the European Union (EU). This community-driven project aims to address the EU's unique needs and challenges, focusing on fostering digital sovereignty, reducing dependency on external vendors, and building a secure, self-sufficient digital ecosystem.
What Is EU OS?
EU OS is not an entirely novel operating system. Instead, it builds upon a Linux foundation derived from Fedora, with the KDE Plasma desktop environment. It draws inspiration from previous efforts such as France's GendBuntu and Munich's LiMux, which aimed to provide Linux-based systems for public sector use. The goal remains the same: to create a standardized Linux distribution that can be adapted to different regional, national, and sector-specific needs within the EU.
Rather than reinventing the wheel, EU OS focuses on standardization, offering a solid Linux foundation that can be customized according to the unique requirements of various organizations. This approach makes EU OS a practical choice for the public sector, ensuring broad compatibility and ease of implementation across diverse environments.
The Vision Behind EU OS
The guiding principle of EU OS is the concept of "public money – public code," ensuring that taxpayer money is used transparently and effectively. By adopting an open-source model, EU OS eliminates licensing fees, which not only lowers costs but also reduces the dependency on a select group of software vendors. This provides the EU’s public sector organizations with greater flexibility and control over their IT infrastructure, free from the constraints of vendor lock-in.
Additionally, EU OS offers flexibility in terms of software migration and hardware upgrades. Organizations can adapt to new technologies and manage their IT evolution at a manageable cost, both in terms of finances and time.
However, there are some concerns about the choice of Fedora as the base for EU OS. While Fedora is a solid and reliable distribution, it is backed by the United States-based Red Hat. Some argue that using European-backed projects such as openSUSE or KDE's upcoming distribution might have aligned better with the EU's goal of strengthening digital sovereignty.
Conclusion
EU OS marks a significant step towards Europe's digital independence by providing a robust, standardized Linux distribution for the public sector. By reducing reliance on proprietary software and vendors, it paves the way for a more flexible, cost-effective, and secure digital ecosystem. While the choice of Fedora as the base for the project has raised some questions, the overall vision of EU OS offers a promising future for Europe's public sector in the digital age.
Source: It's FOSS
European Union
- Linus Torvalds Acknowledges Missed Release of Linux 6.14 Due to Oversight
Linus Torvalds Acknowledges Missed Release of Linux 6.14 Due to Oversight
Linux kernel lead developer Linus Torvalds has admitted to forgetting to release version 6.14, attributing the oversight to his own lapse in memory. Torvalds is known for releasing new Linux kernel candidates and final versions on Sunday afternoons, typically accompanied by a post detailing the release. If he is unavailable due to travel or other commitments, he usually informs the community ahead of time, so users don’t worry if there’s a delay.
In his post on March 16, Torvalds gave no indication that the release might be delayed, instead stating, “I expect to release the final 6.14 next weekend unless something very surprising happens.” However, Sunday, March 23rd passed without any announcement.
On March 24th, Torvalds wrote in a follow-up message, “I’d love to have some good excuse for why I didn’t do the 6.14 release yesterday on my regular Sunday afternoon schedule,” adding, “But no. It’s just pure incompetence.” He further explained that while he had been clearing up unrelated tasks, he simply forgot to finalize the release. “D'oh,” he joked.
Despite this minor delay, Torvalds’ track record of successfully managing the Linux kernel’s development process over the years remains strong. A single day’s delay is not critical, especially since most Linux users don't urgently need the very latest version.
The new 6.14 release introduces several important features, including enhanced support for writing drivers in Rust—an ongoing topic of discussion among developers—support for Qualcomm’s Snapdragon 8 Elite mobile chip, a fix for the GhostWrite vulnerability in certain RISC-V processors from Alibaba’s T-Head Semiconductor, and a completed NTSYNC driver update that improves the WINE emulator’s ability to run Windows applications, particularly games, on Linux.
Although the 6.14 release went smoothly aside from the delay, Torvalds expressed that version 6.15 may present more challenges due to the volume of pending pull requests. “Judging by my pending pile of pull requests, 6.15 will be much busier,” he noted.
You can download the latest kernel here.
Linus Torvalds kernel
- AerynOS 2025.03 Alpha Released with GNOME 48, Mesa 25, and Linux Kernel 6.13.8
Image 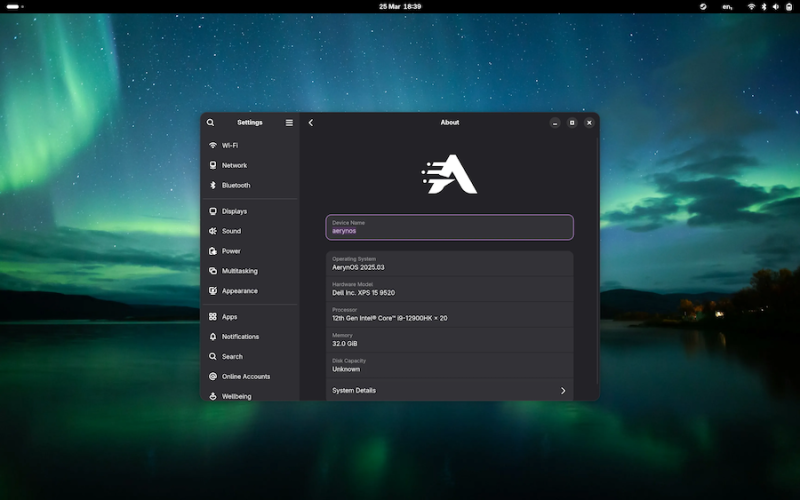
AerynOS 2025.03 has officially been released, introducing a variety of exciting features for Linux users. The release includes the highly anticipated GNOME 48 desktop environment, which comes with significant improvements like HDR support, dynamic triple buffering, and a Wayland color management protocol. Other updates include a battery charge limiting feature and a Wellbeing option aimed at improving user experience.
This release, while still in alpha, incorporates Linux kernel 6.13.8 and the updated Mesa 25.0.2 graphics stack, alongside tools like LLVM 19.1.7 and Vulkan SDK 1.4.309.0. Additionally, the Moss package manager now integrates os-info to generate more detailed OS metadata via a JSON file.
Future plans for AerynOS include automated package updates, easier rollback management, improved disk handling with Rust, and fractional scaling enabled by default. The installer has also been revamped to support full disk wipes and dynamic partitioning.
Although still considered an alpha release, AerynOS 2025.03 can be downloaded and tested right now from its official website.
Source: 9to5Linux
AerynOS
- Xojo 2025r1: Big Updates for Developers with Linux ARM Support, Web Drag and Drop, and Direct App Store Publishing
Image 
Xojo has just rolled out its latest release, Xojo 2025 Release 1, and it’s packed with features that developers have been eagerly waiting for. This major update introduces support for running Xojo on Linux ARM, including Raspberry Pi, brings drag-and-drop functionality to the Web framework, and simplifies app deployment with the ability to directly submit apps to the macOS and iOS App Stores.
Here’s a quick overview of what’s new in Xojo 2025r1:
1. Linux ARM IDE Support
Xojo 2025r1 now allows developers to run the Xojo IDE on Linux ARM devices, including popular platforms like Raspberry Pi. This opens up a whole new world of possibilities for developers who want to create apps for ARM-based devices without the usual complexity. Whether you’re building for a Raspberry Pi or other ARM devices, this update makes it easier than ever to get started.
2. Web Drag and Drop
One of the standout features in this release is the addition of drag-and-drop support for web applications. Now, developers can easily drag and drop visual controls in their web projects, making it simpler to create interactive, user-friendly web applications. Plus, the WebListBox has been enhanced with support for editable cells, checkboxes, and row reordering via dragging. No JavaScript required!
3. Direct App Store Publishing
Xojo has also streamlined the process of publishing apps. With this update, developers can now directly submit macOS and iOS apps to App Store Connect right from the Xojo IDE. This eliminates the need for multiple steps and makes it much easier to get apps into the App Store, saving valuable time during the development process.
4. New Desktop and Mobile Features
This release isn’t just about web and Linux updates. Xojo 2025r1 brings some great improvements for desktop and mobile apps as well. On the desktop side, all projects now include a default window menu for macOS apps. On the mobile side, Xojo has introduced new features for Android and iOS, including support for ColorGroup and Dark Mode on Android, and a new MobileColorPicker for iOS to simplify color selection.
5. Performance and IDE Enhancements
Xojo’s IDE has also been improved in several key areas. There’s now an option to hide toolbar captions, and the toolbar has been made smaller on Windows. The IDE on Windows and Linux now features modern Bootstrap icons, and the Documentation window toolbar is more compact. In the code editor, developers can now quickly navigate to variable declarations with a simple Cmd/Ctrl + Double-click. Plus, performance for complex container layouts in the Layout Editor has been enhanced.
What Does This Mean for Developers?
Xojo 2025r1 brings significant improvements across all the platforms that Xojo supports, from desktop and mobile to web and Linux. The added Linux ARM support opens up new opportunities for Raspberry Pi and ARM-based device development, while the drag-and-drop functionality for web projects will make it easier to create modern, interactive web apps. The ability to publish directly to the App Store is a game-changer for macOS and iOS developers, reducing the friction of app distribution.
How to Get Started
Xojo is free for learning and development, as well as for building apps for Linux and Raspberry Pi. If you’re ready to dive into cross-platform development, paid licenses start at $99 for a single-platform desktop license, and $399 for cross-platform desktop, mobile, or web development. For professional developers who need additional resources and support, Xojo Pro and Pro Plus licenses start at $799. You can also find special pricing for educators and students.
Download Xojo 2025r1 today at xojo.com.
Final Thoughts
With each new release, Xojo continues to make cross-platform development more accessible and efficient. The 2025r1 release is no exception, delivering key updates that simplify the development process and open up new possibilities for developers working on a variety of platforms. Whether you’re a Raspberry Pi enthusiast or a mobile app developer, Xojo 2025r1 has something for you.
Xojo ARM
- New 'Mirrored' Network Mode Introduced in Windows Subsystem for Linux
Microsoft's Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) continues to evolve with the release of WSL 2 version 0.0.2. This update introduces a set of opt-in preview features designed to enhance performance and compatibility.
Key additions include "Automatic memory reclaim" which dynamically optimizes WSL's memory footprint, and "Sparse VHD" to shrink the size of the virtual hard disk file. These improvements aim to streamline resource usage.
Additionally, a new "mirrored networking mode" brings expanded networking capabilities like IPv6 and multicast support. Microsoft claims this will improve VPN and LAN connectivity from both the Windows host and Linux guest.
Complementing this is a new "DNS Tunneling" feature that changes how DNS queries are resolved to avoid compatibility issues with certain network setups. According to Microsoft, this should reduce problems connecting to the internet or local network resources within WSL.
Advanced firewall configuration options are also now available through Hyper-V integration. The new "autoProxy" feature ensures WSL seamlessly utilizes the Windows system proxy configuration.
Microsoft states these features are currently rolling out to Windows Insiders running Windows 11 22H2 Build 22621.2359 or later. They remain opt-in previews to allow testing before final integration into WSL.
By expanding WSL 2 with compelling new capabilities in areas like resource efficiency, networking, and security, Microsoft aims to make Linux on Windows more performant and compatible. This evolutionary approach based on user feedback highlights Microsoft's commitment to WSL as a key part of the Windows ecosystem.
Windows
- Linux Threat Report: Earth Lusca Deploys Novel SprySOCKS Backdoor in Attacks on Government Entities
The threat actor Earth Lusca, linked to Chinese state-sponsored hacking groups, has been observed utilizing a new Linux backdoor dubbed SprySOCKS to target government organizations globally.
As initially reported in January 2022 by Trend Micro, Earth Lusca has been active since at least 2021 conducting cyber espionage campaigns against public and private sector targets in Asia, Australia, Europe, and North America. Their tactics include spear-phishing and watering hole attacks to gain initial access. Some of Earth Lusca's activities overlap with another Chinese threat cluster known as RedHotel.
In new research, Trend Micro reveals Earth Lusca remains highly active, even expanding operations in the first half of 2023. Primary victims are government departments focused on foreign affairs, technology, and telecommunications. Attacks concentrate in Southeast Asia, Central Asia, and the Balkans regions.
After breaching internet-facing systems by exploiting flaws in Fortinet, GitLab, Microsoft Exchange, Telerik UI, and Zimbra software, Earth Lusca uses web shells and Cobalt Strike to move laterally. Their goal is exfiltrating documents and credentials, while also installing additional backdoors like ShadowPad and Winnti for long-term spying.
The Command and Control server delivering Cobalt Strike was also found hosting SprySOCKS - an advanced backdoor not previously publicly reported. With roots in the Windows malware Trochilus, SprySOCKS contains reconnaissance, remote shell, proxy, and file operation capabilities. It communicates over TCP mimicking patterns used by a Windows trojan called RedLeaves, itself built on Trochilus.
At least two SprySOCKS versions have been identified, indicating ongoing development. This novel Linux backdoor deployed by Earth Lusca highlights the increasing sophistication of Chinese state-sponsored threats. Robust patching, access controls, monitoring for unusual activities, and other proactive defenses remain essential to counter this advanced malware.
The Trend Micro researchers emphasize that organizations must minimize attack surfaces, regularly update systems, and ensure robust security hygiene to interrupt the tactics, techniques, and procedures of relentless threat groups like Earth Lusca.
Security
- Linux Kernel Faces Reduction in Long-Term Support Due to Maintenance Challenges
The Linux kernel is undergoing major changes that will shape its future development and adoption, according to Jonathan Corbet, Linux kernel developer and executive editor of Linux Weekly News. Speaking at the Open Source Summit Europe, Corbet provided an update on the latest Linux kernel developments and a glimpse of what's to come.
A major change on the horizon is a reduction in long-term support (LTS) for kernel versions from six years to just two years. Corbet explained that maintaining old kernel branches indefinitely is unsustainable and most users have migrated to newer versions, so there's little point in continuing six years of support. While some may grumble about shortened support lifecycles, the reality is that constantly backporting fixes to ancient kernels strains maintainers.
This maintainer burnout poses a serious threat, as Corbet highlighted. Maintaining Linux is largely a volunteer effort, with only about 200 of the 2,000+ developers paid for their contributions. The endless demands on maintainers' time from fuzz testing, fixing minor bugs, and reviewing contributions takes a toll. Prominent maintainers have warned they need help to avoid collapse. Companies relying on Linux must realize giving back financially is in their interest to sustain this vital ecosystem.
The Linux kernel is also wading into waters new with the introduction of Rust code. While Rust solves many problems, it also introduces new complexities around language integration, evolving standards, and maintainer expertise. Corbet believes Rust will pass the point of no return when core features depend on it, which may occur soon with additions like Apple M1 GPU drivers. Despite skepticism in some corners, Rust's benefits likely outweigh any transition costs.
On the distro front, Red Hat's decision to restrict RHEL cloning sparked community backlash. While business considerations were at play, Corbet noted technical factors too. Using older kernels with backported fixes, as RHEL does, risks creating divergent, vendor-specific branches. The Android model of tracking mainline kernel dev more closely has shown security benefits. Ultimately, Linux works best when aligned with the broader community.
In closing, Corbet recalled the saying "Linux is free like a puppy is free." Using open source seems easy at first, but sustaining it long-term requires significant care and feeding. As Linux is incorporated into more critical systems, that maintenance becomes ever more crucial. The kernel changes ahead are aimed at keeping Linux healthy and vibrant for the next generation of users, businesses, and developers.
kernel
- Linux Celebrates 32 Years with the Release of 6.6-rc2 Version
Today marks the 32nd anniversary of Linus Torvalds introducing the inaugural Linux 0.01 kernel version, and celebrating this milestone, Torvalds has launched the Linux 6.6-rc2. Among the noteworthy updates are the inclusion of a feature catering to the ASUS ROG Flow X16 tablet's mode handling and the renaming of the new GenPD subsystem to pmdomain.
The Linux 6.6 edition is progressing well, brimming with exciting new features that promise to enhance user experience. Early benchmarks are indicating promising results, especially on high-core-count servers, pointing to a potentially robust and efficient update in the Linux series.
Here is what Linus Torvalds had to say in today's announcement:
Another week, another -rc.I think the most notable thing about 6.6-rc2 is simply that it'sexactly 32 years to the day since the 0.01 release. And that's a roundnumber if you are a computer person.Because other than the random date, I don't see anything that reallystands out here. We've got random fixes all over, and none of it looksparticularly strange. The genpd -> pmdomain rename shows up in thediffstat, but there's no actual code changes involved (make sure touse "git diff -M" to see them as zero-line renames).And other than that, things look very normal. Sure, the architecturefixes happen to be mostly parisc this week, which isn't exactly theusual pattern, but it's also not exactly a huge amount of changes.Most of the (small) changes here are in drivers, with some tracingfixes and just random things. The shortlog below is short enough toscroll through and get a taste of what's been going on. Linus Torvalds
- Introducing Bavarder: A User-Friendly Linux Desktop App for Quick ChatGPT Interaction
Want to interact with ChatGPT from your Linux desktop without using a web browser?
Bavarder, a new app, allows you to do just that.
Developed with Python and GTK4/libadwaita, Bavarder offers a simple concept: pose a question to ChatGPT, receive a response, and promptly copy the answer (or your inquiry) to the clipboard for pasting elsewhere.
With an incredibly user-friendly interface, you won't require AI expertise (or a novice blogger) to comprehend it. Type your question in the top box, click the blue send button, and wait for a generated response to appear at the bottom. You can edit or modify your message and repeat the process as needed.
During our evaluation, Bavarder employed BAI Chat, a GPT-3.5/ChatGPT API-based chatbot that's free and doesn't require signups or API keys. Future app versions will incorporate support for alternative backends, such as ChatGPT 4 and Hugging Chat, and allow users to input an API key to utilize ChatGPT3.
At present, there's no option to regenerate a response (though you can resend the same question for a potentially different answer). Due to the lack of a "conversation" view, tracking a dialogue or following up on answers can be challenging — but Bavarder excels for rapid-fire questions.
As with any AI, standard disclaimers apply. Responses might seem plausible but could contain inaccurate or false information. Additionally, it's relatively easy to lead these models into irrational loops, like convincing them that 2 + 2 equals 106 — so stay alert!
Overall, Bavarder is an attractive app with a well-defined purpose. If you enjoy ChatGPT and similar technologies, it's worth exploring.
ChatGPT AI
- LibreOffice 7.5.3 Released: Third Maintenance Update Brings 119 Bug Fixes to Popular Open-Source Office Suite
Today, The Document Foundation unveiled the release and widespread availability of LibreOffice 7.5.3, which serves as the third maintenance update to the current LibreOffice 7.5 open-source and complimentary office suite series.
Approximately five weeks after the launch of LibreOffice 7.5.2, LibreOffice 7.5.3 arrives with a new set of bug fixes for those who have successfully updated their GNU/Linux system to the LibreOffice 7.5 series.
LibreOffice 7.5.3 addresses a total of 119 bugs identified by users or uncovered by LibreOffice developers. For a more comprehensive understanding of these bug fixes, consult the RC1 and RC2 changelogs.
You can download LibreOffice 7.5.3 directly from the LibreOffice website��or from SourceForge as binary installers for DEB or RPM-based GNU/Linux distributions. A source tarball is also accessible for individuals who prefer to compile the software from sources or for system integrators.
All users operating the LibreOffice 7.5 office suite series should promptly update their installations to the new point release, which will soon appear in the stable software repositories of your GNU/Linux distributions.
In early February 2023, LibreOffice 7.5 debuted as a substantial upgrade to the widely-used open-source office suite, introducing numerous features and improvements. These enhancements encompass major upgrades to dark mode support, new application and MIME-type icons, a refined Single Toolbar UI, enhanced PDF Export, and more.
Seven maintenance updates will support LibreOffice 7.5 until November 30th, 2023. The next point release, LibreOffice 7.5.4, is scheduled for early June and will include additional bug fixes.
The Document Foundation once again emphasizes that the LibreOffice office suite's "Community" edition is maintained by volunteers and members of the Open Source community. For enterprise implementations, they suggest using the LibreOffice Enterprise family of applications from ecosystem partners.
LibreOffice

- Keep Android Open
Google has announced that, soon, anyone looking to develop Android apps will have to first register centrally with Google.
- Kernel 7.0 Now in Testing
Linus Torvalds has announced the first Release Candidate (RC) for the 7.x kernel is available for those who want to test it.
- LibreOffice 26.2 Now Available
With new features, improvements, and bug fixes, LibreOffice 26.2 delivers a modern, polished office suite without compromise.
|